Clonal Dissemination of Antifungal-Resistant Candida haemulonii, China
Xinfei Chen, Xinmiao Jia, Jian Bing, Han Zhang, Nan Hong, Yun Liu, Haiyang Xi, Weiping Wang, Zhiyong Liu, Qiangqiang Zhang, Li Li, Mei Kang, Yuling Xiao, Bin Yang, Yulan Lin, Hui Xu, Xin Fan, Jingjing Huang, Jie Gong, Juan Xu, Xiuli Xie, Wenhang Yang, Ge Zhang, Jingjia Zhang, Wei Kang, He Wang, Xin Hou, Meng Xiao
1
, and Yingchun Xu
1
Author affiliations: Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, China (X. Chen, X. Jia, H. Zhang, J. Huang, X. Xie, W. Yang, G. Zhang, J. Zhang, W. Kang, M. Xiao, Y. Xu); State Key Laboratory of Complex Severe and Rare Diseases and Beijing Key Laboratory for Mechanisms Research and Precision Diagnosis of Invasive Fungal Diseases, Beijing (X. Chen, X. Jia, H. Zhang, J. Huang, X. Xie, W. Yang, G. Zhang, J. Zhang, W. Kang, M. Xiao, Y. Xu); Fudan University, Shanghai, China (J. Bing, Q. Zhang, L. Li); Nanjing University School of Medicine, Nanjing, China (N. Hong, H. Xi, W. Wang); Changhai Hospital, Shanghai (Y. Liu); Southwest Hospital Affiliated the Third Military Medical University, Chongqing, China (Z. Liu); Sichuan University, Chengdu, China (M. Kang, Y. Xiao); The First Affiliated Hospital of Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou, China (B. Yang, Y. Lin); The First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China (H. Xu); Capital Medical University, Beijing (X. Fan); Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Beijing (J. Gong, J. Xu); Dynamiker Sub-Center of Beijing Key Laboratory for Mechanisms Research and Precision Diagnosis of Invasive Fungal Disease, Tianjin, China (H. Wang); Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing (X. Hou)
Main Article
Figure 1
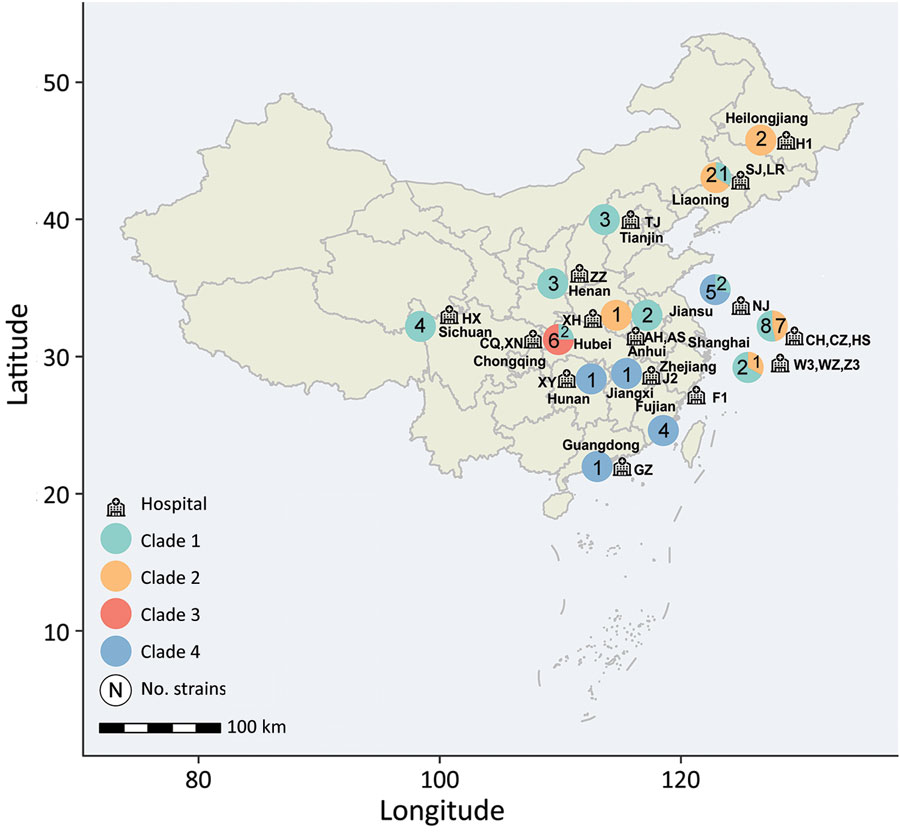
Figure 1. Regional distribution of 58 invasive infections caused by C. haemulonii in China during 2010–2017, collected from the China Hospital Invasive Fungal Surveillance Net study. Province names are listed, and hospital locations are marked by icons; the abbreviation codes of hospitals are listed next to each location. The pie charts adjacent to the province names indicate the number of isolates collected; phylogenetic clades are labeled in different colors.
Main Article
Page created: January 06, 2023
Page updated: February 19, 2023
Page reviewed: February 19, 2023
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
