Volume 31, Number 3—March 2025
Dispatch
Haemophilus influenzae Type b Meningitis in Infants, New York, New York, USA, 2022–2023
Figure
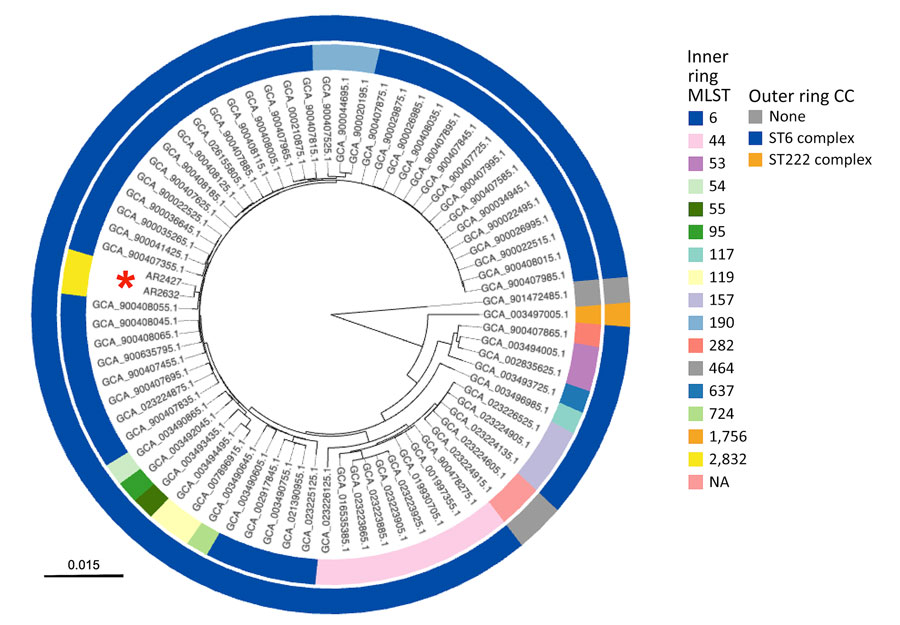
Figure. Genetic distance tree constructed to assess genetic relatedness among strains in study of Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) meningitis in infants, New York, New York, USA, 2022–2023. We constructed the tree using Mashtree (10) for Hib strains from the 2 New York patients (red asterisk) and reference sequences from GenBank (Appendix Table). Rings are color-coded to indicate MLST (inner ring) and CC (outer ring). Tree was rooted using the genome for NCTC 8468 (GenBank accession nos. GCA_90147285.1), a division II, sodC-containing Hib strain distantly related to other sequenced Hib isolates. Branch lengths represent mash distances. CC, clonal complex; MLST, multilocus sequence type; NA, not available.
References
- Briere EC, Rubin L, Moro PL, Cohn A, Clark T, Messonnier N; Division of Bacterial Diseases, National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, CDC. Prevention and control of haemophilus influenzae type b disease: recommendations of the advisory committee on immunization practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm Rep. 2014;63(RR-01):1–14.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gilsdorf JR. Hib vaccines: their impact on Haemophilus influenzae type b disease. J Infect Dis. 2021;224(Suppl 2):S321–30. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Myers AL, Jackson MA, Zhang L, Swanson DS, Gilsdorf JR. Haemophilus influenzae type b invasive disease in Amish children, Missouri, USA, 2014. Emerg Infect Dis. 2017;23:112–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hanze Villavicencio KL, Job MJ, Burghard AC, Taffet A, Banda FM, Vurayai M, et al. Genomic analysis of group B Streptococcus carriage isolates from Botswana reveals distinct local epidemiology and identifies novel strains. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2023;10:
ofad496 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Bouras G, Judd LM, Edwards RA, Vreugde S, Stinear TP, Wick RR. How low can you go? Short-read polishing of Oxford Nanopore bacterial genome assemblies. Microb Genom. 2024;10:
001254 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Wick RR, Judd LM, Cerdeira LT, Hawkey J, Méric G, Vezina B, et al. Trycycler: consensus long-read assemblies for bacterial genomes. Genome Biol. 2021;22:266. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jolley KA, Bray JE, Maiden MCJ. Open-access bacterial population genomics: BIGSdb software, the PubMLST.org website and their applications. Wellcome Open Res. 2018;3:124. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Watts SC, Holt KE. hicap: In silico serotyping of the Haemophilus influenzae capsule locus. J Clin Microbiol. 2019;57:e00190–19. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Argimón S, Abudahab K, Goater RJE, Fedosejev A, Bhai J, Glasner C, et al. Microreact: visualizing and sharing data for genomic epidemiology and phylogeography. Microb Genom. 2016;2:
e000093 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Katz LS, Griswold T, Morrison SS, Caravas JA, Zhang S, den Bakker HC, et al. Mashtree: a rapid comparison of whole genome sequence files. J Open Source Softw. 2019;4:1762. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Adegbola RA, Secka O, Lahai G, Lloyd-Evans N, Njie A, Usen S, et al. Elimination of Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) disease from The Gambia after the introduction of routine immunisation with a Hib conjugate vaccine: a prospective study. Lancet. 2005;366:144–50. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Blain A, MacNeil J, Wang X, Bennett N, Farley MM, Harrison LH, et al. Invasive Haemophilus influenzae disease in adults ≥65 years, United States, 2011. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2014;1:
ofu044 . DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar - Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. ChildVaxView [cited 2024 Oct 01]. https://www.cdc.gov/childvaxview
- Coen PG, Heath PT, Barbour ML, Garnett GP. Mathematical models of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Epidemiol Infect. 1998;120:281–95. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Nolen LD, Topaz N, Miernyk K, Bressler S, Massay SC, Geist M, et al. Evaluating a cluster and the overall trend of invasive Haemophilus influenzae serotype b in Alaska 2005-2019. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2022;41:e120–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: February 04, 2025
Page updated: February 28, 2025
Page reviewed: February 28, 2025
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.