Volume 31, Number 4—April 2025
Dispatch
Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza A(H5N1) Virus Stability in Irradiated Raw Milk and Wastewater and on Surfaces, United States
Figure 1
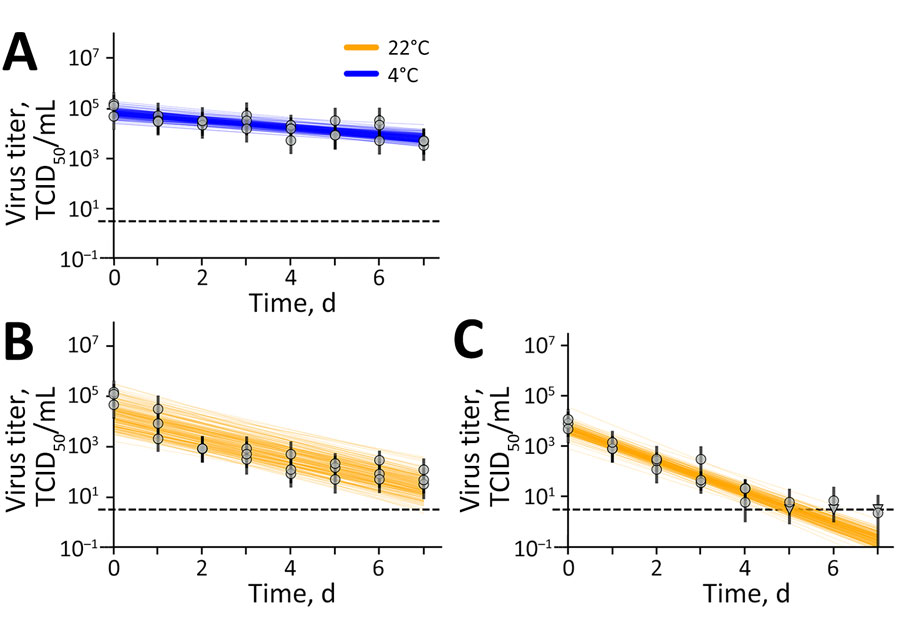
Figure 1. Results of experimental testing of highly pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) virus stability in irradiated raw milk and wastewater, United States. A, B) Virus stability in irradiated raw milk at (A) 4°C and (B) 22°C. C) Virus stability in irradiated wastewater at 22°C (orange). Vertical lines represent random draws from the joint posterior distribution of the exponential decay rate and the initial virus titer, where the intercept of each line is the initial titer and the slope is the negative of the decay rate. Dashed horizontal lines show 100.5 TCID50/mL of medium and represent the approximate detection limit. Individual data points are represented as circles (above limit of detection) or triangles (below limit of detection). TCID50, 50% tissue culture infectious dose.
1These first authors contributed equally to this article.