Volume 29, Number 5—May 2023
Research Letter
COVID-19 Vaccine Uptake by Infection Status in New South Wales, Australia
Figure
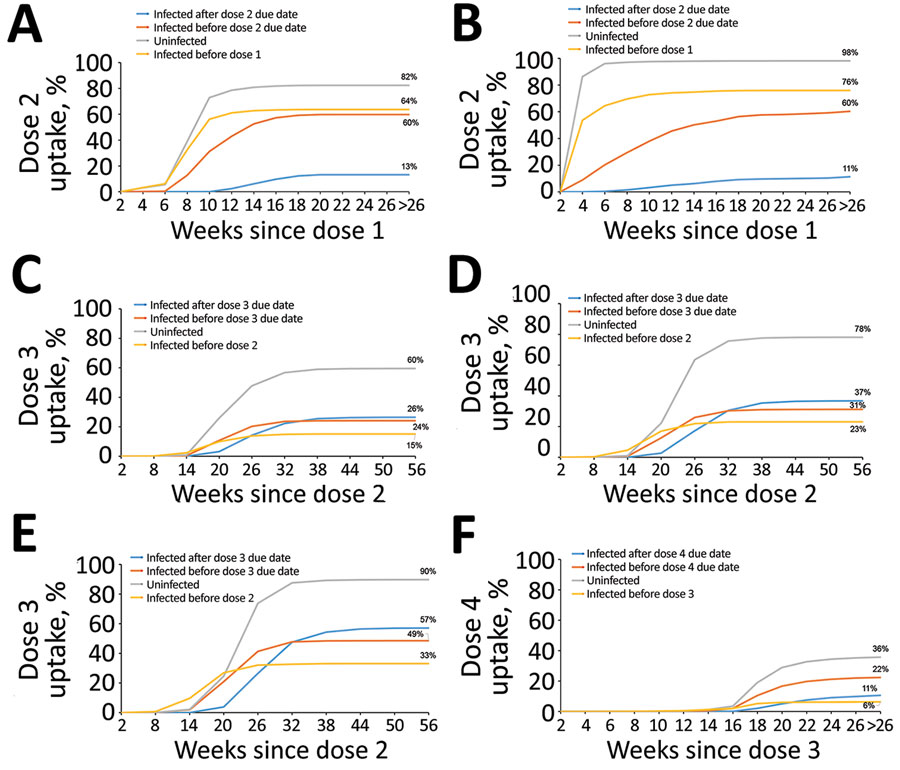
Figure. Cumulative uptake of next dose by time since current dose in study of COVID-19 vaccine uptake, by age group and infection status as at May 29, 2022, Greater Sydney Metropolitan and Hunter New England areas of New South Wales, Australia. A, B) Dose 2 uptake for the 5–11-year (A) and 12–15-year (B) age groups; C–E) dose 3 uptake for the 16–39-year (C), 40–64-year (D), and ≥65-year (E) age groups; F) dose 4 uptake for the ≥65-year age group.
Page created: March 15, 2023
Page updated: April 19, 2023
Page reviewed: April 19, 2023
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.