Volume 30, Number 10—October 2024
Dispatch
Clustering of Polymorphic Membrane Protein E Clade in Chlamydia trachomatis Lineages from Men Who Have Sex with Men
Figure 2
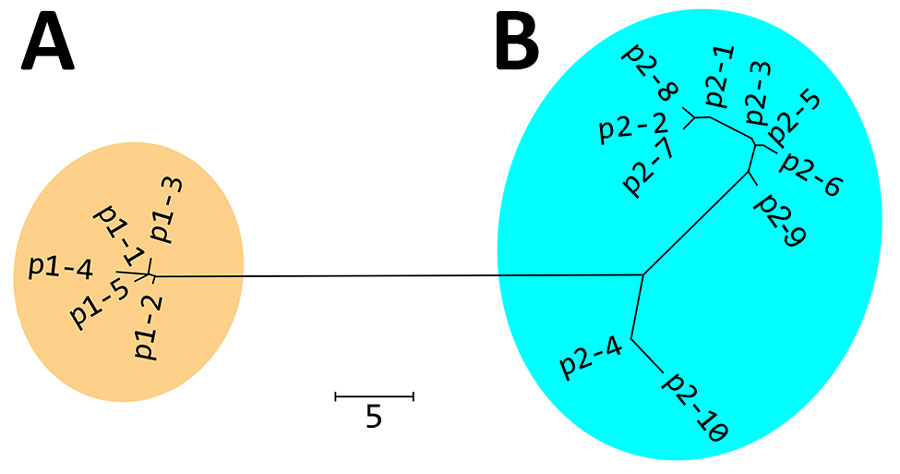
Figure 2. Nonrooted phylogenetic tree created on the basis of polymorphic membrane protein E of 298 Chlamydia trachomatis samples in study of clustering of specific polymorphic membrane protein E clade in C. trachomatis lineages from MSM, Japan. A) Cluster of 96.7% MSM (237 samples) and 0% non-MSM (0 samples); B) cluster of 3.3% MSM (8 samples) and 100% non-MSM (53 samples). p1 and p2 are 2 clades representing the MSM (p1) and non-MSM (p2) populations. The amino acid sequences of p1–1 to p2–10 are shown in Appendix 2 Figure. Numbers of samples included in each sequence: p1-1, n = 178; p1-2, n = 56; p1-3, n = 1; p1-4, n = 1; p1-5, n = 1; p2-1, n = 16; p2-2, n = 14; p2-3, n = 10; p2-4, n = 9; p2-5, n = 6; p2-6, n = 2; p2-7, n = 1; p2-8, n = 1; p2-9, n = 1; and p2-10, n = 1. Scale bar indicates the number of amino acid differences.