Volume 30, Number 5—May 2024
Research Letter
Burkholderia thailandensis Isolated from Infected Wound, Southwest China, 2022
Cite This Article
Citation for Media
Abstract
We report a clinical isolate of Burkholderia thailandensis 2022DZh obtained from a patient with an infected wound in southwest China. Genomic analysis indicates that this isolate clusters with B. thailandensis BPM, a human isolate from Chongqing, China. We recommend enhancing monitoring and surveillance for B. thailandensis infection in both humans and livestock.
Burkholderia thailandensis is a member of the Burkholderia pseudomallei complex and is generally considered nonpathogenic (1). Initially identified in Thailand, B. thailandensis was distinguished from B. pseudomallei by its ability to assimilate arabinose (2). Similar to B. pseudomallei, B. thailandensis is frequently found in soil and water, especially in rice paddies (3,4). Although invasive infections caused by B. thailandensis are rare worldwide, recent reports have documented cases of suppurative infections, such as wound infections, cellulitis, and tissue abscesses (5,6). Previously, we identified a strain of B. thailandensis BPM that caused a human infection in Chongqing, southwest China (7). In this study, we report another clinical isolate of B. thailandensis that we obtained in Dazhu, Sichuan, southwest China, from an infected wound resulting from a cut inflicted by a farm tool in 2022.
A 61-year-old male farmer who had untreated type 2 diabetes mellitus reported a 1-month history of pain and swelling in his left knee. He had injured the middle toe of his left foot with a plow a month earlier, and redness, swelling, and pain developed below the left knee joint. Despite a week of antimicrobial treatment at a local community health center, his symptoms did not improve. In December 2022, the patient began to experience weakness in his right lower limb, and he later fell, sustaining an injury to his left lower limb. During this period, he experienced lower-limb weakness and exhibited symptoms related to the central nervous system. He sought care and was admitted to the orthopedics department of Dazhu County People’s Hospital (Dazhou, China) for treatment of a left lower-limb injury and a left-foot diabetic foot infection. However, because his central nervous system symptoms worsened, he was transferred to the neurology department and receive a diagnosis of osteomyelitis and demyelinating disease. B. thailandensis strain 2022DZh was obtained from a deep-tissue specimen during surgical debridement of the infected wound on the left foot (Appendix Figure 1). The initial empirical antimicrobial therapy consisted of cefradine. However, the hospital laboratory tested the isolate 2022DZh using the VITEK 2 COMPACT system (bioMérieux, https://www.biomerieux.com) and identified it as B. pseudomallei, leading to a switch to intravenous meropenem treatment (Appendix Table 1). Despite treatment with meropenem, the patient’s condition continued to deteriorate; he died 3 days after applying for discharge.
Subsequently, the isolate 2022DZh was submitted to the laboratory for confirmatory identification. Results of arabinose assimilation testing of isolate 2022DZh by API 20NE system (bioMérieux) were positive, consistent with the biochemical characteristics of B. thailandensis (Appendix Figure 2). We extracted DNA from the isolate 2022DZh for confirmation and further characterization. We performed 16S rRNA gene sequencing of 2022DZh using nucleotide BLAST (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi), revealing 100% similarity with B. thailandensis BPM (Appendix Figure 3). The nucleotide sequences of the 2 chromosomes of isolate 2022DZh are >99.5% consistent with those of B. thailandensis E264 and B. thailandensis E254 (Appendix Table 2). We conclusively identified isolate 2022DZh as B. thailandensis based on our phenotypic and molecular data. We deposited the genome sequences of B. thailandensis strain 2022DZh into GenBank (accession nos. CP141809.1 and CP141811.1).
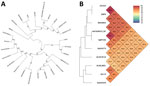
For phylogenetic analysis, we compared the genome of B. thailandensis 2022DZh with a reference panel of publicly available Burkholderia species genomes (Appendix Table 3). The single-copy gene phylogenetic tree analysis indicated that B. thailandensis 2022DZh clusters with B. thailandensis BPM (Figure, panel A). The results of average nucleotide identity revealed that B. thailandensis 2022DZh also clusters with B. thailandensis BPM; genome identity was 99.85%. However, when compared with B. pseudomallei BPC006, genome identity was 92.31% (Figure, panel B), consistent with the commonly used 95% threshold for distinguishing species. Through multilocus sequence type analysis (https://pubmlst.org/organisms/burkholderia-pseudomallei) (8), we determined that B. thailandensis 2022DZh and B. thailandensis BPM both belong to sequence type 76. In addition, there appears to be no known epidemiologic link between B. thailandensis 2022DZh and B. thailandensis BPM; they are geographically separated by a significant distance of ≈200 km (Appendix Table 3).
One limitation of this study is that we did not attempts to identify related isolates of B. thailandensis from environmental samples in this region of southwest China. Further studies are needed to identify the primary molecular mechanisms underlying the pathogenicity of B. thailandensis 2022DZh and to determine its molecular and evolutionary relationships with other strains of B. thailandensis (9).
In conclusion, our findings underscore that B. thailandensis can cause serious infections, and clinical practitioners should be aware of this type of infection (10). Therefore, we strongly recommend enhancing monitoring and surveillance for B. thailandensis infection in both humans and livestock.
Dr. Li is a researcher in the department of laboratory medicine, Daping Hospital, Army Medical University, Chongqing, China. His research primarily focuses on clinical microbiology and infectious disease.
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82072348) and the Youth Project of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82002113).
References
- Ronning CM, Losada L, Brinkac L, Inman J, Ulrich RL, Schell M, et al. Genetic and phenotypic diversity in Burkholderia: contributions by prophage and phage-like elements. BMC Microbiol. 2010;10:202. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lertpatanasuwan N, Sermsri K, Petkaseam A, Trakulsomboon S, Thamlikitkul V, Suputtamongkol Y. Arabinose-positive Burkholderia pseudomallei infection in humans: case report. Clin Infect Dis. 1999;28:927–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Birnie E, van ’t Hof S, Bijnsdorp A, Mansaray Y, Huizenga E, van der Ende A, et al. Identification of Burkholderia thailandensis with novel genotypes in the soil of central Sierra Leone. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019;13:
e0007402 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Hall CM, Stone NE, Martz M, Hutton SM, Santana-Propper E, Versluis L, et al. Burkholderia thailandensis isolated from the environment, United States. Emerg Infect Dis. 2023;29:618–21. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gee JE, Elrod MG, Gulvik CA, Haselow DT, Waters C, Liu L, et al. Burkholderia thailandensis isolated from infected wound, Arkansas, USA. Emerg Infect Dis. 2018;24:2091–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Glass MB, Gee JE, Steigerwalt AG, Cavuoti D, Barton T, Hardy RD, et al. Pneumonia and septicemia caused by Burkholderia thailandensis in the United States. J Clin Microbiol. 2006;44:4601–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chang K, Luo J, Xu H, Li M, Zhang F, Li J, et al. Human infection with Burkholderia thailandensis, China, 2013. Emerg Infect Dis. 2017;23:1416–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tuanyok A, Mayo M, Scholz H, Hall CM, Allender CJ, Kaestli M, et al. Burkholderia humptydooensis sp. nov., a new species related to Burkholderia thailandensis and the fifth member of the Burkholderia pseudomallei complex. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017;83:e02802–16. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Li J, Zhong Q, Li J, Chong HM, Wang LX, Xing Y, et al. Genomic features and virulence characteristics of a rare Burkholderia thailandensis strain causing human infection. J Med Microbiol. 2023;72:72. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cossaboom CM, Marinova-Petkova A, Strysko J, Rodriguez G, Maness T, Ocampo J, et al. Melioidosis in a resident of Texas with no recent travel history, United States. Emerg Infect Dis. 2020;26:1295–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Figure
Cite This ArticleOriginal Publication Date: April 10, 2024
Table of Contents – Volume 30, Number 5—May 2024
| EID Search Options |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Please use the form below to submit correspondence to the authors or contact them at the following address:
Weiping Lu or Qiu Zhong, Department of Laboratory Medicine, Daping Hospital, Army Medical University, Chongqing, 400042, China
Top