Volume 31, Number 3—March 2025
Dispatch
Cefotaxime-Resistant Neisseria meningitidis Sequence Type 4821 Causing Fulminant Meningitis
Figure 1
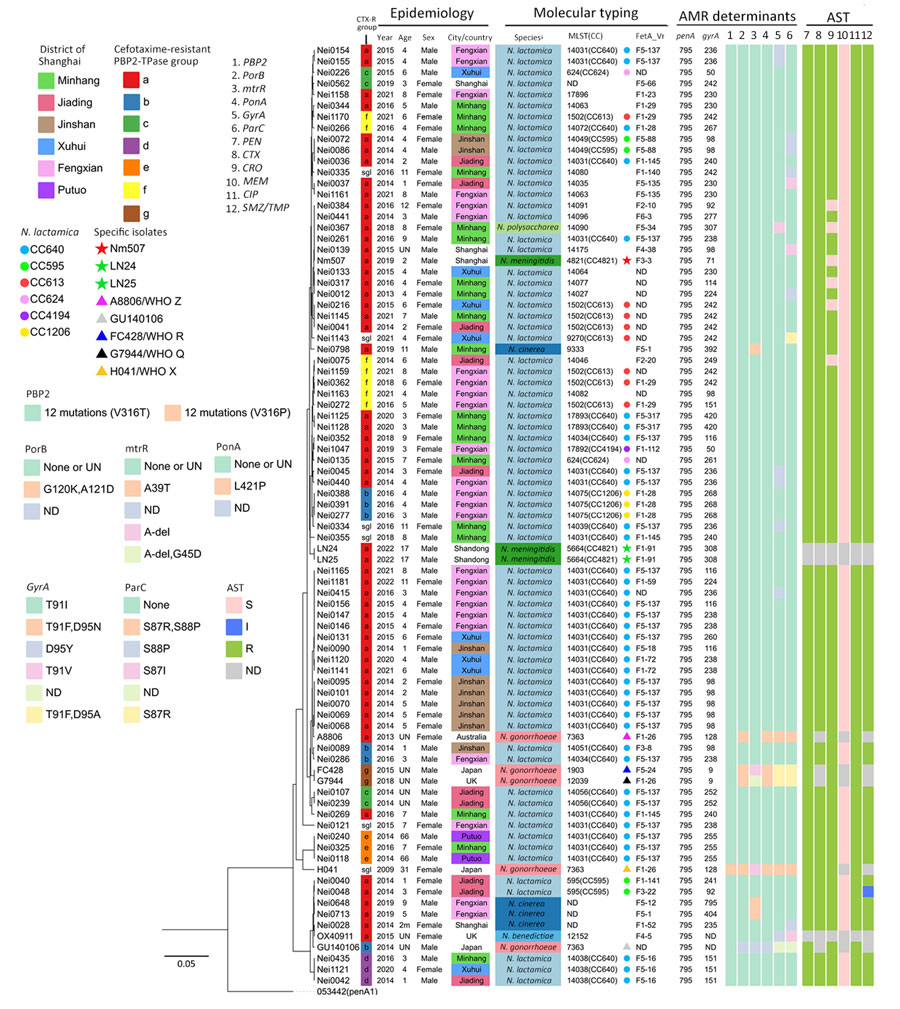
Figure 1. Epidemiologic and molecular characterizations of penA795-bearing Neisseria meningitidis, N. gonorrhoeae, and Neisseria commensals in study of cefotaxime-resistant N. meningitidis sequence type 4821 causing fulminant meningitis. Epidemiology, molecular typing, antimicrobial resistance determinants, and antimicrobial susceptibility testing results of 85 penA795-bearing Neisseria isolates are shown. The leftmost tree depicts the phylogeny of the PBP2-TPase region (penA 718 to 1,746 bp). Analysis of mutations in antimicrobial resistance-associated genes/determinants is provided in the Appendix. Scale bar indicates number of nucleotide substitutions per site. AMR, antimicrobial resistance; AST, antimicrobial susceptibility testing; CC, clonal complex; CIP, ciprofloxacin; CRO, ceftriaxone; CTX, cefotaxime; MEM, meropenem; MLST, multilocus sequence type; I, intermediate; ND, not determined; PEN, penicillin; R, resistant; sgl, singleton; S, susceptible; UN, unknown.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.