Phylogenetic Characterization of Orthohantavirus dobravaense (Dobrava Virus)
Mert Erdin

, Ceylan Polat, Teemu Smura, Sercan Irmak, Ortac Cetintas, Muhsin Cogal, Faruk Colak, Ahmet Karatas, Mustafa Sozen, Ferhat Matur, Olli Vapalahti, Tarja Sironen, and Ibrahim Mehmet Ali Oktem
Author affiliations: University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland (M. Erdin, T. Smura, O. Vapalahti, T. Sironen); Hacettepe University, Ankara, Turkey (C. Polat); Balıkesir University, Balıkesir, Turkey (S. Irmak); Bulent Ecevit University, Zonguldak, Turkey (O. Cetintas, M. Cogal, F. Colak, M. Sozen); Ömer Halisdemir University, Niğde, Turkey (A. Karatas); Dokuz Eylul University, Izmir, Turkey (F. Matur, I.M.A. Oktem)
Main Article
Figure 2
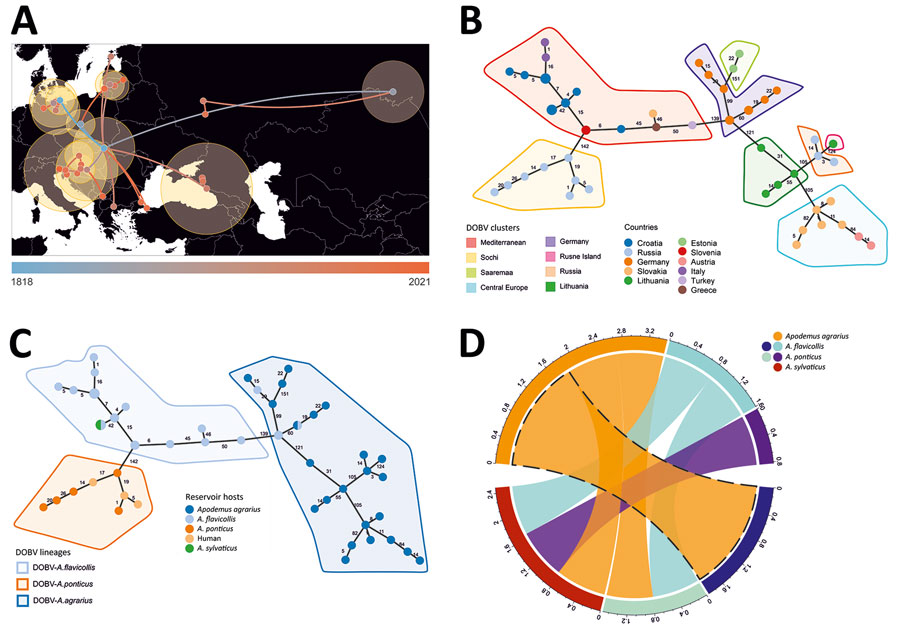
Figure 2. Host switching, phylogeographic reconstruction, and phylogenetic characterization of DOBV according to Bayesian analysis and minimum spanning tree constructions. A) Phylogeographic reconstruction of DOBV in discrete space. Each node is colored according to the estimated year of discovery, from the earliest (blue) to the latest (orange). Yellow shaded circles show the relative intensity of local viruses spread in the covered area. B) Minimum spanning tree showing the geographical cluster separation. C) Minimum spanning tree suggesting 3 major lineages according to reservoir host species. D) Chord diagram representing host switching rates of DOBV between 4 rodent species: Apodemus flavicollis (yellow-necked mouse), A. agrarius (striped field mouse), A. ponticus (Black Sea field mice), and A. sylvaticus (wood mice). DOBV, Dobrava virus (Orthohantavirus dobravaense).
Main Article
Page created: February 06, 2024
Page updated: March 20, 2024
Page reviewed: March 20, 2024
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.
