Volume 31, Number 1—January 2025
Research Letter
Identification and Characterization of Vancomycin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus CC45/USA600, North Carolina, USA, 2021
Figure
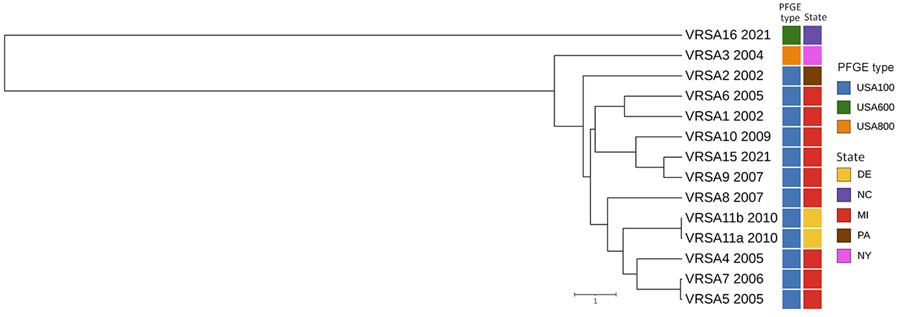
Figure. Whole-genome multilocus sequence typing for identification and characterization of VRSA, North Carolina, USA, 2021. Unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean dendrogram shows the relationship of VRSA16 and previously sequenced VRSA genomes from US patients; sequence data for VRSA 12 (CC5/PFGE type unknown), VRSA 13 (CC30/USA1100), and VRSA 14 (CC5/USA100) were not available. Date of isolation (year), PFGE type (also known as USA type), and geographic location of each VRSA isolate are indicated. Scale bar indicates the whole-genome multilocus sequence typing allelic distance. PFGE, pulsed-field gel electrophoresis; VRSA, vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
Page created: November 20, 2024
Page updated: January 03, 2025
Page reviewed: January 03, 2025
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.