Volume 8, Number 1—January 2002
Dispatch
Primary Liver Abscess Caused by One Clone of Klebsiella pneumoniae with Two Colonial Morphotypes and Resistotypes
Figure 1
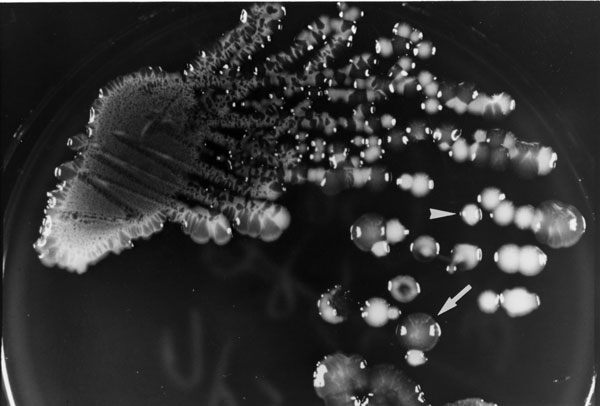
Figure 1. Colonial morphology of Klebsiella pneumoniae grown on a primary isolation plate (trypticase soy agar supplemented with 5% sheep blood) from the abscess aspirate of patient A after 24 hours of incubation. The arrow shows a mucoid opaque colony (isolate A1). The arrowhead shows a nonmucoid white colony (isolate A2).
Page created: July 14, 2010
Page updated: July 14, 2010
Page reviewed: July 14, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.