Volume 30, Number 6—June 2024
Research Letter
Evaluating Humoral Immunity Elicited by XBB.1.5 Monovalent COVID-19 Vaccine
Figure
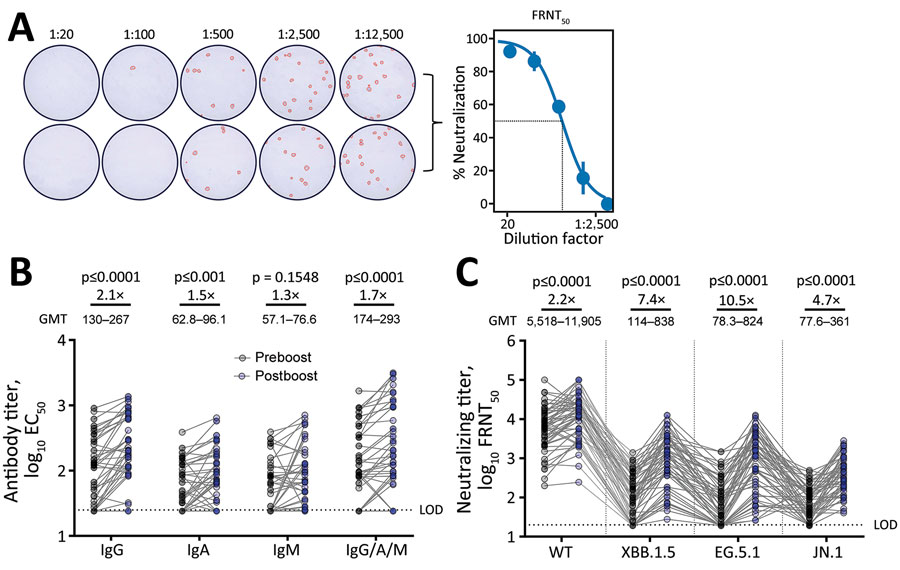
Figure. SARS-CoV-2 antibody titers in an evaluation of humoral immunity elicited by XBB.1.5 monovalent COVID-19 vaccine. A) Duplicate wells infected with live SARS-CoV-2 virus at serially diluted titers. OD was measured at 492 nm using a CLARIOstar plate reader (BMG LABTECH, https://www.bmglabtech.com). Wells were stained and counted to create representative FRNT50 curve at right. B) Preboost and postboost serum antibody isotype titers against spike RBD. C) Neutralizing titers against live ancestral (WT) SARS-CoV-2 and variants. GMT for each bar was calculated in Prism (GraphPad Software Inc., https://www.graphpad.com). All individual data points are displayed as filled circles. Boost ratios were calculated by dividing the post-XBB.1.5 vaccination GMT (postboost) by pre-vaccination GMT (preboost). Reported p values were calculated using restricted effect maximum-likelihood model (B) or 1-way repeated measures analysis of variance (C) with Šídák's multiple comparisons tests. EC50, 50% ELISA effective concentration; FRNT50, 50% focus reduction neutralization; GMT, geometric mean titer; LOD, lower limit of detection; OD, optical density; WT, wild-type.