Volume 30, Number 2—February 2024
Research
Evolution and Spread of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N1) Clade 2.3.4.4b Virus in Wild Birds, South Korea, 2022–2023
Figure 6
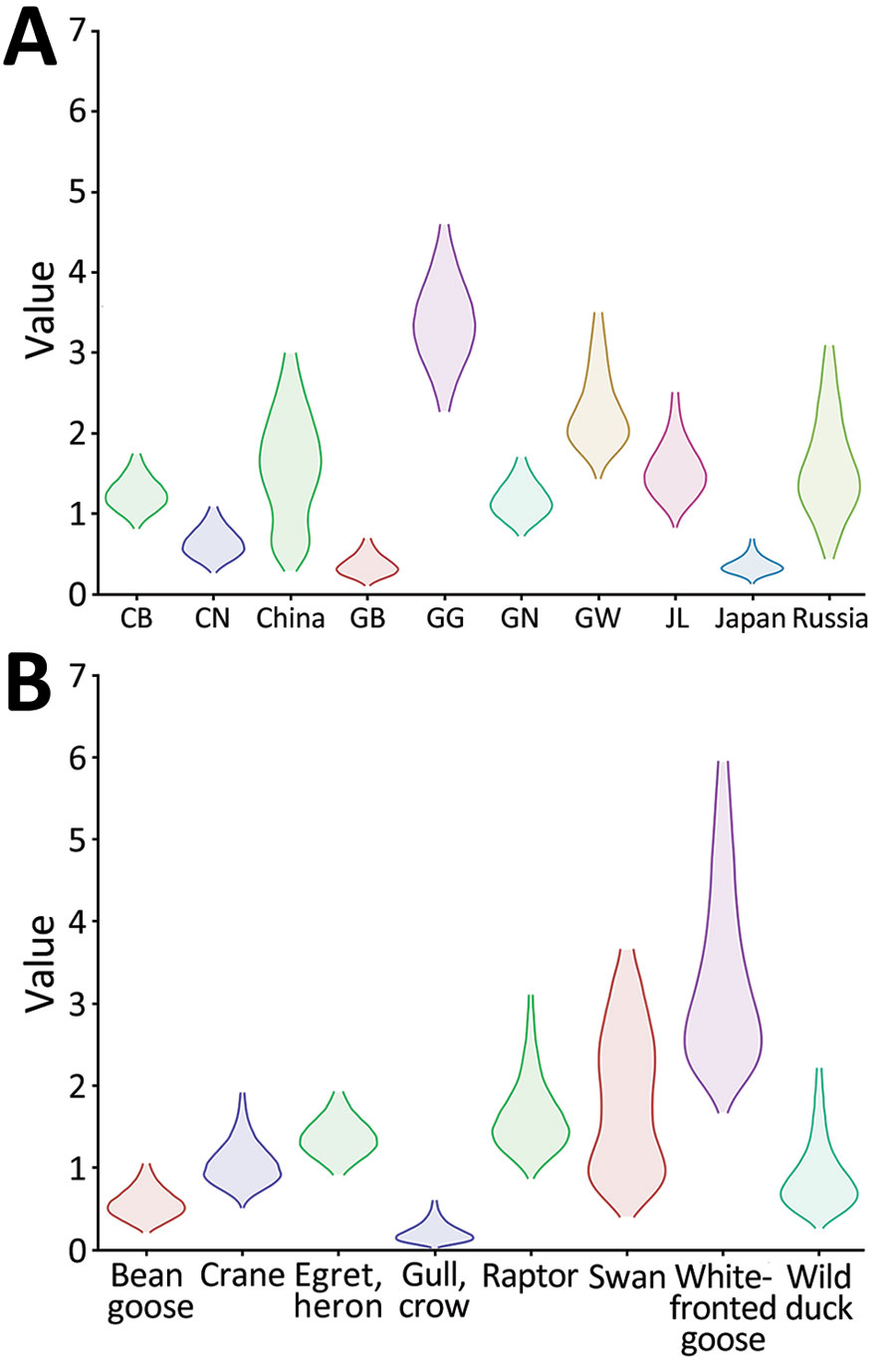
Figure 6. Markov time spent for geographic location (A) and host type (B) among highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) viruses from wild birds, South Korea, October 2022–March 2023. CB, Chungcheongbuk-do; CN, Chungcheongnam-do; GB, Gyeongsangbuk-do; GG, Gyeonggi-do; GN, Gyeongsangnam-do; GW, Gangwon-do; JL, Jeolla-do.
1These first authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: December 19, 2023
Page updated: January 24, 2024
Page reviewed: January 24, 2024
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.