Volume 30, Number 12—December 2024
Research
Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N1) Virus Infection in Cats, South Korea, 2023
Abstract
In July 2023, cases of highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) were reported at 2 shelters for stray cats in Seoul, South Korea. The cause of infection was suspected to be improperly sterilized raw food made from domestic duck meat, which was manufactured in South Korea. All viruses isolated from cats at the shelters and from the raw food belonged to HPAI A(H5N1) clade 2.3.4.4b. The gene constellation of all viruses was most similar to that of viruses isolated in Korea in November 2022. Of note, the viruses isolated from infected cats harbored mutations E627K or D701N in polymerase basic 2, which are indicative of adaptation to mammals. Postmortem examination revealed systemic pathologic lesions and the presence of widespread virus in different tissues. Thus, consumption of raw duck meat contaminated with HPAI virus likely caused systemic symptoms and death in cats, indicating the introduction of mammal-adapted mutations of the virus.
Highly pathogenic avian influenza virus (HPAIV) (H5Nx) subtype descendents of the H5N1 Goose-Guangdong (Gs/Gd) lineage emerged in 1996; since then, derivatives of H5Nx have disseminated intercontinentally through wild migratory waterfowl and human activity (1–3). Since 2020, HPAI H5 viruses belonging to the Gs/Gd lineage have become panzootic, demonstrating continual reassortment with low pathogenicity avian influenza viruses (LPAIV). Those viruses have shown unprecedented global spread among poultry and wild birds, even infecting mammals and humans (1,4). In most cases, mammal infection results from direct or indirect contact with infected birds or from consumption of dead birds, suggesting that the avian virus can be transmitted to mammal hosts (5).
Viruses belonging to H5Nx clade 2.3.4.4b caused major outbreaks in wild birds in Asia, Europe, Africa, and America (6,7); infections even extended to both terrestrial and aquatic mammals (8). Wild mammals, such as red foxes, lynxes, and skunks, and domestic mammals, including pet ferrets, domestic mink, raccoon dogs, and arctic foxes, have been infected by H5N1 clade 2.3.4.4b viruses; moreover, the disease has been detected in aquatic mammal species including seals and sea lions in North and South America (6,9,10). In addition, a report from Italy in July 2023 revealed infected cats and dogs living in close proximity to humans (10); studies conducted since June 2023 report that 29 domestic cats in at least 6 regions of Poland were infected with the H5N1 clade 2.3.4.4b virus (10–12).
In South Korea, HPAIV infection of cats and dogs on poultry farms affected by HPAIV were reported in 2015 and 2016. Those infections are thought to have occurred through close contact with, or consumption of, HPAIV-infected birds (13,14). HPAIV was later confirmed in cats at 2 different cat shelters in 2023. In July 2023, cats housed in a cat shelter in Seoul were found dead, leading the owner to request diagnostic tests at a private diagnostic institution. Subsequently, a veterinary laboratory at Seoul National University (SNU) became involved in the diagnosis of those samples. The SNU laboratory contacted the Animal and Plant Quarantine Agency (APQA) in South Korea with the HPAIV-positive test results; the HPAIVs were isolated from dead cats and belonged to H5N1 clade 2.3.4.4b with a D701N mutation in the polymerase basic (PB) 2 gene (15). A second shelter in Seoul reported suspected clinical signs of HPAIV infection in cats 5 days later. We obtained additional clinical samples from cats and the environments of the 2 shelters and conducted various tests to identify the source of infection and to characterize the viruses.
In this study, we describe identifying the source of infection through environmental sampling, epidemiologic investigations, and genetic analysis. We also evaluate the risk for human infection and transmission between mammals. Furthermore, we explore disease pathogenesis, focusing on virus replication in tissues and associated pathologic sequelae.
Case Description and Sampling
On July 24, 2023, SNU contacted the APQA, the national reference institute headquarters responsible for avian influenza diagnosis in South Korea, to report possible HPAIV infection of cats housed in a shelter located in Yongsan-gu, Seoul (shelter 1). To ensure the results and investigate the case, we collected additional samples from 3 frozen cat carcasses and 2 live cats at the shelter; we also collected blood from 2 live cats, neither of which showed clinical signs for serologic testing. On July 29, 2023, a vet charged with examining hospitalized cats from another cat shelter in Gwanak-gu, Seoul (shelter 2), also reported suspected cases of HPAIV infection. A cat carcass, as well as nasal swab samples from 4 sick cats housed at the animal hospital and from the 122 cats remaining at shelter 2, were collected and tested by the Seoul local veterinary service. The clinical samples and the cat carcasses that tested positive for the H5 gene from shelter 2 were sent to APQA. We performed postmortem examination on all the cat carcasses sent to APQA from the 2 shelters and collected tissue samples from various organs. All those samples and other clinical swab samples were subjected to molecular diagnostic tests for avian influenza or other suspected diseases.
To determine the location and the extent of contamination of the shelters, we conducted environmental sampling (183 swabs) at various locations within 2 shelters within 2–3 days of the report of HPAIV. The swabs were placed in a viral transport medium and delivered to the APQA directly. We categorized environmental samples according to sampling location, type of object sampled, the structures within the shelter itself, whether the items were cat-related (e.g., food), and samples from wildlife residues located outside the shelter.
Furthermore, we conducted epidemiologic environmental sampling at relevant sites associated with contaminated raw food, such as raw duck meat food manufacturers, slaughterhouses, meat storage facilities, suspected duck farms, other cat shelters, and locations associated with feral cats. We collected 214 samples from 9 different locations and tested them at the APQA. In addition, we also sampled and tested all types of raw food for cats or dogs on the market (produced by 10 other manufacturers); in total, we tested 65 raw food products and 24 raw meats of duck or chicken origin.
Molecular Detection, Isolation, and Sequencing
We tested swab samples, tissue samples, and virus isolates by real-time reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR), as described previously (16,17), to detect the matrix (M), H5, or H7 genes of avian influenza (18). If a sample tested positive for H5, we amplified the cleavage site within the H5 hemagglutinin (HA) gene by RT-PCR and determined nucleotide sequences using an Applied Biosystems ABI 3500xL Genetic Analyzer (ThermoFisher Scientific, https://ww.thermofisher.com) for pathotyping (18).
To isolate and characterize the virus, we inoculated H5-positive samples into 10-day-old embryonated chicken eggs and incubated for 48 hours at 37°C. We extracted viral RNA from the infectious allantoic fluid using an NX-48 Viral NA kit (Genolution, https://genolution.co.kr). We amplified all 8 segments of the isolates by RT-PCR (19). We performed complete-genome sequencing using the Illumina Miseq platform with the Nextera DNA Flex Library Prep Kit (https://www.illumina.com) and assembled genomic sequences by using CLC Genomics Workbench version 23 (QIAGEN, https://www.qiagen.com). We deposited the nucleotide sequences of 12 viruses isolated in this study in the GISAID database (https://www.gisaid.org; accession nos. EPI_ISL_18819799–EPI_ISL_18819810). We downloaded the reference datasets for phylogenetic analysis of all the gene segments characterized in this study from GenBank and the GISAID EpiFlu Databases. We aligned those sequences with MAFFT (https://mafft.cbrc.jp/alignment/software) using the default parameters for FASTA alignment. We removed all untranslated regions and retained only the protein-coding sequences of each segment. We constructed maximum-likelihood trees based on the aligned sequences using RAxML on XSEDE version 8.2.12 (20). We used bootstrap analysis with 1,000 replicates to assess the reliability of the trees and generated the tree displays by using the interactive Tree of Life program (21).
Pathologic Examination
We conducted necropsy to confirm HPAIV diagnosis and to examine pathologic lesions. We collected tissue samples (brain, heart, lung, spleen, kidney, liver, pancreas, and intestine), fixed for 24 hours in 10% buffered neutral formalin, and then processed for paraffin embedding. We then cut 4-µm sections, mounted, dewaxed, and stained with hematoxylin and eosin. We analyzed duplicate sections by immunohistochemistry to determine the distribution of influenza virus antigens using a monoclonal antibody specific for influenza A virus nucleoprotein (Bio-Rad Laboratories, https://www.bio-rad.com). We used a biotinylated goat anti-mouse IgG and an avidin-biotin complex system, using the RedMap Kit (all Roche, https://www.roche.com) as the chromogenic substrate. We incubated the negative control slide in phosphate-buffered saline instead of the primary antibody.
Serologic Testing
We treated serum samples from 2 surviving cats from shelter 1 with a receptor-destroying enzyme (Denka Seiken, https://www.denka.co.jp), inactivated at 56°C for 30 minutes, and chilled at 10°C. We performed hemagglutination inhibition assays using standard methods and homologous antigens (22).
Detecting, Isolating, and Characterizing Viruses from Cats in the Shelters
We detected the H5 gene in nasal swab samples and all tested organs from the 3 carcasses at shelter 1 and 1 cat carcass from the shelter 2–related animal hospital (Table 1). In addition, nasal swab samples from the 3 living cats at the animal hospital and its related shelter 2, were positive for the H5 gene (Table 1). All H5-positive samples had multiple basic amino acid residues at the cleavage site of the HA gene (PLREKRRKR/G), corresponding to the motif that denotes the HPAI virus, was detected. In addition, the analysis of the neuraminidase (NA) sequences assigned all the viruses sequenced to the N1 subtype. As expected, HPAI H5N1 viruses were isolated from the affected cats from the 2 shelters. The 2 surviving cats in shelter 1 had H5-specific antibodies (hemagglutination inhibition titer, 25) (Table 1).
The 3 H5N1 viruses isolated from dead cats in shelter 1 were designated A/feline/Korea/M302-5/2023, A/feline/Korea/M302-6/2023, and A/feline/Korea/M302-7/2023, referred to hereafter as M302-5, M302-6, and M302-7. The 4 H5N1 isolates from shelter 2 were named A/feline/Korea/M305-11/2023 (for the dead cat in the hospital), A/feline/Korea/M305-7/2023 (for the sick cat in the hospital), A/feline/Korea/M305-3/2023 and A/feline/Korea/M305-4/2023, referred to hereafter M305-11, M305-7, M305-3, and M305-4.
Pathologic Lesions
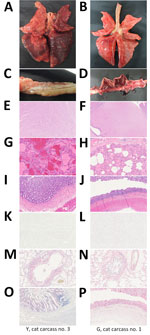
We first examined the carcasses (Figure 1) and assigned a body condition score (1–3, poor weight; 4–6, ideal weight; 7–9, overweight) (23); all 3 cat carcasses from shelter 1 (Y cat nos. 1–3) had a score of 7 (Appendix Table 1). Two carcasses (1 from shelter 1 [Y cat no. 3] and 1 from shelter 2 [G cat no. 1]) grossly exhibited diffuse moderate to severe congestion and edema in the lungs (Figure 1, panels A and B), as well as interstitial pneumonia characterized by infiltration of macrophages and degenerated neutrophils into the vascular and alveolar lumina (Figure 1, panels G and H). Y cat no. 3 did not have gross or microscopic lesions in the brain or small intestine (Figure 1, panels C, E, and I); that finding was true for all 3 carcasses from shelter 1. However, the carcass from shelter 2 had multifocal encephalitis, with gliosis and perivascular cuffing in the brain, and bloody diarrhea in the small intestine (Figure 1, panels D, F, and J). Immunohistochemistry revealed influenza virus antigens in alveolar macrophages and bronchial epithelial cells in all 4 cats (Figure 1, panels M, N). The carcass from shelter 2 also had influenza antigens in neurons, glial cells (Figure 1, panel L), and intestinal epithelial cells in the small intestine (Figure 1, panel P). No influenza viral antigens were present in the brains of carcasses from shelter 1, but H5 genes were detected (Table 1; Appendix Table 2).
Environment Sampling
To investigate the source and extent of contamination at the cat shelters, we collected 183 environmental samples from both inside and outside the cat shelters and tested them by real-time RT-PCR. In shelter 1, we detected the M gene in samples taken from staff’s shoes and clothing, floors, doors, walls, and refrigerators. In shelter 2, we detected the M gene in vacuum cleaners and in cat feces, whereas we detected the M and H5 gene in the 4 unopened containers of raw cat food manufactured by a company using domestic duck meat as a main ingredient (Appendix Table 3).
Thereafter, we isolated H5N1 virus from the cat raw food, manufactured on July 6; we named the isolte A/environment/Korea/M305E-13/2023(H5N1), referred to hereafter as EV/M305E-13 (Table 2; Table 3). Upon conducting a nationwide recall and investigating the raw food produced by the manufacturer in question, we collected all raw food products of the same brand from customers. Of note, we isolated identical viruses not only from the same brand of food at the manufacturer but also in the food bought by customers, which was manufactured using the same lot of raw duck meat, albeit on different dates (May 26, June 15, and July 6 and 27). The level of viral infectivity in the raw food products was 102.5–103.5 50% egg infectious dose (EID50)/g (Table 2). The viruses isolated from them were designated as A/environment/Korea/M305E2-24/2023 (M305E2-24), A/environment/Korea/M305E2-25/2023 (M305E2-25), and A/environment/Korea/M305E3-1/2023 (M305E3-1) (Table 2).
We identified all facilities or companies that had handled the duck meat contained in the infectious raw cat food and tested for the presence of virus; those facilities consisted of suspected duck farms, slaughterhouses, meat processing companies, middlemen, and retailers. No virus could be detected in 214 samples from 9 locations. In addition, all types of raw foods (65 products and 24 meats from 10 manufacturers) for pet cats or dogs on the market were tested and determined to be avian influenza–negative (data not shown).
Genetic Analysis
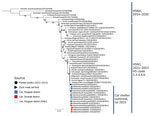
To identify the source of the H5N1 virus isolated from cats and raw food, we analyzed representative viruses isolated at each location alongside other viruses within H5Nx clade 2.3.4.4b (Figures 2, 3). The 8 genes of the 3 viruses, M302-5, M305-11, and M305E-13, were almost identical among them (99.9% for nucleoprotein, HA, and PB1 and 100% for polymerase acidic [PA], NA, M, and nonstructural [NS]). Phylogenetic analysis revealed that the HA and NA genes of the 3 viruses are most closely related to those of the H5N1 clade 2.3.4.4b identified in 2022–2023 (Figures 2, 3), 1 of which was A/duck/Korea/H537/2022(H5N1); nucleotide identities to them were 99.46%–100% across the 8 genes (Appendix Table 4). All the cat viruses isolated from shelter 1, including M302-5, possessed mutation D701N in the PB2 gene, whereas all the cat viruses isolated from shelter 2, including M305-11, possessed mutation E627K in the PB2 gene (Table 3; Appendix Table 4). The D701N and E627K mutations in the PB2 gene are critical markers of virus adaptation to mammals (12).
The owner of shelter 1 in Seoul, in which 38 of 40 cats died within a month beginning in late June 2023 (15), had taken sick cats with respiratory and neurologic symptoms to a private animal hospital in early July. Of the 38 cats that died, HPAIV was diagnosed in only 5; the other 33 cat carcasses had been disposed of without diagnosis (15). After the report of the HPAI case in shelter 1, all cat owners, shelters, and veterinarians were urged to report influenza-like illnesses to the government, and another suspicious case in cats originating from shelter 2 was disclosed.
The HPAI infections of dogs (2015) and cats (2016) previously reported in South Korea were related to infected wild birds (13,14). However, the infections of cats in 2 shelters located in a metropolitan city in 2023 could not be attributed to direct contact with wild birds or poultry. Therefore, the HPAI-contaminated raw cat food found at shelter 2 was regarded as a critical and direct source of infection. Furthermore, the viruses isolated from the cats (M305-11) and the raw food from shelter 2 (M305E-13) presented a genetic similarity >99.9% for all the genes, and that similarity strongly supports the idea that the raw food was the direct source of infection, particularly in shelter 2. The gene constellation of M302-4, M305-11, and M305E-13 was most similar to that of viruses isolated in Korea in November 2022; 1 of those was A/duck/Korea/H537/2022(H5N1), which had a nucleotide identity of 99.46%–100% across the 8 genes (Appendix Table 4). These viruses possess a gene constellation representing that of a group, including A/duck/Korea/H537/2022(H5N1), dominant in South Korea (R.M. Cha, unpub. data) in the winter of 2022–2023, which was also isolated from birds in Japan during the same period (15).
The viral infectivity of the contaminated raw food product ranged from 102.5 to 103.5 EID50/g, which is similar to the minimal dose required to infect cats (102–104 EID50/g) (24). The high viral load in most organs from the dead cats suggests that the virus replicated systemically and affected the host severely, similar to the effects of HPAI in chickens. The pattern of distribution of viral load, virus particles, and lesions observed in the cat carcasses was very similar to that observed in other HPAI H5N1–infected cats (both naturally and experimentally infected cases) (24). Previous studies report that gastrointestinal exposure is sufficient to infect cats with HPAIV; the liver and lungs are the main organs affected (25,26). We also found that the liver, lungs, and especially the intestines of cats from shelter 2 had the highest viral load among all organs (cycle threshold 12–19), along with clear pathologic lesions (Figure 1). Our results support the fact that oral consumption of contaminated raw food products can induce extensive lesions in the digestive system, along with concurrent infection of the respiratory and digestive systems (Figure 1) (27). The dead cats, and those with clinical signs, at shelter 2 had likely ingested the cat raw food repeatedly, resulting in substantial exposure to the virus. By contrast, the cat carcasses from shelter 1 had been stored in a frozen state, making it difficult to determine the route of HPAI infection on the basis of pathologic lesions alone. Although no direct evidence of contaminated food was found at shelter 1, the cause of infection is presumed to be the same as at shelter 2; that presumption is based on a statement from the owner of shelter 1 that cats had been fed a variety of types of raw food and the discovery of a receipt for the purchase of the same brand of raw cat food consumed in shelter 2. Of note, the 2 kinds of mutations related to mammalian adaptations, PB2-E627K and PB2-D701N, were observed in the viruses isolated from cats in shelter 1 (PB2-E627K) and shelter 2 (PB2-D701N). However, in the viruses isolated from the raw cat food, none of these point mutations were observed. The mammal-adaptive mutations at the critical genome sites of the HPAI virus are the same as those reported previously (28,29).
In other genomic regions, the viruses isolated from the cats in shelter 2 had amino acid differences in a few locations (Appendix Table 5). Each of those cat viruses in shelter 2, notably, had quasispecies containing minor populations with glutamic acid (E) at 627th in PB2 and major populations with lysine (K) at the same location (data not shown). Therefore, in the case of shelter 2, all the cats were likely infected from the direct ingestion of the contaminated raw foods. For the cat viruses from shelter 1, most of the deceased cats and raw food were disposed of before testing, and feeding records for the infected animals were not maintained, making the route of infection and transmission in that shelter difficult to infer. HPAI infection of cats in Poland during the summer of 2023 was suspected to be caused primarily by cat food made from poultry meat (11,12).
The main ingredient of the raw food collected from shelter 2 was domestic duck meat, and we suspect some infected broiler ducks were slaughtered despite intensive and regular active avian influenza surveillance on broiler duck farms during the HPAI incursion period; broiler duck farms should be tested 3–4 times for avian influenza before ducks are moved to the slaughterhouse (30). Further epidemiologic investigations revealed that the cat food manufacturer had not performed the required electron beam sterilization process during production, and the omission of the sterilization process is considered the most direct cause of cat infection in the shelters (data not shown). Thus, all facilities or companies that handled duck meat were contacted and ordered to clean and disinfect the premises to prevent secondary infections by avian influenza viruses. Promptly identifying the source of infection in shelter 2 led to the recall of all contaminated raw cat food products or products at risk for contamination; all were discarded.
The cases of HPAI infection at 2 cat shelters caring primarily for stray cats located in Seoul, South Korea, were sporadic and irregular. The source of infection at shelters was improperly sterilized raw cat food. We identified systemic virus and pathologic manifestations in the carcasses of cats that had consumed this raw food and confirmed the presence of mammalian-adaptive mutations in the viruses isolated from the cats. From these results, ways to increase disease surveillance sensitivity on poultry farms continue to be sought on the basis of the risk-based surveillance principle (31). In addition, more strict disease monitoring in the slaughterhouse is also necessary, especially for subclinical infection of duck species. As a last resort, the risk for avian influenza virus infection in pets should be mitigated by achieving compliance and enforcing regulations for sterilization of raw food. Moreover, it was also perceived that humans exposed to the risk for HPAI infection must be identified and monitored, and various preventive measures have been implemented by the authorities for human health. In conclusion, strict management and adequate sterilization for raw poultry meat are required, along with active surveillance, to prevent influenza-like illnesses that could become a public health concern.
Dr. Kang is a researcher with the Animal and Plant Quarantine Agency and is also a professor at the College of Veterinary Medicine, Kyungpook National University in South Korea. He primary research interest is the diagnosis, vaccine development, and genetic characterization of avian influenza.
Acknowledgments
We thank Jeong-Eui Lee, Byeong-Suk Jeon, and Chae-Rin Lee for excellent technical assistance. We also thank the Animal and Plant Quarantine Agency; Ministry of Agriculture, Food, and Rural Affairs; and the Regional office for Animal Disease Control for their efforts to control avian influenza. Finally, we thank our colleagues worldwide for their laboratory contributions, which were made available through GISAID.
This research was supported by a grant from the Animal and Plant Quarantine Agency (B-1543418-2023-23-01) of the Republic of Korea.
K.-N.L. and Y.-M.K. conceptualized the study. Y.-M.K. and G.-B.H. wrote the original draft. Visualization: S.-H.A., A.-Y.K. and J.K. visualized the study and K.L. and B.K. conducted formal analysis. Data were curated by Y.J., E.-K.L. and R.M.C. M.S. and S.H.K. constructed the methodology. Investigations were conducted by H.L. and E.P. and study was supervised by Y.-J.L., K.L. and K.-N.L. All authors reviewed the manuscript. All authors approved the final version.
References
- Kalthoff D, Globig A, Beer M. (Highly pathogenic) avian influenza as a zoonotic agent. Vet Microbiol. 2010;140:237–45. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Verhagen JH, Fouchier RAM, Lewis N. Highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses at the wild-domestic bird interface in Europe: future directions for research and surveillance. Viruses. 2021;13:212. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gauthier-Clerc M, Lebarbenchon C, Thomas F, Thomas F. Recent expansion of highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1: a critical review. Ibis. 2007;149:202–14. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Yamaji R, Saad MD, Davis CT, Swayne DE, Wang D, Wong FYK, et al. Pandemic potential of highly pathogenic avian influenza clade 2.3.4.4 A(H5) viruses. Rev Med Virol. 2020;30:
e2099 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - de Wit E, Kawaoka Y, de Jong MD, Fouchier RA. Pathogenicity of highly pathogenic avian influenza virus in mammals. Vaccine. 2008;26(Suppl 4):D54–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Abolnik C, Phiri T, Peyrot B, de Beer R, Snyman A, Roberts D, et al. The molecular epidemiology of clade 2.3.4.4B H5N1 high pathogenicity avian influenza in Southern Africa, 2021–2022. Viruses. 2023;15:1383. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jimenez-Bluhm P, Siegers JY, Tan S, Sharp B, Freiden P, Johow M, et al. Detection and phylogenetic analysis of highly pathogenic A/H5N1 avian influenza clade 2.3.4.4b virus in Chile, 2022. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2023;12:
2220569 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Lindh E, Lounela H, Ikonen N, Kantala T, Savolainen-Kopra C, Kauppinen A, et al. Highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) virus infection on multiple fur farms in the South and Central Ostrobothnia regions of Finland, July 2023. Euro Surveill. 2023;28:
2300400 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Adlhoch C, Fusaro A, Gonzales JL, Kuiken T, Mirinavičiūtė G, Niqueux É, et al.; European Food Safety Authority; European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control; European Union Reference Laboratory for Avian Influenza. Avian influenza overview June-September 2023. EFSA J. 2023;21:
e08328 .PubMedGoogle Scholar - Moreno A, Bonfante F, Bortolami A, Cassaniti I, Caruana A, Cottini V, et al. Asymptomatic infection with clade 2.3.4.4b highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) in carnivore pets, Italy, April 2023. Euro Surveill. 2023;28:
2300441 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Rabalski L, Milewska A, Pohlmann A, Gackowska K, Lepionka T, Szczepaniak K, et al. Emergence and potential transmission route of avian influenza A (H5N1) virus in domestic cats in Poland, June 2023. Euro Surveill. 2023;28:
2300390 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Domańska-Blicharz K, Świętoń E, Świątalska A, Monne I, Fusaro A, Tarasiuk K, et al. Outbreak of highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) clade 2.3.4.4b virus in cats, Poland, June to July 2023. Euro Surveill. 2023;28:
2300366 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Lee K, Lee EK, Lee H, Heo GB, Lee YN, Jung JY, et al. Highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N6) in domestic cats, South Korea. Emerg Infect Dis. 2018;24:2343–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Animal and Plant Quarantine Agency. 2014–2016 HPAI epidemiological investigation analysis report. Gimcheon-si (South Korea): The Agency; 2016.
- Lee K, Yeom M, Vu TTH, Do HQ, Na W, Lee M, et al. Characterization of highly pathogenic avian influenza A (H5N1) viruses isolated from cats in South Korea, 2023. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2024;13:
2290835 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Sagong M, Lee YN, Song S, Cha RM, Lee EK, Kang YM, et al. Emergence of clade 2.3.4.4b novel reassortant H5N1 high pathogenicity avian influenza virus in South Korea during late 2021. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2022;69:e3255–60. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Heo GB, Kye SJ, Sagong M, Lee EK, Lee KN, Lee YN, et al. Genetic characterization of H9N2 avian influenza virus previously unrecognized in Korea. J Vet Sci. 2021;22:
e21 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Slomka MJ, Coward VJ, Banks J, Löndt BZ, Brown IH, Voermans J, et al. Identification of sensitive and specific avian influenza polymerase chain reaction methods through blind ring trials organized in the European Union. Avian Dis. 2007;51(Suppl):227–34. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lee DH. Complete genome sequencing of influenza A viruses using next-generation sequencing. Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2123:69–79. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Miller MA, Pfeiffer W, Schwartz T. Creating the CIPRES Science Gateway for inference of large phylogenetic trees. In: 2010 Gateway Computing Environments Workshop (GCE); New Orleans, LA; 2010 Nov 14. p. 1–8.
- Letunic I, Bork P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v5: an online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021;49(W1):W293–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- World Health Organization. Manual for the laboratory diagnosis and virological surveillance of influenza. Geneva: The Organization; 2011.
- Teng KT, McGreevy PD, Toribio JALML, Raubenheimer D, Kendall K, Dhand NK. Associations of body condition score with health conditions related to overweight and obesity in cats. J Small Anim Pract. 2018;59:603–15. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Vahlenkamp TW, Harder TC, Giese M, Lin F, Teifke JP, Klopfleisch R, et al. Protection of cats against lethal influenza H5N1 challenge infection. J Gen Virol. 2008;89:968–74. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Songserm T, Amonsin A, Jam-on R, Sae-Heng N, Meemak N, Pariyothorn N, et al. Avian influenza H5N1 in naturally infected domestic cat. Emerg Infect Dis. 2006;12:681–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Vahlenkamp TW, Teifke JP, Harder TC, Beer M, Mettenleiter TC. Systemic influenza virus H5N1 infection in cats after gastrointestinal exposure. Influenza Other Respir Viruses. 2010;4:379–86. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lipatov AS, Kwon YK, Pantin-Jackwood MJ, Swayne DE. Pathogenesis of H5N1 influenza virus infections in mice and ferret models differs according to respiratory tract or digestive system exposure. J Infect Dis. 2009;199:717–25. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Alkie TN, Cox S, Embury-Hyatt C, Stevens B, Pople N, Pybus MJ, et al. Characterization of neurotropic HPAI H5N1 viruses with novel genome constellations and mammalian adaptive mutations in free-living mesocarnivores in Canada. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2023;12:
2186608 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Gabriel G, Czudai-Matwich V, Klenk HD. Adaptive mutations in the H5N1 polymerase complex. Virus Res. 2013;178:53–62. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kang YM, Heo GB, An SH, Lee YN, Cha RM, Cho HK, et al. Introduction of multiple novel high pathogenicity avian influenza (H5N1) virus of clade 2.3.4.4b into South Korea in 2022. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2023;2023:
ID8339427 . DOIGoogle Scholar - Kim Y, Fournié G, Métras R, Song D, Donnelly CA, Pfeiffer DU, et al. Lessons for cross-species viral transmission surveillance from highly pathogenic avian influenza Korean cat shelter outbreaks. Nat Commun. 2023;14:6958. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Figures
Tables
Cite This ArticleOriginal Publication Date: November 04, 2024
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
Table of Contents – Volume 30, Number 12—December 2024
| EID Search Options |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|

Please use the form below to submit correspondence to the authors or contact them at the following address:
Kwang-Nyeong Lee or Kyunghyun Lee, Avian Influenza Research and Diagnostic Division, Animal and Plant Quarantine Agency, 177, Hyeoksin 8-ro, Gimcheon-si, Gyeongsangbuk-do 39660, South Korea
Top