Volume 13, Number 8—August 2007
Research
Classic Scrapie in Sheep with the ARR/ARR Prion Genotype in Germany and France
Figure 1
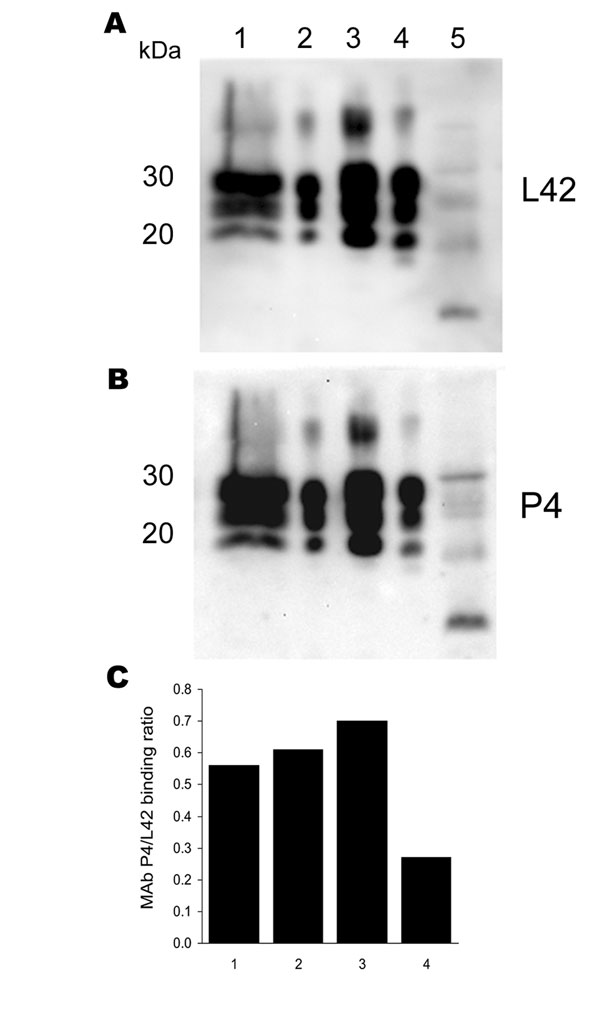
Figure 1. Antibody-binding patterns of the prion protein (PrPSc) associated with cases of ARR/ARR scrapie in France and Germany. A) and B) Western blots showing the differences in monoclonal antibody (MAb) P4 binding compared with the internal standard MAb L42 of PrPSc derived from S115/04 (ARR/ARR Germany), S83 (ARR/ARR France), ovine ARQ/ARQ bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE), and S95 (classic scrapie) cases. Banding intensities were quantified by photoimaging, and binding ratios were calculated. Note the significantly weaker P4 binding to the ovine BSE sample. Lane 1, S115/04; lane 2, S83; lane 3, S95; lane 4, ovine BSE; lane 5, atypical S15. C) Relative MAb binding ratios for lane nos. 1–4 in the Western blots shown in A) and B).
Page created: June 30, 2010
Page updated: June 30, 2010
Page reviewed: June 30, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.