Volume 30, Number 6—June 2024
Research
Yersinia ruckeri Infection and Enteric Redmouth Disease among Endangered Chinese Sturgeons, China, 2022
Figure 3
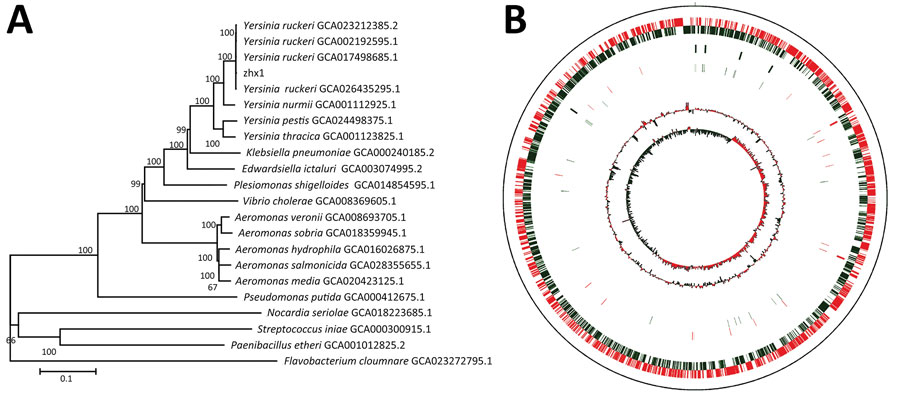
Figure 3. Genome characteristics of Yersinia ruckeri strain zhx1 isolated from artificially bred Chinese sturgeon offspring, China. A) Phylogenetic tree based on the whole genome of zhx1 and other pathogenic bacteria. B) Genome map of zhx1. The distribution of the circle from the outside indicates the genome size, forward coding DNA sequence (CDS), reverse CDS, repeat sequence, transfer RNA (black), ribosomal RNA (blue), and guanine-cytosine (GC) ratio. Colors indicate regions where the GC ratio is higher than average (red) and lower than average (green), and GC skewed either positive (red) or negative (green).
Page created: May 02, 2024
Page updated: May 22, 2024
Page reviewed: May 22, 2024
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.