Volume 5, Number 3—June 1999
Perspective
Bacterial Vaccines and Serotype Replacement: Lessons from Haemophilus influenzae and Prospects for Streptococcus pneumoniae
Figure 2
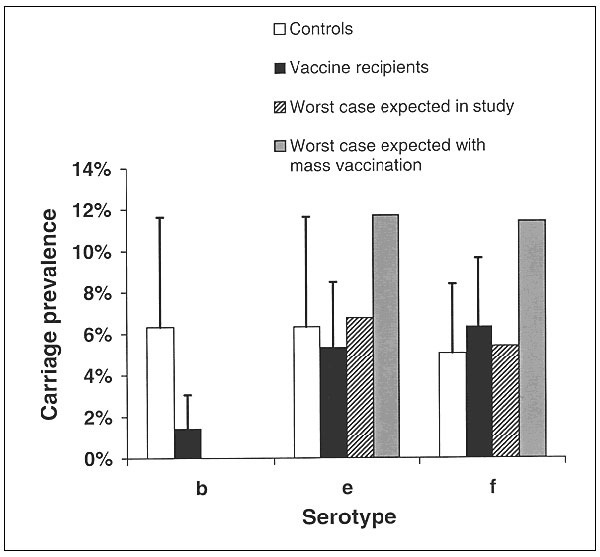
Figure 2. Carriage of three serotypes of Haemophilus influenzae in children vaccinated against serotype b (black bars) and in controls (white bars) (14). Error bars indicate 95% confidence interval (binomial approximation). Shaded bars show the maximum carriage of serotypes e and f in vaccine recipients that could result from replacement in a population where only a small proportion of susceptibles are vaccinated (as in the study). Striped bars show the equivalent figures in a hypothetical study in which virtually all susceptibles were vaccinated.
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Prevention of pneumococcal disease: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1997;46:RR8.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Progress toward elimination of Haemophilus influenzae type b disease among infants and children—United States, 1987-1995. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1996;45:901–6.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Booy R, Kroll JS. Is Haemophilus influenzae finished? J Antimicrob Chemother. 1997;40:149–53. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dagan R, Melamed R, Muallem M, Piglansky L, Greenberg D, Abramson O, Reduction of nasopharyngeal carriage of pneumococci during the second year of life by a heptavalent conjugate pneumococcal vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1996;174:1271–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Obaro SK, Adegbola RA, Banya WAS, Greenwood BM. Carriage of pneumococci after pneumococcal vaccination. Lancet. 1996;348:271–2. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mbelle N, Wasas A, Huebner R, Kimura A, Chang I, Klugman K. Immunogenicity and impact on carriage of 9-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine given to infants in Soweto, South Africa. Proceedings from the Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy; September 28-October 1, 1997; Toronto, Canada. LB-12, p. 13.
- Dagan R, Givon N, Yagupsky P, Porat N, Janco J, Chang I, Effect of a 9-valent pneumococcal vaccine conjugated to CRM197 (PncCRM9) on nasopharyngeal (NP) carriage of vaccine type and non-vaccine type S. pneumoniae (Pnc) strains among day-care-center (DCC) attendees. Proceedings from the 38th Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy; September 24-27, 1998; San Diego, California. G52.
- Black S, Shinefield H, Ray P, Lewis E, Fireman B; The Kaiser Permanente Vaccine Study Group. Efficacy of heptavalent conjugate pneumococcal vaccine (Wyeth Lederle) in 37,000 infants and children: results of the Northern California Kaiser Permanente Efficacy Trial. Proceedings from the 38th Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy; September 24-27, 1998; San Diego, California. LB-9.
- Barbour ML. Conjugate vaccines and the carriage of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Emerg Infect Dis. 1996;2:176–82. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Moxon ER. The carrier state: Haemophilus influenzae. J Antimicrob Chemother 1986;18 Suppl A:17-24.
- Austrian R. Some aspects of the pneumococcal carrier state. J Antimicrob Chemother 1986;18 Suppl A:35-45.
- Lipsitch M, Moxon ER. Virulence and transmissibility of pathogens: what is the relationship? Trends Microbiol. 1997;5:31–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Topley WWC. The spread of bacterial infection. Lancet 1919;July 5:1-5.
- Levin BR, Bull JJ. Short-sighted evolution and the virulence of pathogenic microbes. Trends Microbiol. 1994;2:76–81. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Barbour ML, Mayon-White RT, Coles C, Crook DWM, Moxon ER. The impact of conjugate vaccine on carriage of Haemophilus influenzae type b. J Infect Dis. 1995;171:93–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Adams WG, Deaver KA, Cochi SL, Plikaytis BD, Zell ER, Broome CV, Decline of childhood Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) disease in the Hib vaccine era. JAMA. 1993;269:221–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Wenger JD, Pierce R, Deaver K, Franklin R, Bosley G, Pigott N, Invasive Haemophilus influenzae disease: a population-based evaluation of the role of capsular polysaccharide serotype. J Infect Dis. 1992;165(Suppl 1):S34–5.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Farley MM, Stephens DS, Brachman PS Jr. Invasive Haemophilus influenzae disease in adults: a prospective, population-based surveillance. Ann Intern Med. 1992;116:806–12.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Nitta DM, Jackson MA, Burry VF, Olson LC. Invasive Haemophilus influenzae type f disease. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1995;14:157–60. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Greene GR. Meningitis due to Haemophilus influenzae other than type b: case report and review. Pediatrics. 1978;62:1021–5.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Takala AK, Eskola J, Leinonen M, Kayhty H, Nissinen A, Pekkanen E, Reduction of oropharyngeal carriage of Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) in children immunized with an Hib conjugate vaccine. J Infect Dis. 1991;164:982–6.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Booy R, Heath P, Willocks L, Mayon-White D, Slack M, Moxon R. Invasive pneumococcal infections in children. Lancet. 1995;345:1245–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Urwin G, Krohn JA, Deaver-Robinson K, Wenger JD, Farley MM, Group HIS. Invasive disease due to Haemophilus influenzae serotype f: clinical and epidemiological characteristics in the H. influenzae serotype b vaccine era. Clin Infect Dis. 1996;22:1069–76.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Baer M, Vuento R, Vesikari T. Increase in bacteraemic pneumococcal infections in children. Lancet. 1995;345:661. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Schuchat A, Robinson K, Wenger JD, Harrison LH, Farley M, Reingold AL, Bacterial meningitis in the United States in 1995. N Engl J Med. 1997;337:970–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Anderson RM, May RM. Infectious diseases of humans: dynamics and control. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1991.
- Hodges RG, MacLeod CM, Bernhard WG. Epidemic pneumococcal pneumonia. III. Carrier studies. Am J Hyg. 1946;44:207–30.
- Pradier C, Dunais B, Carsenti-Etesse H, Largillier R, Bernard E, Dellamonica P. Nasopharyngeal carriage of penicillin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae (PRSP): prevalence and incidence in three children's day-care centres in Nice, France, from 1994 to 1995. Proceedings from the 36th Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy; September 15-18, 1996; New Orleans, Louisiana. C56.
- Reichler MR, Allphin AA, Breiman RF, Schreiber JR, Arnold JE, McDougal LK, The spread of multiply resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae at a day care center in Ohio. J Infect Dis. 1992;166:1346–53.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sanders CC, Sanders WE Jr, Harrowe DJ. Bacterial interference: effects of oral antibiotics on the normal throat flora and its ability to interfere with group A streptococci. Infect Immun. 1976;13:808–12.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Johanson WG Jr, Blackstock R, Pierce AK, Sanford JP. The role of bacterial antagonism in pneumococcal colonization of the human pharynx. J Lab Clin Med. 1970;75:946–52.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Venezia RA, Robertson RG. Bactericidal substance produced by Haemophilus influenzae type b. Can J Microbiol. 1975;21:1587–94. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lipsitch M. Vaccination against colonizing bacteria with multiple serotypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997;94:6571–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sutton A, Schneerson R, Kendall-Morris S, Robbins JB. Differential complement resistance mediates virulence of Haemophilus influenzae type b. Infect Immun. 1982;35:95–104.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Smith T, Lehmann D, Montgomery J, Gratten M, Riley ID, Alpers MP. Acquisition and invasiveness of different serotypes of Streptococcus pneumoniae in young children. Epidemiol Infect. 1993;111:27–39. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ewald PW. Vaccines as evolutionary tools: the virulence-antigen strategy. In: Kaufmann SHE, editor. Concepts in vaccine development. Berlin: Walter de Gruyter; 1996.
- Moxon ER, Vaughn KA. The type b capsular polysaccharide as a virulence determinant of Haemophilus influenzae: studies using clinical isolates and laboratory transformants. J Infect Dis. 1981;14:517–24.
- Kelly T, Dillard JP, Yother J. Effect of genetic switching of capsular type on virulence of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1994;62:1813–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Barnes DM, Whittier S, Gilligan PH, Soares S, Tomasz A, Henderson FW. Transmission of multidrug-resistant serotype 23F Streptococcus pneumoniae in group day care: evidence suggesting capsular transformation of the resistant strain in vivo. J Infect Dis. 1995;171:890–6.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Takala AK, Vuopio-Varkila J, Tarkka E, Leinonen M, Musser JM. Subtyping of common pediatric pneumococcal serotypes from invasive disease and pharyngeal carriage in Finland. J Infect Dis. 1996;173:128–35.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gratten M, Montgomery J, Gerega G, Gratten H, Siwi H, Poli A, Multiple colonization of the upper respiratory tract of Papua New Guinea children with Haemophilus influenzae and Streptococcus pneumoniae. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 1989;20:501–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gilks WR, Spiegelhalter DJ. A language and program for complex Bayesian modeling. Statistician. 1994;43:169–78. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Spiegelhalter DJ, Thomas A, Best NG, Gilks WR. BUGS: Bayesian inference using Gibbs sampling. Version 0.50. Cambridge: MRC Biostatistics Unit; 1995.
- Musher DM, Groover JE, Reichler MR, Riedo FX, Schwarz B, Watson DA, Emergence of antibody to capsular polysaccharides of Streptococcus pneumoniae during outbreaks of pneumonia: association with nasopharyngeal colonization. Clin Infect Dis. 1997;24:441–6.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dagan R, Melamed R, Muallem M, Piglansky L, Yagupsky P. Nasopharyngeal colonization in southern Israel with antibiotic-resistant pneumococci during the first 2 years of life: relation to serotypes likely to be included in pneumococcal conjugate vaccines. J Infect Dis. 1996;174:1352–5.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Butler JC. Epidemiology of pneumococcal serotypes and conjugate vaccine formulations. Microb Drug Resist. 1997;3:125–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Paton JC. Novel pneumococcal surface proteins: role in virulence and vaccine potential. Trends Microbiol. 1998;6:85–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: December 10, 2010
Page updated: December 10, 2010
Page reviewed: December 10, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.