Volume 29, Number 8—August 2023
Research Letter
Aneurysm Infection Caused by Desulfovibrio desulfuricans
Figure
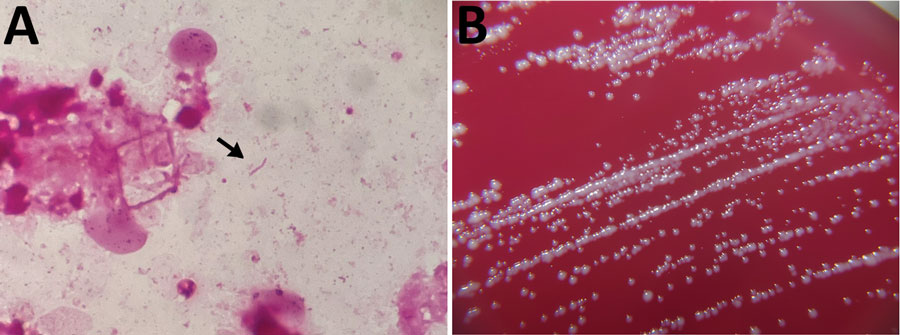
Figure. Detection and colonization of Desulfovibrio desulfuricans in an 84-year-old man in Japan who had undergone endovascular aortic repair 9 years earlier. A) Gram stain of pus. D. desulfuricans MB has a gram-negative spiral rod appearance (arrow). Original magnification ×1,000. B) Colonies of D. desulfuricans MB on ABHK agar. Biochemical properties showed positive results for catalase and negative for indole and urease. In vitro susceptibility testing revealed that it had the following MICs: meropenem, <2 μg/mL; cefotaxime, <2 μg/mL; ampicillin/sulbactam, <4 μg/mL; piperacillin/tazobactam, <16 μg/mL; and clindamycin, >8 μg/mL.
Page created: June 07, 2023
Page updated: July 20, 2023
Page reviewed: July 20, 2023
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.