Volume 30, Number 3—March 2024
Dispatch
Bedaquiline Resistance after Effective Treatment of Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis, Namibia
Figure 2
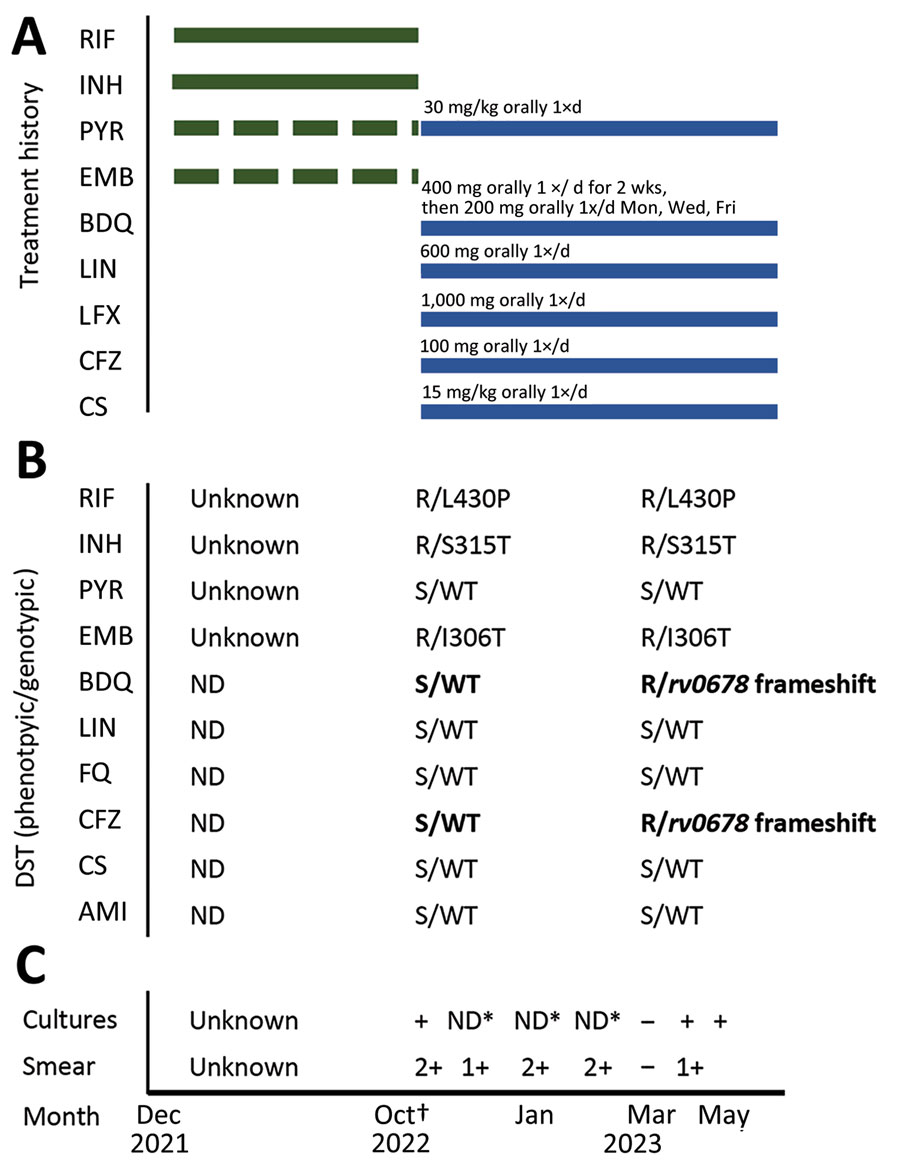
Figure 2. Timeline for a case of tuberculosis in a patient in Namibia whose infection became drug resistant after effective treatment. The case was originally diagnosed and treated beginning in December 2021. Interruptions in treatment were caused by stockout. Second-line drugs were not used. Full detailed treatment history is unknown. The patient sought care in Namibia in September 2022; we diagnosed MDR TB in October 2022. Treatment failed and rv0678 mutation was identified in a culture from June 2023. A) Patient’s treatment history. Green bars represent treatment of drug-susceptible TB; blue bars represent treatment of MDR TB. B) Evolution of phenotypic and genotypic drug susceptibility testing with resistance-associated variants using Deeplex Myc TB (https://www.deeplex.com). Testing was done at time of diagnosis of MDR TB and after culture reversion. Bold text de novo indicates mutations. Months show time of specimen collection. C) Culture and smear test results. Asterisks indicate that tests were not done because of stockouts. Months show time of specimen collection. Dagger indicates start of MDR TB treatment. AMI, amikacin; BDQ, bedaquiline; CFZ, clofazimine; CS, cycloserine; DS, drug-susceptible; EMB, ethambutol; FQ, fluoroquinolones; INH, isoniazid; LIN, linezolid; LFX, levofloxacin; MDR, multidrug-resistant; ND, not done; PYR, pyrazinamide; R, resistant; RIF, rifampin; S, susceptible; TB, tuberculosis; WT, wild type.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.