Volume 3, Number 2—June 1997
THEME ISSUE
From the 1st International Conference on Emerging Zoonoses
From the 1st International Conference on Emerging Zoonoses
The Hantaviruses of Europe: from the Bedside to the Bench
Figure
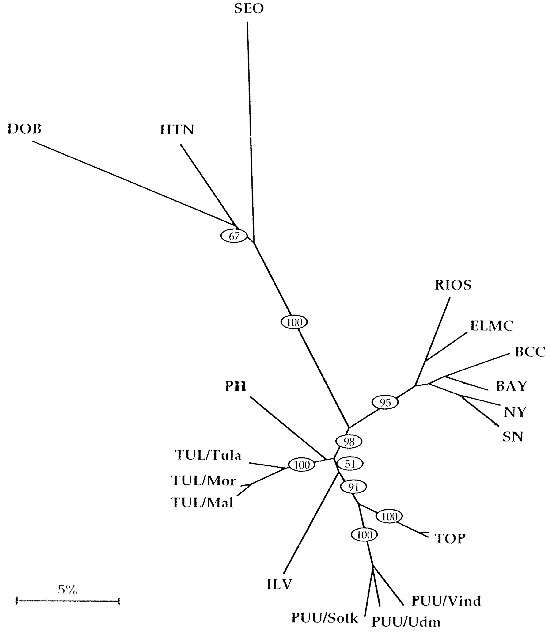
Figure. Dendrogram of Old World hantaviruses (upper, left, and lower part of the tree) vs. New World hantaviruses (right part of the tree). Reproduced with permission (42). Branch lengths are proportional to genetic distances. The bootstrap support percentages of particular branching points calculated from 500 replicates are given in ovals. HTN = Hantaan virus, strain 76-118; SEO = Seoul virus, strain SR-11; DOB = Dobrava virus, PH = Prospect Hill virus; TUL = Tula virus, strains Tula/76Ma/87, Moravia/5286Ma/94 and Malacky/Ma32/94; ILV = Isla Vista virus, strain MC-SB-1; TOP = Topografov virus; PUU = Puumala virus, strains Sotkamo, Vindeln/83-L20 and Udmurtia/458g/88; RIOS = Rio Segundo virus, strain RMx-Costa-1; ELMC = El Moro Canyon virus, strain RM-97; BAY = Bayou virus, strain Louisiana; BCC = Black Creek Canal virus; SN = Sin Nombre virus, strain H10; NY = New York virus, strain RI-1; KBR = Khabarovsk virus, another PUU-like virus, is not depicted here. PH & ILV (and BLL, not depicted here) are the only New World genotypes with PUU-like characteristics, hence their position close to the TUL-clade.
References
- Myhrman G. A renal disease with particular symptoms. Nordisk Medicinsk Tidskrift. 1934;7:793–4.
- Stuhlfauth K. Bericht über ein neues schlammfieberähnliches Krankheitsbild bei Deutscher Truppen in Lappland. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1943;439:474–7. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Mustonen J, Vaheri A, Clement J. Congress report: Third International Conference on Haemorrhagic Fever with Renal Syndrome (HFRS) and Hantaviruses. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1996;11:730–3.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Le Guenno B, Coudrier D. Epidemiology of hantavirus infections in France (1977-1995). Proceedings of the Third International Conference on HFRS and Hantaviruses 1994 May 31-June 3; Helsinki, Finland. Helsinki: Haartman Institute, University of Helsinki, 1994;11.
- Clement J, Underwood P, Ward D, Pilaski J, LeDuc J. Hantavirus outbreak during military manoeuvres in Germany. Lancet. 1996;347:336. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Papadimitriou MG, Antoniadis A. Hantavirus nephropathy in Greece. Lancet. 1994;343:1038. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gerding M, Groen J, Jordans JGM, Osterhaus ADME. Hantavirus nephropathy in the Netherlands: clinical, histopathological and epidemiological findings. Neth J Med. 1995;47:106–12. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Vapalahti O, Vaheri A, Henttonen H. Eurosurveillance. Commission of the European Communities, Brussels, Belgium; 1995 Sept. European Communicable Disease Bulletin, No.0:3-4.
- Niklasson B, LeDuc J. Epidemiology of nephropathia epidemica in Sweden. J Infect Dis. 1987;155:269–76.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Zöller L, Faulde M, Meisel H, Ruh B, Kimmig P, Schelling U, Seroprevalence of hantavirus antibodies in Germany as determined by a new recombinant enzyme immunoassay. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1995;14:305–13. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Groen J, Gerding MN, Jordans JG, Clement JP, Nieuwenhuijs JH, Osterhaus AD. Hantavirus infections in The Netherlands: epidemiology and disease. Epidemiol Infect. 1995;114:373–83. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Clement J, van der Groen G. Acute Hantavirus nephropathy in Belgium: preliminary results of a sero-epidemiological study. In: Amerio A, Coratelli B, editors. Acute Renal Failure. Advances in experimental medicine and biology. New York: Plenum Press, 1987:251-63.
- Rodriguez JA, Vaque J. Hantavirus disease: an emerging infection [editorial]. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 1994;12:477–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Niklasson B, Leduc JW, Nystrom K, Nyman L. Nephropathia epidemica: incidence of clinical cases and antibody prevalence in an endemic area of Sweden. Epidemiol Infect. 1987;99:559–62. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Colson P, Damoiseaux P, Brisbois J, Duvvier E, Levecque P, Roger JM, Hantavirose dans l'Entre-Sambre-et-Meuse. Acta Clin Belg. 1995;50:197–206.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Clement J, Colson P, McKenna P. Hantavirus pulmonary syndrome in New England and Europe. N Engl J Med. 1994;331:545–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Stuart LM, Rice PS, Lloyd G, Beale RJ. A soldier in respiratory distress. Lancet. 1996;347:30. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- World Health Organization Working Group on the development of a rapid diagnostic method and vaccine for hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. Seoul, Republic of Korea, 1991 Sep 26-28; WPR/OCD/CDS(O)/1/91/IB3.
- Groen J, Jordans H, Clement J, Rooijakkers E, Uytdehaag F, Dalrymple J, Identification of hantavirus serotypes by testing of post-infection sera in immunofluorescence and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. J Med Virol. 1991;33:26–32. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Alexeyev O, Elgh F, Zhestkov A, Wadell G, Juto P. Hantaan and Puumala virus antibodies in blood donors in Samara, an HFRS-endemic region in European Russia. Lancet. 1996;347:1483. DOIGoogle Scholar
- LeDuc JW, Smith GA, Childs JE, Pinheiro FP, Maiztegui JI, Niklasson B, Global survey of anti-body to hantaan related viruses among peridomestic rodents. Bull World Health Organ. 1986;64:139–44.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Monteiro J, Mesquita M, Alves MJ, Filipi AR. Febre Hemorragica com Sindroma Renal - Primeiro caso clinico diagnosticado em Portugal. Separata da Revista Portuguesa de Doenas Infecciosas. 1993;16:209–14.
- Filipe AR, Andrade HR, Sommer AI, Traavik T. Hantaviral antigens and antibodies in wild rodents in Portugal. Acta Virol. 1991;35:287–91.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- McKenna P, Clement J, Matthys P, Coyle PV, McCaughey C. Serological evidence of hantavirus disease in Northern Ireland. J Med Virol. 1994;43:33–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- McCaughey C, Montgomery WI, Twomey N, Addley M, O'Neill HJ, Coyle PV. Evidence of hantavirus in wild rodents in Northern Ireland. Epidemiol Infect. 1996;117:361–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dzagurova T, Myasnikov Y, Dekonenko A, Tkachenko E. Seoul-type hantavirus isolated from HFRS patient in European Russia. Proceedings of the Third International Conference on HFRS and Hantaviruses; 1994 May 1-June 3; Helsinki, Finland. Helsinki: Haartman Institute, University of Helsinki, 1994; 69.
- McKenna P, van der Groen G, Hoofd G, Beelaert G, Leirs H, Verhagen R. Eradication of hantavirus infection among laboratory rats by application of caesarian section and a foster mother technique. J Infect. 1992;25:181–90. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Heneberg D, Vuksic L, Morelj M, Lepes I, Djordjevic Z, Mikes M, Epidemic of hemorrhagic fever in certain workplaces in Fruska Gora. Zbornik radova VMA 1962:236-71.
- Antoniadis A, Greekas D, Rossi CA, LeDuc JW. Isolation of a hantavirus from a severely ill patient with hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in Greece. J Infect Dis. 1987;156:1010–3.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Avsic-Zupanc T, Poljak M, Furlan P, Kaps R. Shu Yuan Xiao, LeDuc JW. Isolation of a strain of a hantaan virus from a fatal case of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in Slovenia. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1994;51:393–400.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gligic A, Dimkovic N, Xiao SY, Buckle GJ, Jovanovic D, Velimirovic D, Belgrade virus: a new hantavirus causing severe hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in Yugoslavia. J Infect Dis. 1992;166:113–20.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Avsic-Zupanc T, Xiao S-Y, Stojanovic R, Gligic A, van der Groen G, LeDuc JW. Characterisation of Dobrava virus: a hantavirus from Slovenia, Yugoslavia. J Med Virol. 1992;38:132–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Antoniadis A, Stylianakis A, Papa A, Alexiou-Daniel S, Lampropoulos A, Nichol ST, Direct genetic detection of Dobrava virus in Greek and Albanian patients with hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1996;174:407–10.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hukic M, Kurt A, Torstensson S, Lundkvist A, Wiger D, Niklasson B. Haemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in northeast Bosnia. Lancet. 1996;347:56–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lundkvist A, Hukic M, Hörling J, Gilljam M, Nichol S, Niklasson B. Puumala and Dobrava viruses cause haemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) in Bosnia-Herzegovina: evidence of highly cross-neutralizing antibody responses in early patient sera. J Med Virol. In press.
- Clement J, Mc Kenna P, Avsic Zupanc T, Skinner CR. Rat-transmitted hantavirus disease in Sarajevo. Lancet. 1994;344:131. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Clement J, Heyman P, Colson P, Groeneveld PH. Spread of hantavirus infections in Europe. Lancet. 1996;347:771. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Plyusnin A, Vapalahti O, Lankinen H, Lehvaslaiho H, Apekina N, Myasnikov Y, Tula virus : a newly detected hantavirus carried by European common voles. J Virol. 1994;68:7833–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Song W, Torrez Martinez N, Irwin W, Harrison FJ, Davis R, Ascher M, Isla Vista virus: a genetically novel hantavirus of the California vole Microtus californicus. J Gen Virol. 1995;76:3195–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Vapalahti O, Lundkvist A, Kukkonen S, Cheng Y, Giljam M, Kaverna M. Isolation and characterisation of Tula virus, a distinct serotype in the genus Hantavirus, family Bunyaviridae. J Gen Virol. In press.
- Plyusnin A, Vapalahti O, Lundkvist A, Henttonen H, Vaheri A. Newly recognized hantavirus in Siberian lemmings. Lancet. 1996;347:1835. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Brummer Korvenkontio M, Vaher A, Hovi T, von Bonsdoff C, Vuorimies J, Manni T, Nephropathia epidemica: detection of antigen in bank voles and serologic diagnosis of human infection. J Infect Dis. 1980;141:131–4.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kariwa H, Yoshizumi S, Arikawa J, Yoshimatsu K, Takahashi K, Takashima I, Evidence for the existence of Puumula-related virus among Clethrio-nomys rufocanus in Hokkaido, Japan. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1995;53:222–7.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lee PW, Amyz HL, Gajdusek DC, Yanagihara RT, Goldgaber D, Gibbs CJ. New haemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome-related virus in indigenous wild rodents in United States. Lancet. 1982;2:1405.
- Hörling J, Chizhikov V, Lundkvist A, Jonsson M, Ivanov L, Dekonenko A, Khabarovsk virus: a phylogenetically and serologically distinct hantavirus isolated from Microtus fortis trapped in far-east Russia. J Gen Virol. 1996;77:687–94. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar