Volume 9, Number 3—March 2003
Research
Influenza AH1N2 Viruses, United Kingdom, 2001–02 Influenza Season
Figure 1
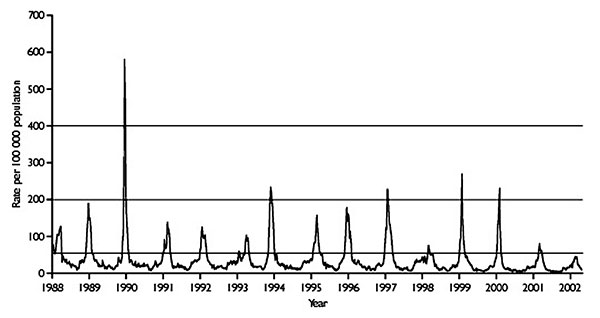
Figure 1. Consultation rate (per 100,000 population) for influenzalike illnesses with sentinel physicians in England in 1988–2002 (from the Royal College of General Practitioners Weekly Returns Service). Baseline activity is defined by a consultation rate <50/100,000; normal seasonal activity, 50–200/100,000; higher than seasonal activity, 200–400/100,000, and epidemic activity is defined as >400/100,000 population.
Page created: December 07, 2010
Page updated: December 07, 2010
Page reviewed: December 07, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.