Volume 13, Number 7—July 2007
Synopsis
Large Water Management Projects and Schistosomiasis Control, Dongting Lake Region, China
Figure 6
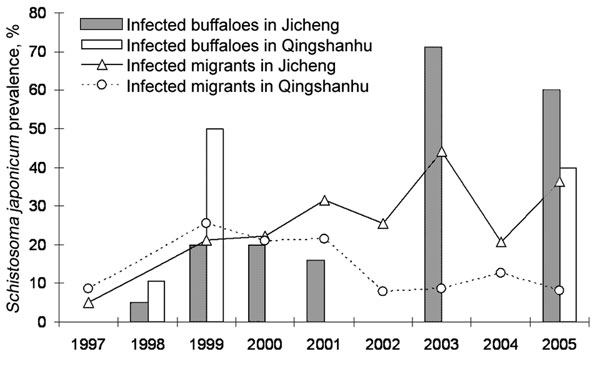
Figure 6. Schistosoma japonicum infection prevalences of migrants and water buffaloes in 2 areas in Dongting Lake over 9 years where the Return Land to Lake Program has been implemented (27). No bovine prevalence data were available for both villages for 1997, 2002, and 2004, and no human prevalence data were available for both villages for 1998. No buffaloes were present in Qingshanhu in 2000, 2001, and 2003.
References
- Li BN, Ying ZL. The resettlement in the reservoir. The series books of Three Gorges Project [in Chinese]. Beijing: Water Conservancy and Electricity Press; 1991. p. 1–73.
- Zheng J, Gu XG, Xu YL, Ge JH, Yang XX, He CH, Relationship between the transmission of schistosomiasis japonica and the construction of the Three Gorge Reservoir. Acta Trop. 2002;82:147–56. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chen ZJ. Relationship between Three Gorges Project and the Dongting Lake [in Chinese]. Economic and Technical Committee of Hunan Provincial Political Consultative Conference. Changsha (P.R. China): Hunan Science and Technology Press; 2002. p. 9–10, 259–60, 305.
- Cai KP, He WL, Wang T, Li YS, Chen Y. Survey of Schistosoma japonicum infection in the area “Returning Reclaimed Farmland to Lakes,” Qingshanghu, Hunan Pprovince. Practical Preventive Medicine. 2005;12:1266–8.
- Cai KP, Hou XY, Li YY, Xiao F, Liu JJ, Yi XZ, Oncomelania snail survey in 41 areas of “breaking dikes or open sluice for waterstore” in Dongting Lake regions [in Chinese]. Chinese Journal of Schistosomiasis Control. 2005;17:86–8.
- Ross AGP, Sleigh AC, Li YS, Davis GM, Williams GM, Jiang Z, Schistosomiasis in the People’s Republic of China: prospects and challenges for the 21st century. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2001;14:270–95. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Zhou XN, Wang LY, Chen MG, Wu XH, Jiang QW, Chen XY, The public health significance and control of schistosomiasis in China—then and now. Acta Trop. 2005;96:97–105. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mao SP, Shao BR. Schistosomiasis control in the People's Republic of China. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1982;31:92–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chen MG, Feng Z. Schistosomiasis control in China. Parasitol Int. 1999;48:11–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Zhao GM, Zhao Q, Jiang QW, Chen XY, Wang LY, Yuan HC. Surveillance for schistosomiasis japonica in China from 2000 to 2003. Acta Trop. 2005;96:288–95. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wu Z, Bu KM, Yuan LP, Yang GF, Zhu JH, Liu QL. Factors contributing to reinfection with schistosomiasis japonica after treatment in the lake region of China. Acta Trop. 1993;54:83–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Yuan HC. Epidemiological features and control strategies of schistosomiasis japonica in China. Chin Med J (Engl). 1993;106:563–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Engels D, Chitsulo L, Montresor A, Savioli L. The global epidemiological situation of schistosomiasis and new approaches to control and research. Acta Trop. 2002;82:139–46. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Li YS, Cai KP. The epidemic trend and challenges for schistosomiasis in China [in Chinese]. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2004;25:553–4.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ross AGP, Li YS, Sleigh AC, McManus DP. Schistosomiasis control in the People’s Republic of China. Parasitol Today. 1997;13:152–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Liang S, Yang C, Zhong B, Qiu D. Re-emerging schistosomiasis in hilly and mountainous areas of Sichuan, China. Bull World Health Organ. 2006;84:139–44. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Fang JC, Wu ZW. Research on schistosomiasis control in Hunan Province. Changsha (China): Hunan People Press; 2000.
- Steinmann P, Keiser J, Bos R, Tanner M, Utzinger J. Schistosomiasis and water resources development: systematic review, meta-analysis, and estimates of people at risk. Lancet Infect Dis. 2006;6:411–25. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lin BN. Project siltation. The series books of Three Gorges Project [in Chinese]. Beijing: Water Conservancy and Electricity Press; 1991. p. 1–93.
- Cai KP, Zuo JZ, He HB, Zhuo SJ. Impact of changes in mud siltation of Dongting Lake on the endemic factors of schistosomiasis after building the Three Gorges Dam. Practical Preventive Medicine. 2000;7:1–3.
- Zhou YB, Liu QL, Zhao ZY, Chen Y. Report on snail spread after floods in five villages of Dongting Lake region. Chinese Journal of Schistosomiasis Control. 1999;11:116–7.
- Chen XY. The challenges of strategies in schistosomiasis control program in China. Acta Trop. 2002;82:279–82. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Richardson CJ, Reiss P, Hussain NA, Alwash AJ, Pool DJ. The restoration potential of the Mesopotamian marshes of Iraq. Science. 2005;307:1307–11. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Guo J, Li Y, Gray D, Ning A, Hu G, Chen H, A drug-based intervention study on the importance of buffaloes for human Schistosoma japonicum infection around Poyang Lake, People’s Republic of China. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2006;74:335–41.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chen Y, Cai KP, He YK, Li SZ. Endemic diversity and control strategies on schistosomiasis after reserving plain for flooding in Jichenyuan, the Yangtze River. Chinese Journal of Schistosomiasis Control. 2002;14:196–9.
- Wu ZW. Talk about the current technical and management problem on schistosomiasis control. Practical Preventive Medicine. 2005;12:704–6.
- Cai KP, He HB, Peng GZ, He WL, Li YS. Endemic diversity and interventions on schistosomiasis after reserving plain for flooding in Jincheng and Qingshanhu. Chinese Journal of Schistosomiasis Control. 2006;18:261–4.
- Cai KP, Chen Y, Hu YH. The epidemic changes of schistosomiasis in resettlement areas against hills in Dongting Lake region. Practical Preventive Medicine. 2003;10:457–9.
- Bian Y, Sun Q, Zhao Z, Blas E. Market reform: a challenge to public health - the case of schistosomiasis control in China. Int J Health Plann Manage. 2004;19(Suppl 1):S79–94. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lee L. The current state of public health in China. Annu Rev Public Health. 2004;25:327–39. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Yu D, Manderson L, Yuan L, Wei W, He H, Chen Y. Is equity being sacrificed? Willingness and ability to pay for schistosomiasis control in China. Health Policy Plan. 2001;16:292–301. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hu GH, Jia H, Song KY, Lin DD, Zhang J, Cao CL, The role of health education and health promotion in the control of schistosomiasis: experiences from a 12-year intervention study in the Poyang Lake area. Acta Trop. 2005;96:232–41. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Yuan LP, Manderson L, Ren MY, Li GP, Yu DB, Fang JC. School-based interventions to enhance knowledge and improve case management of schistosomiasis: a case study from Hunan, China. Acta Trop. 2005;96:248–54. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: June 21, 2010
Page updated: June 21, 2010
Page reviewed: June 21, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.