Volume 30, Number 2—February 2024
Research Letter
Severe Infective Endocarditis Caused by Bartonella rochalimae
Figure
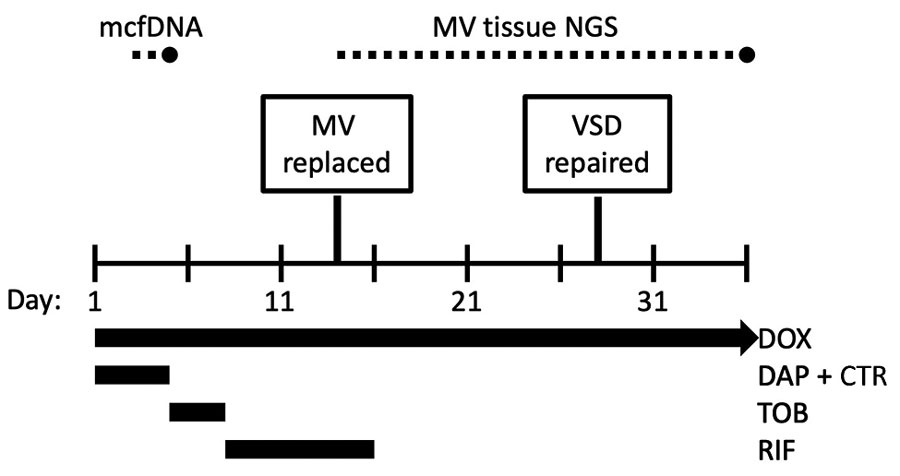
Figure. Diagnostics and treatments for Bartonella rochalimae endocarditis during a 36-day hospitalization. Dotted lines indicate the time between specimen collection and test result for mcfDNA and MV tissue NGS tests. CTR, ceftriaxone; DAP, daptomycin; DOX, doxycycline; mcfDNA, microbial cell-free DNA; MV, mitral valve; NGS, next-generation sequencing; RIF, rifampin; TOB, tobramycin; VSD, ventricular septal defect.
Page created: December 31, 2023
Page updated: January 24, 2024
Page reviewed: January 24, 2024
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.