Volume 30, Number 3—March 2024
Research
Effect of Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine on Pneumonia Incidence Rates among Children 2–59 Months of Age, Mongolia, 2015–2021
Figure 3
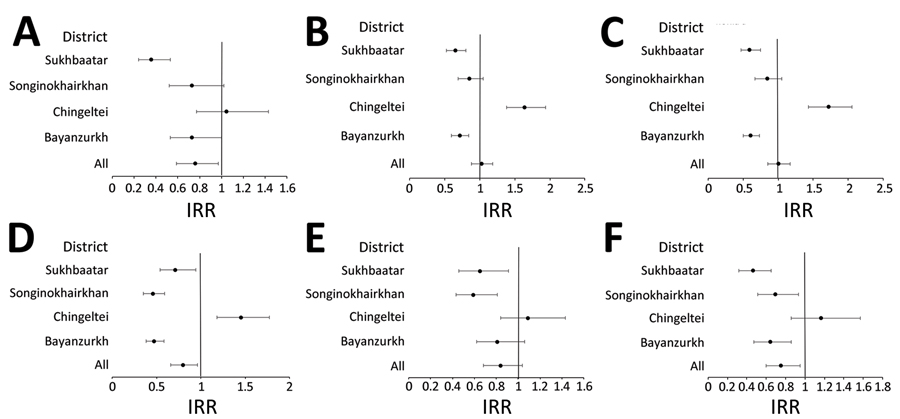
Figure 3. Adjusted IRRs for pneumonia endpoints post-vaccine period (April 2015–June 2021, including COVID-19 pandemic period) in study of effect of pneumococcal conjugate vaccine on pneumonia incidence rates among children 2–59 months of age, Mongolia, 2015–2021. A) Primary endpoint pneumonia; B) all pneumonia; C) severe pneumonia; D) very severe pneumonia; E) hypoxic pneumonia; F) probable pneumococcal pneumonia. Error bars indicate 95% CIs. IRR, incidence rate ratio.
Page created: January 31, 2024
Page updated: February 22, 2024
Page reviewed: February 22, 2024
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.