Volume 30, Number 5—May 2024
Research Letter
Novel Variant and Known Mutation in 23S rRNA Gene of Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Northern Vietnam, 2023
Figure
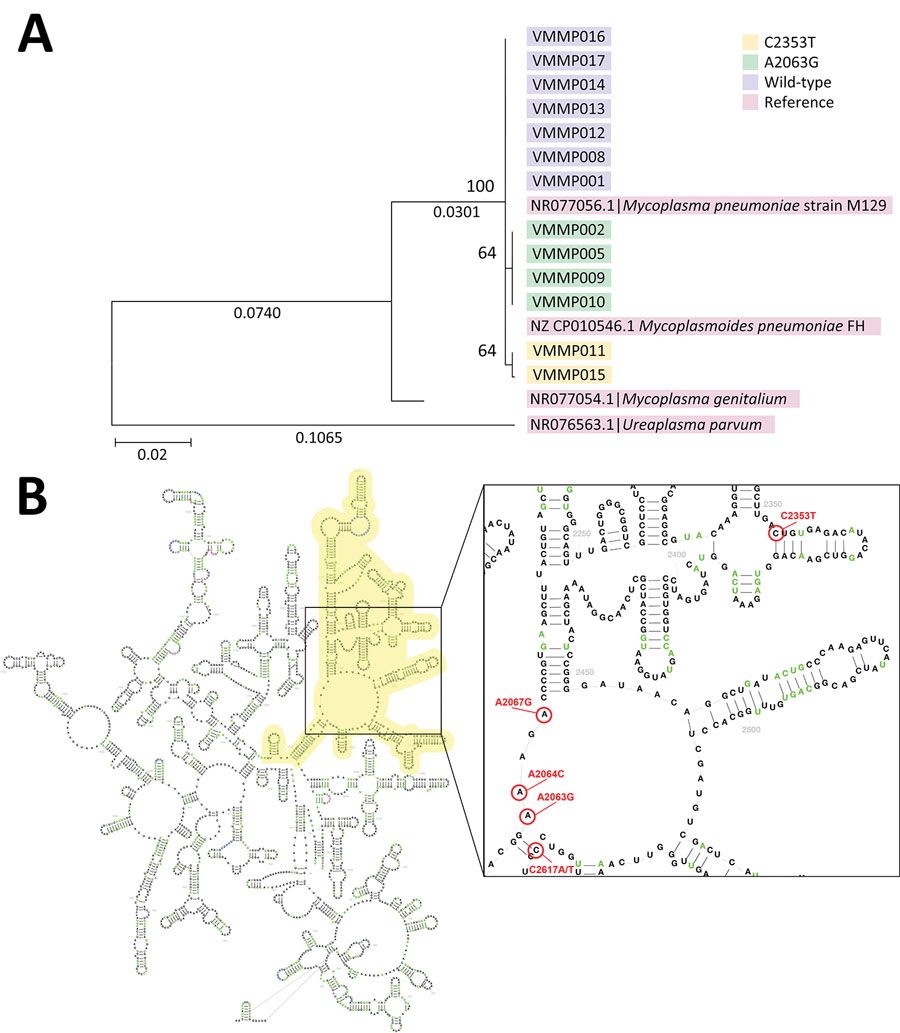
Figure. Phylogenetic tree and location of mutations for Mycoplasma pneumoniae strains identified in pediatric patients hospitalized with community-acquired pneumonia, Hanoi, Vietnam, spring/summer 2023. A) Maximum-likelihood phylogenetic analysis of the domain V region of the 23S rRNA gene. B) Predicted RNA secondary structure of 23S rRNA gene constructed with the description of known mutations (A2063G/C/T, A2064G, A2067G, C2617G) and novel variant (C2353T). Yellow highlights indicate the domain V region of 23S rRNA. Scale bar indicates base substitutions per site.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
Page created: March 28, 2024
Page updated: April 24, 2024
Page reviewed: April 24, 2024
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.