Volume 30, Number 1—January 2024
Research
COVID-19–Related School Closures, United States, July 27, 2020–June 30, 2022
Figure 1
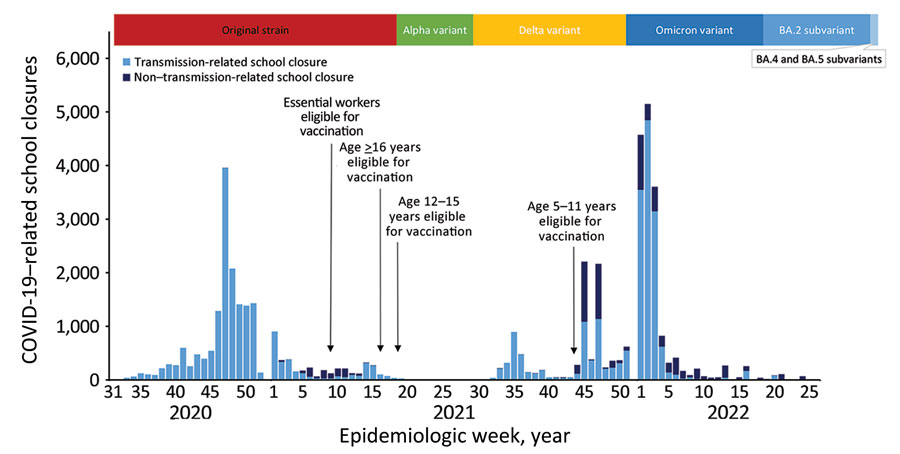
Figure 1. COVID-19–related school closures, dominant COVID-19 variants, and timing of vaccination availability, United States, July 27, 2020–June 30, 2022. School closure was defined as a transition from being open to being closed for in-person instruction excluding any scheduled days off; fully in-person and hybrid learning modalities were classified as open, and fully remote and closed were classified as closed. Transmission-related reasons were COVID-19 cases, suspected cases, increased student absenteeism, increased staff absenteeism, cluster or widespread transmission in the community, state or local guidance or mandate to close schools in response to COVID-19, to clean or disinfect school facilities, and other. Non–transmission-related reasons were COVID-19 vaccinations and side effects of vaccination of staff or students, teacher or staff shortage, for student or staff mental health, and other reasons associated with COVID-19. Timeline of COVID-19 variants derived from Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Museum COVID-19 Timeline (11) and defined as the point at which a variant accounted for the largest proportion of cases. Emergency Use Authorization by the Food and Drug Administration authorized COVID-19 vaccination for teachers and staff as part of the essential workforce on March 2, 2021, and all persons >16 years of age on April 19, 2021 (12). Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices recommended COVID-19 vaccination for persons 12–15 years of age on May 12, 2021, and for persons 5–11 years of age on November 2, 2021 (11).
References
- Wong KK, Shi J, Gao H, Zheteyeva YA, Lane K, Copeland D, et al. Why is school closed today? Unplanned K-12 school closures in the United States, 2011-2013. PLoS One. 2014;9:
e113755 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Zviedrite N, Hodis JD, Jahan F, Gao H, Uzicanin A. COVID-19-associated school closures and related efforts to sustain education and subsidized meal programs, United States, February 18-June 30, 2020. PLoS One. 2021;16:
e0248925 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Parks SE, Zviedrite N, Budzyn SE, Panaggio MJ, Raible E, Papazian M, et al. COVID-19–related school closures and learning modality changes—United States, August 1–September 17, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70:1374–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- MCH Strategic Data. COVID-19 impact: school district operational status, updates for Spring 2021. 2021 [cited 2022 Nov 18]. https://www.mchdata.com/covid19/schoolclosings
- Burbio, Inc. K–12 school opening tracker. 2022 [cited 2022 Nov 18]. https://about.burbio.com/school-opening-tracker
- National Center for Education Statistics. Common core of data. [cited 2023 Apr 5]. https://nces.ed.gov/ccd
- National Center for Education Statistics. Private School Universe Survey [cited 2022 Mar 21]. https://nces.ed.gov/surveys/pss
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID-19 response. COVID-19 case surveillance public data access, summary, and limitations [cited 2023 Mar 15]. https://data.cdc.gov/Case-Surveillance/COVID-19-Case-Surveillance-Public-Use-Data/vbim-akqf
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID-NET: COVID-19–Associated Hospitalization Surveillance Network [cited 2023 Mar 7]. https://gis.cdc.gov/grasp/covidnet/covid19_5.html
- US Department of Health and Human Services. COVID-19 diagnostic laboratory testing (PCR testing) time series [cited 2023 Mar 15]. https://beta.healthdata.gov/dataset/COVID-19-Diagnostic-Laboratory-Testing-PCR-Testing/j8mb-icvb
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. CDC Museum COVID-19 timeline [cited 2023 Apr 7]. https://www.cdc.gov/museum/timeline/covid19.html
- US Department of Health and Human Services. Coronavirus: COVID-19 vaccines. 2022 [cited 2023 Apr 7]. https://www.hhs.gov/coronavirus/covid-19-vaccines/index.html
- Shapiro E. New York City to close public schools again as virus cases rise. The New York Times. 2021 [cited 2023 Feb 21]. https://www.nytimes.com/2020/11/18/nyregion/nyc-schools-covid.html
- Commonwealth of Kentucky Office of the Governor. Executive order 2020-969: state of emergency. 2020 Nov 18 [cited 2023 Feb 21]. https://governor.ky.gov/attachments/20201118_Executive-Order_2020-969_State-of-Emergency.pdf
- Michigan Department of Health and Human Services. Emergency order under MCL 333.2253: gatherings and face mask order. 2020 Nov 15 [2023 Feb 21]. https://www.michigan.gov/coronavirus/resources/orders-and-directives/lists/executive-directives-content/gatherings-and-face-mask-order-4
- Kann L, Kinchen S, Modzelski B, Sullivan M, Carr D, Zaza S, et al. ILI-related school dismissal monitoring system: an overview and assessment. Disaster Med Public Health Prep. 2012;6:104–12. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Delahoy MJ, Ujamaa D, Taylor CA, Cummings C, Anglin O, Holstein R, et al. Comparison of influenza and coronavirus disease 2019-associated hospitalizations among children younger than 18 years old in the United States: FluSurv-NET (October–April 2017–2021) and COVID-NET (October 2020–September 2021). Clin Infect Dis. 2023;76:e450–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Shein SL, Carroll CL, Remy KE, Rogerson CM, McCluskey CK, Lin A, et al. Epidemiology and outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 infection or multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children vs influenza among critically ill children. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5:
e2217217 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Schmitt J, deCourcy K. The pandemic has exacerbated a long-standing national shortage of teachers. 2022 Dec 6 [cited 2023 May 8]. https://www.epi.org/publication/shortage-of-teachers
- National Center for Education Statistics. US schools report increased teacher vacancies due to COVID-19 pandemic, new NCES data show. 2022 Mar 3 [cited 2023 May 8]. https://nces.ed.gov/whatsnew/press_releases/3_3_2022.asp
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID data tracker. 2023 Mar 21 [cited 2023 Mar 21]. https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker
- Fox M. CDC recommends against travel for Thanksgiving. CNN. 2020 Nov 19 [cited 2023 Mar 28]. https://www.cnn.com/2020/11/19/health/cdc-thanksgiving-travel-wellness-bn/index.html
- US Bureau of Transportation Statistics. Thanksgiving week travel: total number of trips down, long distance trips up over last year. 2020 [cited 2023 Mar 28]. https://www.bts.gov/data-spotlight/thanksgiving-travel-long-distance-trips-are-up
- Perrone M, Renault M. Heading into holidays, US COVID-19 testing strained again. AP News. 2020 [cited 2023 Mar 8]. https://apnews.com/article/us-covid-19-testing-strained-holidays-db20ebbcc1fa8a411be8f9ebc241af3b
- Mangrum M. All metro Nashville public schools students to stay remote after Thanksgiving. The Tennessean. 2020 [cited 2023 Mar 8]. https://www.tennessean.com/story/news/education/2020/11/23/mnps-schools-stay-closed-after-thanksgiving-coronavirus-spike/6342873002
- Kelley JP. Dayton schools to hold no classes for next 6 weeks, go to school in June instead. Dayton [Ohio] Daily News. 2020 [cited 2023 Mar 2]. https://www.daytondailynews.com/local/six-week-break-part-of-big-change-to-dps-academic-calendar/V6ML2EHHVZCEPOU2YJJJDFT33E
- Sawchuk S, Gewertz C. Schools are retreating to remote learning as COVID-19 surges. Do they have to? Education Week. 2020 [cited 2023 Mar 2]. https://www.edweek.org/leadership/schools-are-retreating-to-remote-learning-as-covid-19-surges-do-they-have-to/2020/11
- US Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves first COVID-19 vaccine—approval signifies key achievement for public health. 2021 Aug 23 [cited 2023 Apr 7]. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-first-covid-19-vaccine
- Earnest R, Uddin R, Matluk N, Renzette N, Turbett SE, Siddle KJ, et al.; New England Variant Investigation Team. Comparative transmissibility of SARS-CoV-2 variants Delta and Alpha in New England, USA. Cell Rep Med. 2022;3:
100583 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Twohig KA, Nyberg T, Zaidi A, Thelwall S, Sinnathamby MA, Aliabadi S, et al.; COVID-19 Genomics UK (COG-UK) consortium. Hospital admission and emergency care attendance risk for SARS-CoV-2 delta (B.1.617.2) compared with alpha (B.1.1.7) variants of concern: a cohort study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2022;22:35–42. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- White House. Fact sheet: President Biden to announce new actions to get more Americans vaccinated and slow the spread of the Delta variant. 2021 [cited 2023 Mar 22]. https://www.whitehouse.gov/briefing-room/statements-releases/2021/07/29/fact-sheet-president-biden-to-announce-new-actions-to-get-more-americans-vaccinated-and-slow-the-spread-of-the-delta-variant
- Liu Y, Rocklöv J. The effective reproductive number of the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2 is several times relative to Delta. J Travel Med. 2022;29:taac037.
- Pampati S, Rasberry CN, Timpe Z, McConnell L, Moore S, Spencer P, et al. Disparities in implementing COVID-19 prevention strategies in public schools, United States, 2021–22 school year. Emerg Infect Dis. 2023;29:937–44. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Qualls N, Levitt A, Kanade N, Wright-Jegede N, Dopson S, Biggerstaff M, et al.; CDC Community Mitigation Guidelines Work Group. Community mitigation guidelines to prevent pandemic influenza—United States, 2017. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2017;66:1–34. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Donovan CV, Rose C, Lewis KN, Vang K, Stanley N, Motley M, et al. SARS-CoV-2 incidence in K–12 school districts with mask-required versus mask-optional policies—Arkansas, August–October 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022;71:384–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
1Current affiliation: Henry M. Jackson Foundation, Bethesda, Maryland, USA.