Volume 31, Number 10—October 2025
Dispatch
Investigation of Possible Intraoperative Transmission of Brucella melitensis, Slovenia
Figure 2
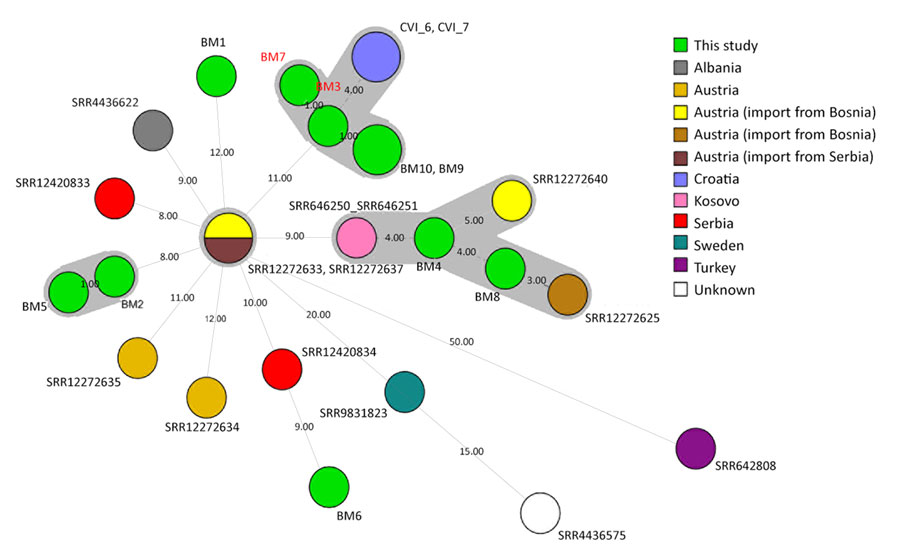
Figure 2. Minimum spanning tree based on whole-genome multilocus sequence typing allele profiles showing the relatedness of 25 Brucella melitensis isolates in study investigating possible intraoperative transmission of Brucella melitensis, Slovenia. Numbers above the branches correspond to the number of allele differences. Gray shading indicates clusters of isolates differing by ≤6 alleles. Isolates sequenced in this study shown in green: BM1 (National Center for Biotechnolgoy Information Sequence Read Archive accession no. SRR32696437), BM2 (accession no. SRR32696436), BM4 (accession no. SRR32696434), BM5 (accession no. SRR32696433), BM7 (red text, the patient; accession no. SRR32696431), BM9 (accession no. SRR32696429), BM10 (imported from Bosnia and Herzegovina; accession no. SRR32696428); BM8 (imported from Croatia; accession no. SRR32696430), BM6 (imported from North Macedonia; accession no. SRR32696432), and BM3 (red text, the surgeon; accession no. SRR32696435).