Volume 30, Number 5—May 2024
Dispatch
Seasonal Patterns of Mpox Index Cases, Africa, 1970–2021
Figure 2
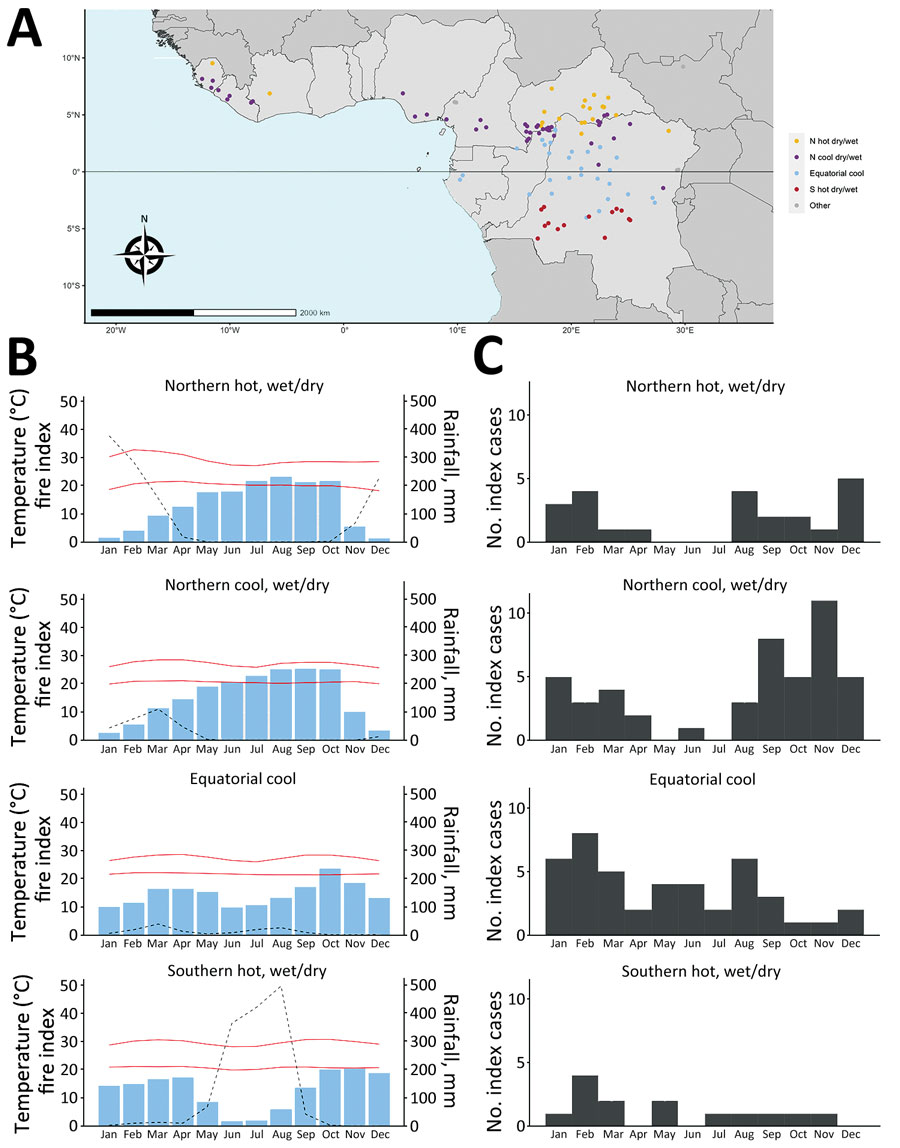
Figure 2. Seasonal distribution of mpox index cases according to the climate profile in Africa, 1970–2021. A) Climate/seasonal profile by site. B) Average monthly rainfall, temperature, and fire index (dotted line) for each climate/seasonal profile. C) Distribution of outbreak index cases by month for each climate/seasonal profile.
Page created: March 28, 2024
Page updated: April 24, 2024
Page reviewed: April 24, 2024
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.