Volume 13, Number 11—November 2007
Dispatch
Viral Load as Predictor of Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever Outcome
Figure
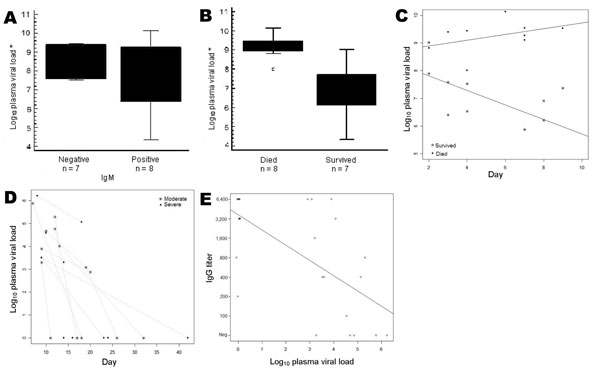
Figure. Correlation between clinical outcome, serologic data, and Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever (CCHF) viral load measurements. A) Viral load versus immunoglobulin (Ig) M result taken during the first week of illness. B) Viral load versus outcome. Average viral loads were 1.6 × 109 copies/mL in persons who died and 5 × 106 copies/mL in persons who survived (difference highly significant, p<0.0001). The dot is a datum point that has been identified as an outlier. C) Statistically significant difference (p<0.001) in CCHF viral load and day of illness between group who died and group who survived. D) No correlation in viral load and day of illness between severe and moderate CCHF cases. E) Inverse correlation of quantitative IgG levels with viral loads (p<0.0001) in samples taken after first week of illness. Black dot, >1 sample; *, first week samples.