Volume 8, Number 2—February 2002
Research
Broad-Range Bacterial Detection and the Analysis of Unexplained Death and Critical Illness
Figure
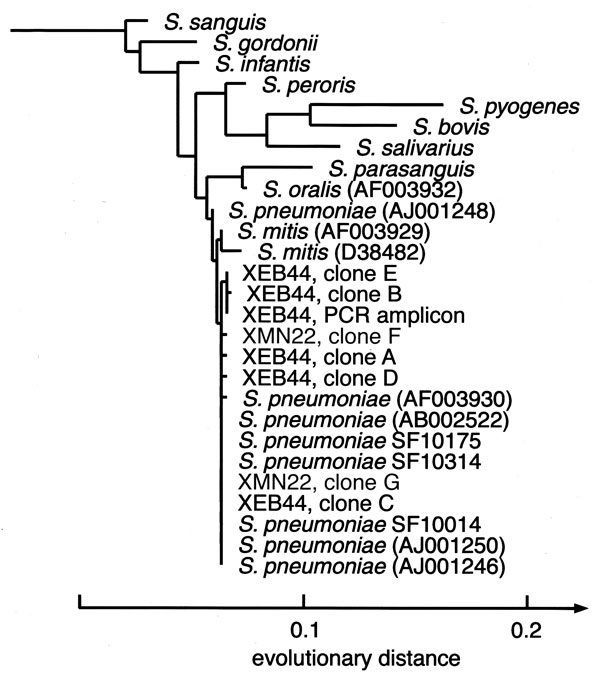
Figure. Phylogenetic analysis of the bacterial 16S rDNA sequences obtained from cases XEB44 and XMN22. The tree was rooted with Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli as outgroups and constructed with a maximum-likelihood algorithm using 468 homologous sequence positions that were selected from a sequence dataset of 497 total positions. Streptococcus pneumoniae clinical isolates sequenced for this study are marked as SF10175, SF10314, and SF10014. GenBank database accession numbers for published sequences are given in parentheses. All six sequences from the case XCA73 cerebrospinal fluid were identical to those of the S. pneumoniae reference strain (accession no. AJ001246). PCR = polymerase chain reaction.
Page created: July 14, 2010
Page updated: July 14, 2010
Page reviewed: July 14, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.