Volume 31, Number 7—July 2025
Dispatch
Human Infections by Novel Zoonotic Species Corynebacterium silvaticum, Germany
Figure 1
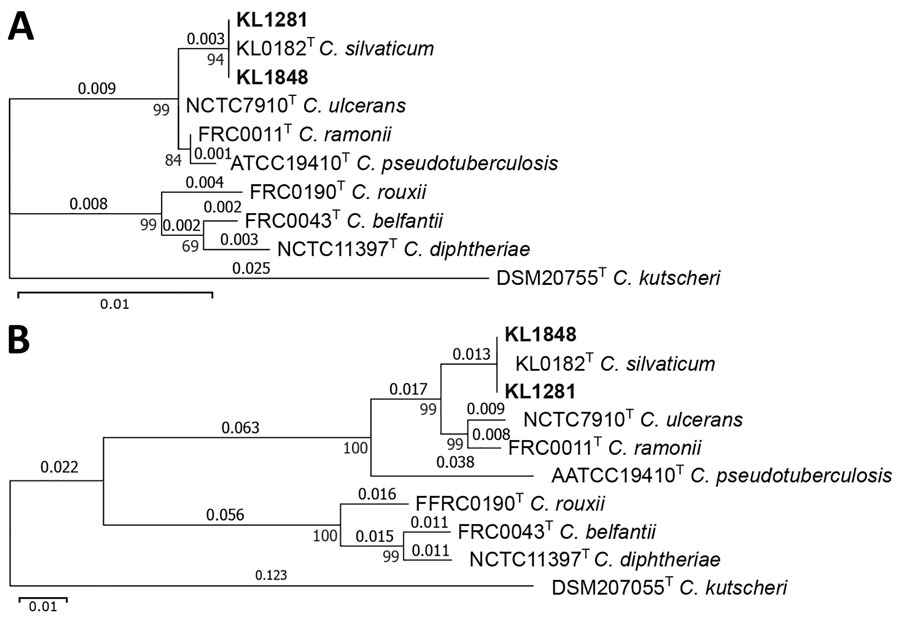
Figure 1. Gene phylogenies of isolates from 2 cases of infection by the novel zoonotic species Corynebacterium silvaticum, Germany (isolates KL1281 and KL1848), compared with reference sequences from publicly available type strain sequences of C. diphtheriae complex species and a close relative outgroup (C. kutscheri). A) 16S; B) rpoB. Substitutions per aligned site are indicated above branches and local supporting values at intersections of branches. Scale bars indicate number of substitutions per site.
1These authors contributed equally to this article.
2Current affiliation: University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK.
Page created: May 01, 2025
Page updated: June 25, 2025
Page reviewed: June 25, 2025
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.