Volume 15, Number 2—February 2009
Dispatch
Chikungunya Virus and Central Nervous System Infections in Children, India
Figure 2
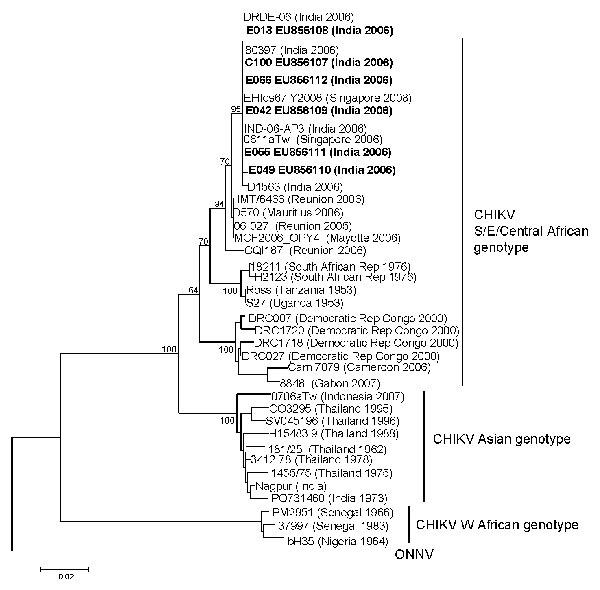
Figure 2. Phylogenetic analysis of chikungunya virus (CHIKV) sequences on the basis of partial E1 gene sequence (position 10620–11148 of the prototype CHIKV S27 genomic sequence). Sequences obtained in this study are in boldface. The analysis was performed using MEGA version 4 software (8), by using the neighbor-joining (p-distance) method. The length of the tree branches indicates the percentage of divergence; the percentage of successful bootstrap replicates is specified at the nodes (1,000 replicates). ONNV (o’nyong-nyong virus) prototype sequence was included to root the tree. Scale bar indicates number of nucleotide substitutions per site.
References
- Pialoux G, Gauzere BA, Jaureguiberry S, Strobel M. Chikungunya, an epidemic arbovirosis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2007;7:319–27. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Chatterjee SN, Chakravarti SK, Mitra AC, Sarkar JK. Virological investigation of cases with neurological complications during the outbreak of haemorrhagic fever in Calcutta. J Indian Med Assoc. 1965;45:314–6.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mazaud R, Salaun JJ, Montabone H, Goube P, Bazillio R. Acute neurologic and sensorial disorders in dengue and chikungunya fever. Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1971;64:22–30.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Parola P, de Lamballerie X, Jourdan J, Rovery C, Vaillant V, Minodier P, Novel chikungunya virus variant in travelers returning from Indian Ocean islands. Emerg Infect Dis. 2006;12:1493–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Yergolkar PN, Tandale BV, Arankalle VA, Sathe PS, Sudeep AB, Gandhe SS, Chikungunya outbreaks caused by African genotype, India. Emerg Infect Dis. 2006;12:1580–3.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mavalankar D, Shastri P, Bandyopadhyay T, Parmar J, Ramani KV. Increased mortality rate associated with chikungunya epidemic, Ahmedabad, India. Emerg Infect Dis. 2008;14:412–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Edwards CJ, Welch SR, Chamberlain J, Hewson R, Tolley H, Cane PA, Molecular diagnosis and analysis of Chikungunya virus. J Clin Virol. 2007;39:271–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S. MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol. 2007;24:1596–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cardosa MJ, Wang SM, Sum MS, Tio PH. Antibodies against prM protein distinguish between previous infection with dengue and Japanese encephalitis viruses. BMC Microbiol. 2002;2:9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pyke AT, Smith IL, Van Den Hurk AF, Northill JA, Chuan TF, Westacott AJ, Detection of Australasian flavivirus encephalitic viruses using rapid fluorogenic TaqMan RT-PCR assays. J Virol Methods. 2004;117:161–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Schuffenecker I, Iteman I, Michault A, Murri S, Frangeul L, Vaney MC, Genome microevolution of chikungunya viruses causing the Indian Ocean outbreak. PLoS Med. 2006;3:e263. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- de Lamballerie X, Leroy E, Charrel RN, Ttsetsarkin K, Higgs S, Gould EA. Chikungunya virus adapts to tiger mosquito via evolutionary convergence: a sign of things to come? Virol J. 2008;5:33. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tsetsarkin KA, Vanlandingham DL, McGee CE, Higgs S. A single mutation in Chikungunya virus affects vector specificity and epidemic potential. PLoS Pathog. 2007;3:e201. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rampal SM, Meena H. Neurologic complications in Chikungunya fever. J Assoc Physicians India. 2007;55:765–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wielanek AC, Monredon JD, Amrani ME, Roger JC, Serveaux JP. Guillain-Barré syndrome complicating a Chikungunya virus infection. Neurology. 2007;69:2105–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Robin S, Ramful D, Le Seach F, Jaffar-Bandjee MC, Rigou G, Alessandri JL. Neurologic manifestations of pediatric Chikungunya infection. J Child Neurol. 2008;23:1028–35. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Beasley DW, Lewthwaite P, Solomon T. Current use and development of vaccines for Japanese encephalitis. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2008;8:95–106. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Global Advisory Committee on Vaccine Safety. 29–30 November 2006. Wkly Epidemiol Rec. 2007;82:18–24.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Grivard P, Le Roux K, Laurent P, Fianu A, Perrau J, Gigan J, Molecular and serological diagnosis of Chikungunya virus infection. Pathol Biol (Paris). 2007;55:490–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: December 08, 2010
Page updated: December 08, 2010
Page reviewed: December 08, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.