Volume 16, Number 1—January 2010
Dispatch
Human Group A Streptococci Virulence Genes in Bovine Group C Streptococci
Figure 2
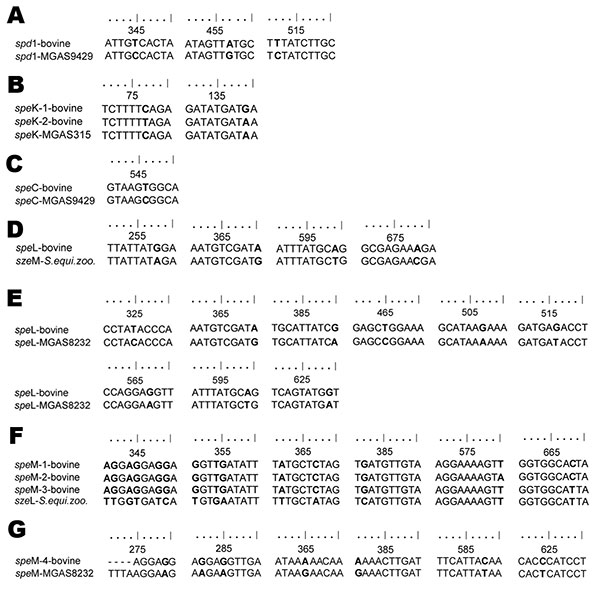
Figure 2. Alignments of bovine group C streptococci (Streptococcus dysgalactiae subsp. dysgalactiae) alleles of virulence genes from 8 dairy herds, Portugal, with sequences from the National Center for Biotechnology (Bethesda, MD, USA) database showing base differences between sequences. The alignments were created by using BioEdit sequence alignment editor (www.mbio.ncsu.edu/BioEdit/bioedit.html). Nucleotide differences are shown in boldface. A) spd1 (99% maximum identity); B) speK (99% maximum identity); C) speC (99% maximum identity); D) speL–szeM (99% maximum identity); E) speL (97% maximum identity; F) speM alleles 1, 2, and 3–szeL (98%–99% maximum identity); G) speM allele 4 (98% maximum identity). S. equi. zoo., S. equi subsp. zooepidemicus.