Volume 29, Number 7—July 2023
Research Letter
Long-Term SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Seroprevalence in Blood Donors, Italy
Figure
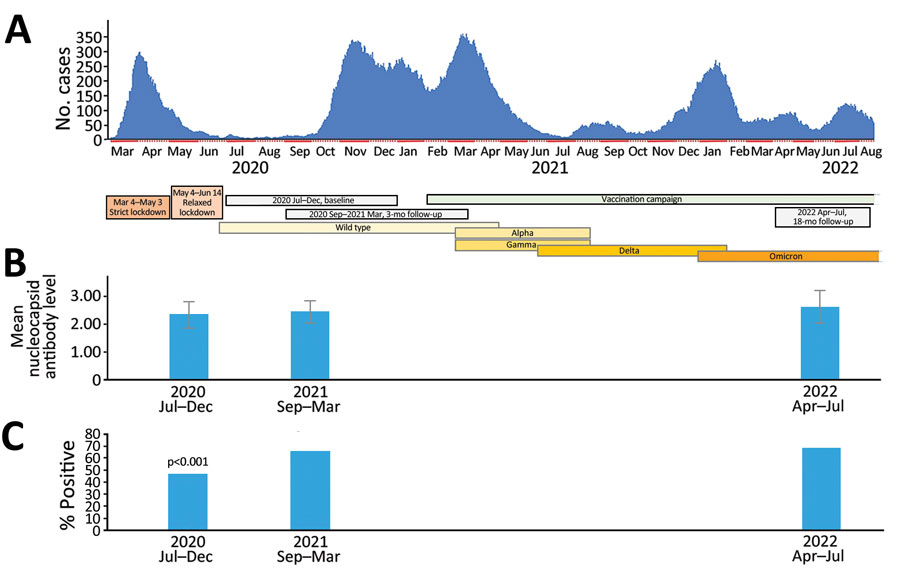
Figure. Study timepoints plotted against hospital admissions for COVID-19 in study of SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence among voluntary blood donors in Modena, Italy. A) After the first wave of COVID-19 in March 2020–April 2020, which followed 2-month strict and 1-month relaxed lockdown periods, a 4-month period (June 2020–September 2020) of almost no hospital admissions associated with low (3.5%) SARS-CoV-2 antibody seroprevalence ensued. Thereafter, a sequence of intercurrent waves occurred with only a very short period of few admissions in July 2021. Titers of antibodies against the virus nucleocapsid (tested in the same donors at baseline and after 3 and 22 months) increased throughout the observation period although not significantly. Colored horizontal bars indicate prevalent variants throughout the observation periods. B) Mean antibody titers against nucleocapsid among strongly positive donors were significantly higher at the 2nd and 3rd testing points compared with baseline. Error bars indicate standard deviation. C) Percentages of donors with strongly positive antibody response against the nucleocapsid, tested on the whole cohort. p value indicates the comparison of percentages at 2nd and 3rd testing points to percentage at baseline.