Volume 31, Number 10—October 2025
Dispatch
Bat-Associated Hemotropic Mycoplasmas in Immunosuppressed Children, Spain, 2024
Figure
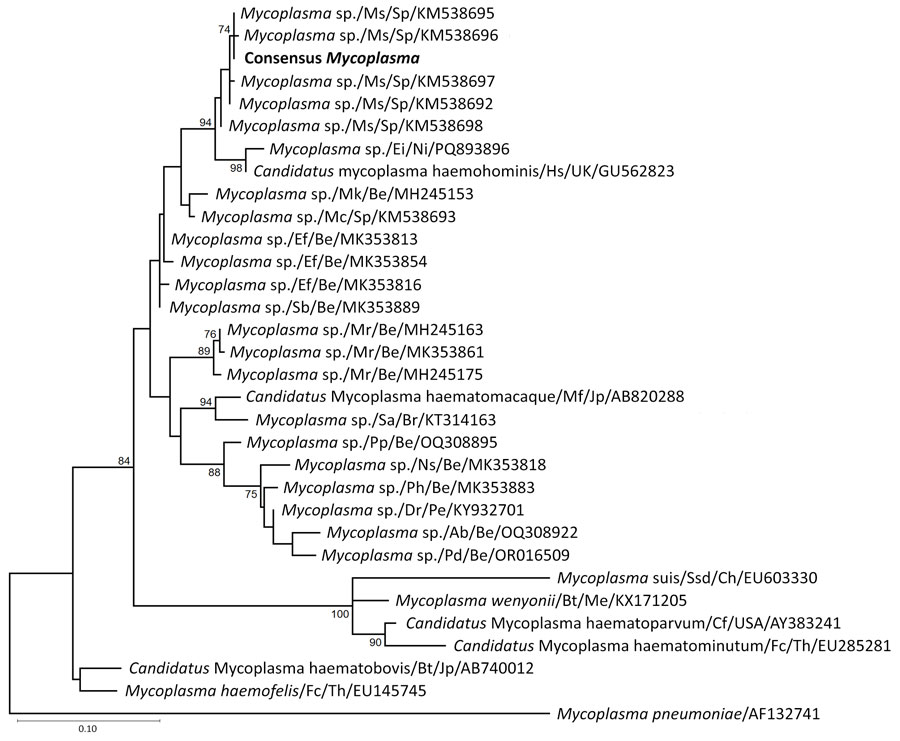
Figure. Phylogenetic analysis of sequences from samples collected in 2024 from mycoplasma-positive pediatric patients in study of bat-associated hemotropic mycoplasmas in immunosuppressed children, Spain, 2024. Bold indicates sequence from this study. Numbers at the nodes represent bootstrap support values; values >75% are not shown. GenBank accession numbers are indicated for reference sequences. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site. Hosts are indicated as follows: Ab, Artibeus phaeotis (pygmy fruit-eating bat); Bt, Bos taurus (cattle); Cf, Canis familiaris (dog); Dr, Desmodus rotundus (common vampire bat); Ef, Eptesicus furinalis (Argentine brown bat); Ei, Eidolon sp. (palm bat); Fc, Felis catus (cat); Hs, Homo sapiens (human); Mc, Myotis capaccinii (long-fingered bat); Mf, Macaca fuscata (Japanese macaque); Mk, Myotis keaysi (hairy-legged myotis bat); Mr, Molossus rufus (black mastiff bat); Ms, Miniopterus schreibersii (bent-wing bat); Ns, Natalus stramineus mexicanus (Mexican funnel-eared bat); Pd, Phyllostomus discolor (pale spear-nosed bat); Pp, Pteronotus parnellii (Parnell's mustached bat); Ph, Platyrrhinus helleri (Heller's broad-nosed bat); Sa, Sapajus apella (tufted capuchin); Sb, Saccopteryx bilineata (greater sac-winged bat); Ssd, Sus scrofa domesticus (domestic pig). Countries are indicated as follows: Be, Belize; Br, Brazil; C, China; Jp, Japan; Me, Mexico; Ni, Nigeria; Pe, Peru; Sp, Spain; Th, Thailand; UK, United Kingdom.