Volume 29, Number 9—September 2023
Research
Genomic Characteristics of Emerging Intraerythrocytic Anaplasma capra and High Prevalence in Goats, China
Figure 3
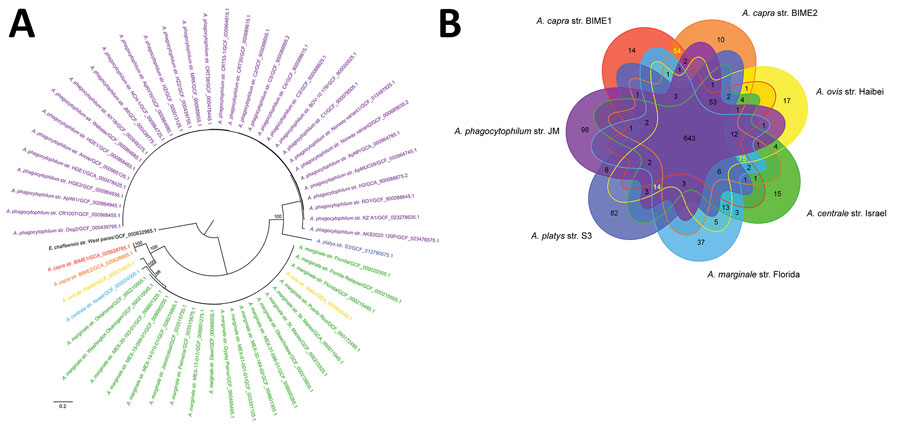
Figure 3. Phylogenetic tree and genomic comparison among Anaplasma species in study of emerging intraerythrocytic A. capra and high prevalence in goats, China. A) Phylogenetic tree of Anaplasma species based on all the genomic sequences deposited in GenBank, constructed by using maximum-likelihood method with Ehrlichia chaffeensis as an outgroup. The percentages of replicate trees in which the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test (1,000 replicates) are shown next to the branches. B) Differences in gene contents among Anaplasma species strains. Venn diagrams show the distribution of shared and unique gene clusters among representative Anaplasma species.
1These senior authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: July 08, 2023
Page updated: August 20, 2023
Page reviewed: August 20, 2023
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.