Volume 31, Number 3—March 2025
Research Letter
Community-Acquired Pneumonia Caused by Avian Chlamydia abortus, the Netherlands
Figure 2
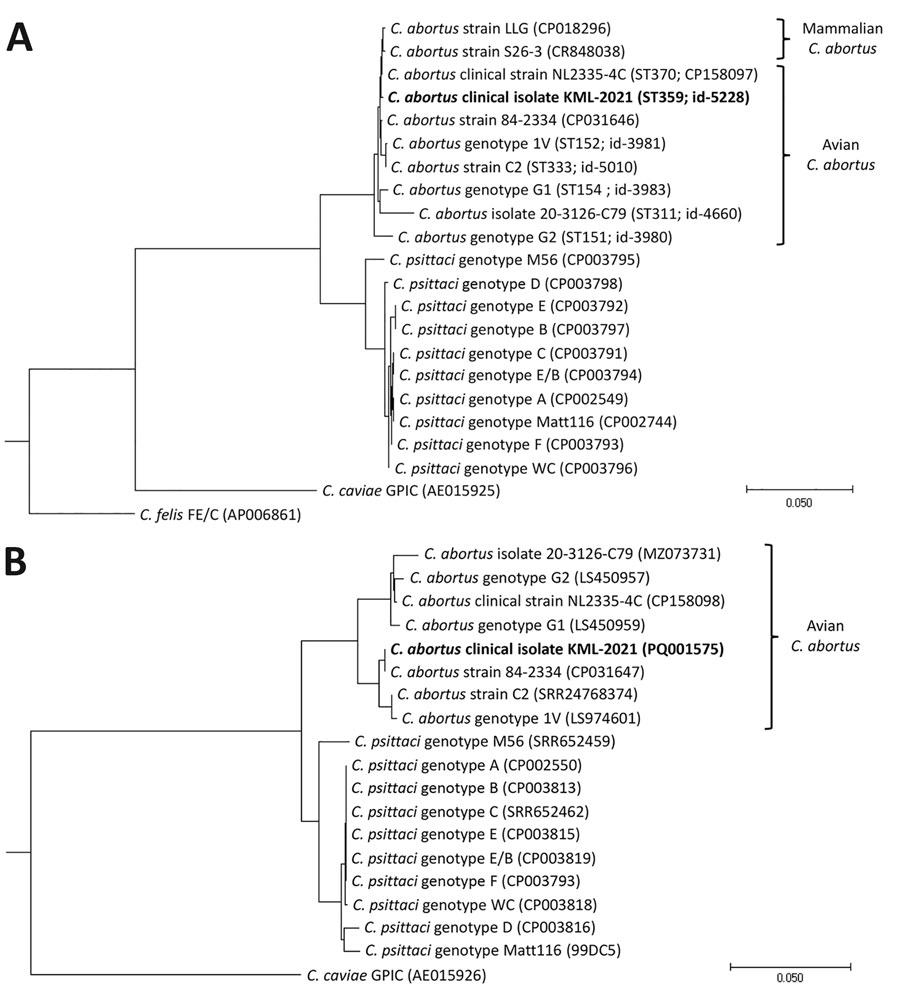
Figure 2. Chlamydial phylogeny of isolates from a patient with community-acquired pneumonia caused by avian Chlamydia abortus, the Netherlands, and reference sequences. Chlamydial phylogenetic trees were constructed by using concatenated MLST gatA, oppA, hflX, gidA, enoA, hemN, and fumC gene sequences (A) or by using plasmid II xerC gene sequences (B) of clinical isolate KML-2021 (bold; PubMLST sequence type 359; id-5228, https://pubmlst.org) and reference Chlamydia isolates (GenBank accession no. or PubMLST id shown) that were aligned and analyzed in MEGA11 (https://www.megasoftware.net). The phylogenetic tree was constructed by using maximum-likelihood approximation with FastTree v2.1.11 (https://kbase.us/applist/apps/kb_fasttree/run_FastTree/release) and rooted with C. felis (FE/C) or C. caviae (GPIC reference strains). Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per 100 sites. id, identification; MLST, multilocus sequence typing.