Volume 8, Number 2—February 2002
Research
Epidemiology of Burkholderia cepacia Complex in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis, Canada
Figure
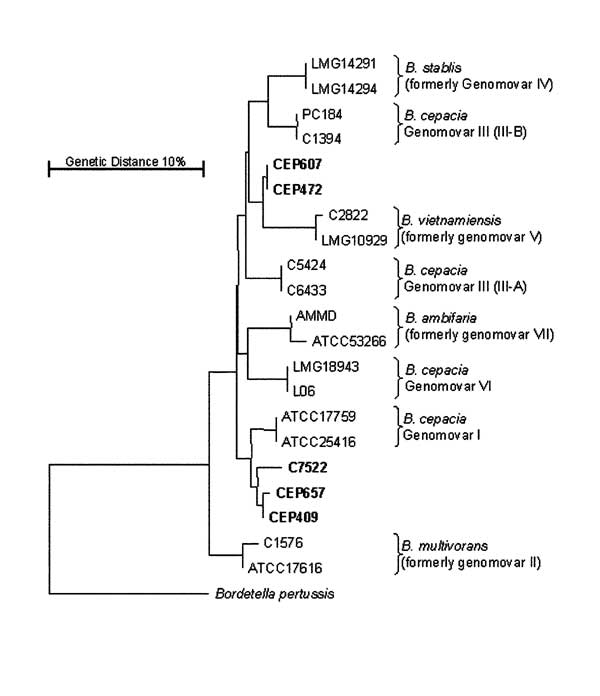
Figure. . Phylogenetic analysis of the recA gene from the Burkholderia cepacia complex. The phylogenetic diversity of the B. cepacia complex observed after nucleotide sequence analysis of the recA gene is shown. Isolates recovered from Canadian CF patients that are representative of strains of currently indeterminate genomovar status (Table 2) appear in bold and lack species identification; all fall within the current B. cepacia complex. The tree was drawn as described (16). The recA sequence from Bordetella pertussis was used as a root, and the genetic distance is indicated by the bar.
References
- Govan JRW, Deretic V. Microbial pathogenesis in cystic fibrosis: mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Burkholderia cepacia. Microbiol Rev. 1996;60:539–74.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Speert DP, Bond M, Woodman RC, Curnutte JT. Infection with Pseudomonas cepacia in chronic granulomatous disease: role of nonoxidative killing by neutrophils in host defense. J Infect Dis. 1994;170:1524–31.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Isles A, Maclusky I, Corey M, Gold R, Prober C, Fleming P, Pseudomonas cepacia infection in cystic fibrosis: an emerging problem. J Pediatr. 1984;104:206–10. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Govan JR, Brown PH, Maddison J, Doherty CJ, Nelson JW, Dodd M, Evidence for transmission of Pseudomonas cepacia by social contact in cystic fibrosis. Lancet. 1993;342:15–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Johnson WM. Intercontinental spread of a highly transmissible clone of Pseudomonas cepacia proved by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis and ribotyping. Can J Infect Dis. 1994;5:86–8.
- LiPuma JJ, Dasen SE, Nielson DW, Stern RC, Stull TL. Person-to-person transmission of Pseudomonas cepacia between patients with cystic fibrosis. Lancet. 1990;336:1094–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Medical/Scientific Advisory Committee—Canadian Cystic Fibrosis Foundation. Epidemiology of Pseudomonas cepacia in cystic fibrosis. Can J Infect Dis. 1993;4:163–5.
- Pegues CF, Pegues DA, Ford DS, Hibberd PL, Carson LA, Raine CM, Burkholderia cepacia respiratory tract acquisition: epidemiology and molecular characterization of a large nosocomial outbreak. Epidemiol Infect. 1996;116:309–17.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pegues DA, Carson LA, Tablan OC, FitzSimmons SC, Roman SB, Miller JM, Acquisition of Pseudomonas cepacia at summer camps for patients with cystic fibrosis. J Pediatr. 1994;124:694–702. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Corey M, Farewell V. Determinants of mortality from cystic fibrosis in Canada, 1970-1989. Am J Epidemiol. 1996;143:1007–17.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Vandamme P, Holmes B, Vancanneyt M, Coenye T, Hoste B, Coopman R, Occurrence of multiple genomovars of Burkholderia cepacia in cystic fibrosis patients and proposal of Burkholderia multivorans sp. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1997;47:1188–200.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- LiPuma JJ. Burkholderia cepacia: management issues and new insights. Clin Chest Med. 1998;19:473–86. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sun L, Jiang R, Steinbach S, Holmes A, Campanelli C, Forstner J, The emergence of a highly transmissible lineage of cbl+ Pseudomonas (Burkholderia) cepacia causing CF centre epidemics in North America and Britain. Nat Med. 1995;1:661–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mahenthiralingam E, Simpson DA, Speert DP. Identification and characterization of a novel DNA marker associated with epidemic Burkholderia cepacia strains recovered from patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1997;35:808–16.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Henry DA, Mahenthiralingam E, Vandamme P, Coenye T, Speert DP. Phenotypic methods for determining genomovar status of the Burkholderia cepacia complex. J Clin Microbiol. 2001;39:1073–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Henry DA, Campbell ME, LiPuma JJ, Speert DP. Identification of Burkholderia cepacia isolates from patients with cystic fibrosis and use of a simple new selective medium. J Clin Microbiol. 1997;35:614–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mahenthiralingam E, Bischof J, Byrne SK, Radomski C, Davies JE, Av-Gay, et al. DNA-based diagnostic approaches for the identification of Burkholderia cepacia complex, Burkholderia vietnamiensis, Burkholderia multivorans, Burkholderia stabilis, Burkholderia cepacia genomovars I and III. J Clin Microbiol. 2000;38:3165–73.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Coenye T, Mahenthiralingam E, Henry D, LiPuma JJ, Laevens S, Gillis M, Burkholderia ambifaria sp. nov., a novel member of the Burkholderia cepacia complex including biocontrol and cystic fibrosis-related isolates. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2001;51:1481–90.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Whitby PW, Pope LC, Carter KB, LiPuma JJ, Stull TL. Species-specific PCR as a tool for the identification of Burkholderia gladioli. J Clin Microbiol. 2000;38:282–5.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mahenthiralingam E, Campbell ME, Henry DA, Speert DP. Epidemiology of Burkholderia cepacia infection in patients with cystic fibrosis: analysis by random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) fingerprinting. J Clin Microbiol. 1996;34:2914–20.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mahenthiralingam E, Campbell ME, Foster J, Lam JS, Speert DP. Random amplified polymorphic DNA typing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates recovered from patients with cystic fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1996;34:1129–35.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Coenye T, Falsen E, Hoste B, Ohlen M, Goris J, Govan JRW, Description of Pandoraea gen. nov. with Pandoraea pulmonicola sp. nov., Pandoraea apista sp. nov., Pandoraea pnomenusa sp. nov., Pandoraea sputorum sp. nov. and Pandoraea norimbergensis comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2000;50:887–99.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Coenye T, Laevens S, Willems A, Ohlen M, Hannant W, Govan JRW, Burkholderia fungorum sp. nov. and Burkholderia caledonica sp. nov., two new species isolated from the environment, animals and human clinical samples. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2001;51:1099–107.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mahenthiralingam E, Vandamme P, Campbell ME, Henry DA, Gravelle AM, Wong LTK, Infection with Burkholderia cepacia complex genomovars in patients with cystic fibrosis: virulent transmissible strains of genomovar III can replace B. multivorans. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;33:1469–75. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Burdge DR, Noble MA, Campbell ME, Krell VL, Speert DP. Xanthomonas maltophilia misidentified as Pseudomonas cepacia in cultures of sputum from patients with cystic fibrosis: a diagnostic pitfall with major clinical implications. Clin Infect Dis. 1995;20:445–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- McMenamin JD, Zaccon TM, Coenye T, Vandamme P, LiPuma JJ. Misidentification of Burkholderia cepacia in U.S. cystic fibrosis treatment centers: an analysis of 1051 recent sputum isolates. Chest. 2000;117:1661–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Balandreau J, Viallard V, Cournoyer B, Coenye T, Laevens S, Vandamme P. Burkholderia cepacia genomovar III is a common plant-associated bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2001;67:982–5.[REMOVED ADVANCE FIELD][REMOVED ADVANCE FIELD] DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Fiore A, Laevens S, Bevivino A, Dalmastri C, Tabacchioni S, Vandamme P, Burkholderia cepacia complex: distribution of genomovars among isolates from the maize rhizosphere in Italy. Environ Microbiol. 2001;3:137–43. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Whiteford ML, Wilkinson JD, McColl JH, Conlon FM, Michie JR, Evans TJ, Outcome of Burkholderia (Pseudomonas) cepacia colonisation in children with cystic fibrosis following a hospital outbreak. Thorax. 1995;50:1194–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Segonds C, Heulin T, Marty N, Chabanon G. Differentiation of Burkholderia species by PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of the 16S rRNA gene and application to cystic fibrosis isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1999;37:2201–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cheng K, Smyth RL, Govan JRW, Doherty C, Winstanley C, Denning N, Spread of B-lactam-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a cystic fibrosis clinic. Lancet. 1996;348:639–42. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jones AM, Govan JRW, Doherty CJ, Dodd ME, Isalska BJ, Stanbridge TN, Spread of multiresistant strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in an adult cystic fibrosis clinic. Lancet. 2001;358:557–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Armstrong DS, Nixon G, Carlin J, Carzino R, Grimwood K. Long-term outbreak of a transmissible virulent strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a pediatric cystic fibrosis clinic. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2000;Suppl 20:393A.
- Snell GI, de Hoyos A, Krajden M, Winton T, Maurer JR. Pseudomonas cepacia in lung transplant recipients with cystic fibrosis. Chest. 1993;103:466–71. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Butler SL, Doherty CJ, Hughes JE, Nelson JW, Govan JRW. Burkholderia cepacia and cystic fibrosis: do natural environments present a potential hazard? J Clin Microbiol. 1995;33:1001–4.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mortensen JE, Fisher MC, LiPuma JJ. Recovery of Pseudomonas cepacia and other Pseudomonas species from the environment. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 1995;16:30–2.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Govan JRW, Hughes JE, Vandamme P. Burkholderia cepacia: medical, taxonomic and ecological issues. J Med Microbiol. 1996;45:1–15.PubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: April 18, 2012
Page updated: April 18, 2012
Page reviewed: April 18, 2012
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.