Volume 13, Number 3—March 2007
Dispatch
Leishmania donovani and Cutaneous Leishmaniasis, Sri Lanka
Figure 2
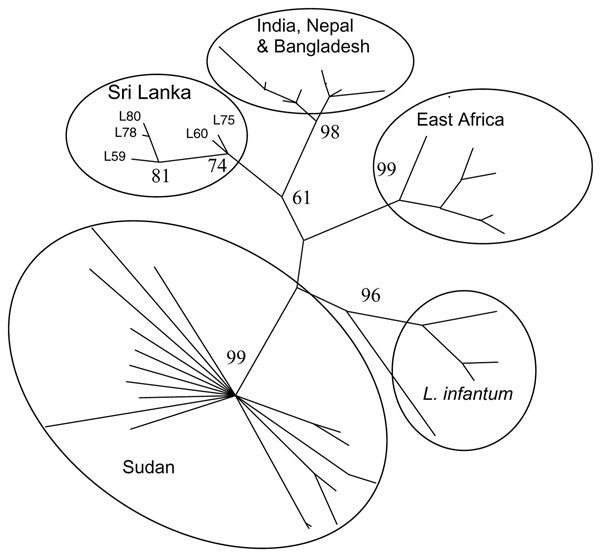
Figure 2. Classification of Leishmania donovani and L. infantum isolates constructed by using microsatellite data with parsimony in PAUP (Sinauer Associates Inc., Sunderland, MA, USA). Numbers at branch points are bootstrap values compiled by using 100 replicates. Isolates formed geographically based groups (circled). Sri Lanka isolates L59, L60, L75, L78, and L80 are indicated. The tips of other branches are from a dataset of other previously analyzed isolates, including all those identified as L. donovani or L. infantum and isolates from the Indian subcontinent (10).
References
- Bates PA. Leishmania. In: Encyclopedia of life sciences. Hoboken (NJ): John Wiley & Sons, Inc; 2006. [cited 2007 Jan 25]. Available from http://els.wiley.com/els/ (doi:10.1038/npg.els.0001968)
- Davies CR, Kaye P, Croft SL, Sundhar S. Leishmaniasis: new approaches to disease control.BMJ. 2003;326:377–82. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ashford RW. The leishmaniases as emerging and reemerging zoonoses.Int J Parasitol. 2000;30:1269–81. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Desjeux P. The increase in risk factors for leishmaniasis worldwide.Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2001;95:239–43. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Karunaweera ND, Pratlong F, Siriwardana HVYD, Ihalamulla RL, Dedet JP. Sri Lankan cutaneous leishmaniasis is caused by Leishmania donovani MON 37.Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2003;97:380–1. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mebrahtu YB, Van Eys G, Guizani I, Lawyer PG, Pamba H, Koech D, Human cutaneous leishmaniasis caused by Leishmania donovani s.l. in Kenya.Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1993;87:598–601. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pratlong F, Bastein P, Perello R, Lami P, Dedet JP. Human cutaneous leishmaniasis caused by Leishmania donovani sensu stricto in Yemen.Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1995;89:398–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ben-Ami R, Schnur LF, Golan Y, Jaffe CL, Mardi T, Zeltser D. Cutaneous involvement in a rare case of adult visceral leishmaniasis acquired in Israel.J Infect. 2002;44:181–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sharma NL, Mahajan VK, Kanga A, Sood A, Katoch VM, Mauricio I, Localized cutaneous leishmaniasis due to Leishmania donovani and Leishmania tropica: preliminary findings of the study of 161 new cases from a new endemic focus in Himachal Pradesh, India.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2005;72:819–24.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Jamjoom MB, Ashword RW, Bates PA, Chance ML, Kemp SJ, Watts PC, Leishmania donovani is the only cause of visceral leishmaniasis in East Africa; previous descriptions of L. infantum and L. archibaldi from this region are a consequence of convergent evolution in the iso-enzyme data.Parasitology. 2004;129:399–409. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lachaud L, Chabbert E, Dubessay P, Reynes J, Lamothe J, Bastien P. Comparison of various sample preparation methods for PCR diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis using peripheral blood.J Clin Microbiol. 2001;39:613–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Greenblatt CL, Schnur LF, Bar-Gal GK, Ermolaev H, Peleg N, Barret MP. Polymorphism among alleles of the 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase gene from Leishmania major and Leishmania tropica.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2002;125:185–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pratlong F, Dereure J, Bucheton B, El-Saf S, Dessein A, Lanotte G, Sudan: the possible original focus of visceral leishmaniasis.Parasitology. 2001;122:599–605. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Zemanova E, Jirku M, Mauricio I, Miles MA, Lukes J. Genetic polymorphisms within the Leishmania donovani complex: correlation with geographic origin.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2004;70:613–7.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sundar S, Maurya R, Singh RK, Bharti K, Chakravarty K, Parekh A, Rapid, noninvasive diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis in India: comparison of two immunochromatographic strip tests for detection of anti-RK39 antibody.J Clin Microbiol. 2006;44:251–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: June 29, 2010
Page updated: June 29, 2010
Page reviewed: June 29, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.