Volume 30, Number 4—April 2024
Research Letter
Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Moldova, and Ukraine, 2017–2022
Figure
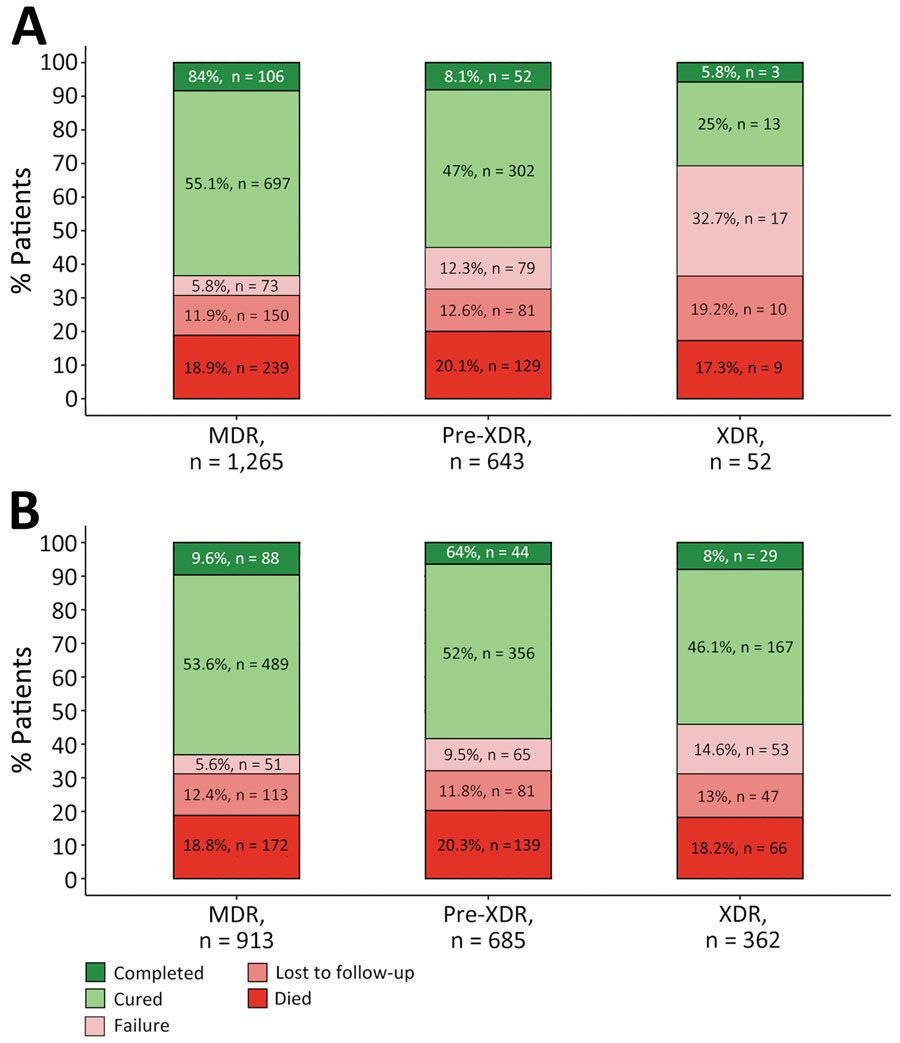
Figure. Treatment outcomes for patients with MDR, pre-XDR, and XDR tuberculosis (TB) in Georgia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Moldova, and Ukraine during 2017–2022 by current (A) and former (B) definitions of drug resistance. We excluded 9 patients with an unevaluated outcome and 15 patients without outcome data. TB treatment outcomes were defined according to WHO recommendations (6,7). MDR TB was defined as TB caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains resistant to at least both rifampin and isoniazid (1). We used the current definition of pre-XDR TB from 2021 as TB caused by M. tuberculosis strains fulfilling the definition of MDR TB but including resistance to any fluoroquinolone (levofloxacin or moxifloxacin), whereas XDR TB was defined as additional resistance to >1 group A drug (bedaquiline or linezolid) (A). The previous, informal definition of pre-XDR TB was MDR TB plus additional resistance to any fluoroquinolone, or any second-line injectable, but not both, whereas the definition of XDR TB from 2006 was TB resistant to any fluoroquinolone and to >1 of 3 second-line injectable drugs (capreomycin, kanamycin, and amikacin), in addition to MDR TB. MDR, multidrug-resistant; XDR, extensively drug-resistant.
References
- World Health Organization. Meeting report of the WHO expert consultation on the definition of extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis [cited 2023 Dec 6]. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240018662
- Roelens M, Battista Migliori G, Rozanova L, Estill J, Campbell JR, Cegielski JP, et al. Evidence-based definition for extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2021;204:713–22. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pedersen OS, Holmgaard FB, Mikkelsen MKD, Lange C, Sotgiu G, Lillebaek T, et al. Global treatment outcomes of extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Infect. 2023;87:177–89. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kherabi Y, Fréchet-Jachym M, Rioux C, Yazdanpanah Y, Méchaï F, Pourcher V, et al.; MDR-TB Management Group. Revised definitions of tuberculosis resistance and treatment outcomes, France, 2006–2019. Emerg Infect Dis. 2022;28:1796–804. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mikiashvili L, Kempker RR, Chakhaia T, Bablishvili N, Avaliani Z, Lomtadze N, et al. Impact of prior TB treatment with new/companion drugs on clinical outcomes in patients receiving concomitant bedaquiline and delamanid for MDR/RR-TB. Clin Infect Dis. 2023;
ciad694 ; Epub ahead of print. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Pedersen OS, Butova T, Kapustnyk V, Miasoiedov V, Kuzhko M, Hryshchuk L, et al. Treatment outcomes and risk factors for an unsuccessful outcome among patients with highly drug-resistant tuberculosis in Ukraine. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2024;30:360–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- World Health Organization. Definitions and reporting framework for tuberculosis—2013 revision: updated December 2014 and January 2020 [cited 2023 Dec 6]. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241505345
- Veziris N, Bonnet I, Morel F, Guglielmetti L, Maitre T, Fournier Le Ray L, et al.; CNR MyRMA; Members of the CNR-MyRMA (French National Reference Center for Mycobacteria. Impact of the revised definition of extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis. Eur Respir J. 2021;58:
2100641 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Collaborative Group for the Meta-Analysis of Individual Patient Data in MDR-TB treatment–2017; Ahmad N, Ahuja SD, Akkerman OW, et al. Treatment correlates of successful outcomes in pulmonary multidrug-resistant tuberculosis: an individual patient data meta-analysis. Lancet. 2018;392:821–34.
- Ismail NA, Omar SV, Moultrie H, Bhyat Z, Conradie F, Enwerem M, et al. Assessment of epidemiological and genetic characteristics and clinical outcomes of resistance to bedaquiline in patients treated for rifampicin-resistant tuberculosis: a cross-sectional and longitudinal study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2022;22:496–506. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar