Volume 10, Number 1—January 2004
Research
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome–associated Coronavirus in Lung Tissue
Figure
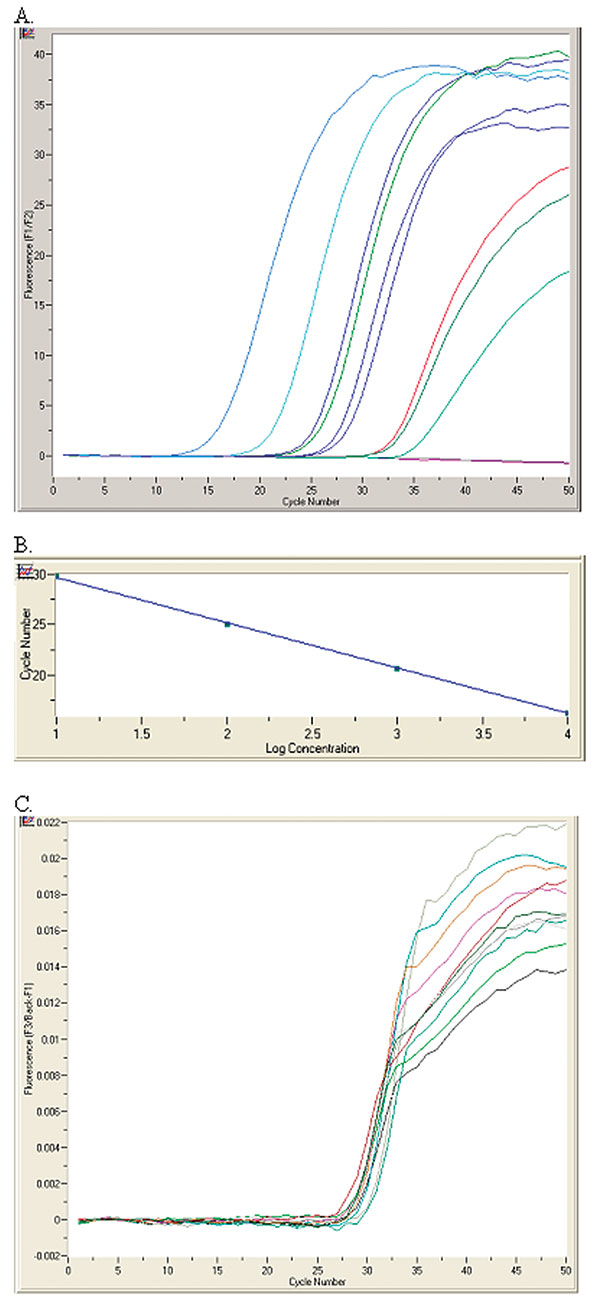
Figure. RealArt HPA-Coronavirus LightCycler (RealArt HPA Coronavirus RT-PCR) reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (PCR) Assay results. PCR results from 5 μL RNA are displayed in channel F1/F2 of the LightCycler instrument (A). Four quantification standards are included in the assay to generate a standard curve (B). An internal control, added at the RNA isolation stage, is used to monitor both the quality of the RNA isolation as well as possible PCR inhibition (C).
1Drs. Mazzulli and Farcas contributed equally to the manuscript. All authors jointly conceived and designed the study and wrote the report. Gabriella A. Farcas performed the majority of the reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction assays.
Page created: December 21, 2010
Page updated: December 21, 2010
Page reviewed: December 21, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.