Volume 8, Number 5—May 2002
Synopsis
Typical and Atypical Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli
Figure 1
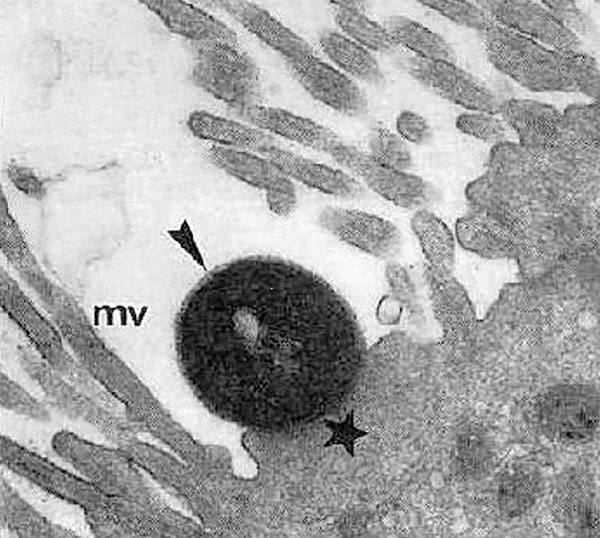
Figure 1. Attaching and effacing lesion showing effacement of microvilli (mv) and pedestal (star) with adherent enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) (arrow). Reprinted from reference 2, with permission of the director of American Society of Microbiology Journals.
References
- Nataro JP, Kaper JB. Diarrheogenic Escherichia coli. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1998;11:142–201.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pedroso MZ, Freymuller E, Trabulsi LR, Gomes TA. Attaching-effacing lesions and intracellular penetration in HeLa cells and human duodenal mucosa by two Escherichia coli strains not belonging to the classical enteropathogenic E. coli serogroups. Infect Immun. 1993;61:1152–6.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Knutton S, Baldwin T, Williams PH, McNeish AS. Actin accumulation at sites of bacterial adhesion to tissue culture cells: basis of a new diagnostic test for enteropathogenic and enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1989;57:1290–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- McDaniel TK, Jarvis KG, Donnenberg MS, Kaper JB. A genetic locus of enterocyte effacement conserved among diverse enterobacterial pathogens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995;92:1664–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Sperandio V, Kaper JB, Bortolini MR, Neves BC, Keller R, Trabulsi LR. Characterization of the locus of enterocyte effacement (LEE) in different enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) and Shiga-toxin producing Escherichia coli (STEC) serotypes. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1998;164:133–9. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Adu-Bobie J, Frankel G, Bain C, Goncalves AG, Trabulsi LR, Douce G, Detection of intimins alpha, beta, gamma, and delta, four intimin derivatives expressed by attaching and effacing microbial pathogens. J Clin Microbiol. 1998;36:662–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Frankel G, Phillips AD, Rosenshine I, Dougan G, Kaper JB, Knutton S. Enteropathogenic and enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli: more subversive elements. Mol Microbiol. 1998;30:911–21. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kenny B, Devinney R, Stein M, Reinscheid DJ, Frey EA, Finlay BB. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) transfers its receptor for intimate adherence into mammalian cells. Cell. 1997;91:511–20. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Scaletsky ICA, Silva MLM, Trabulsi LR. Distinctive patterns of adherence of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli to HeLa cells. Infect Immun. 1984;45:534–6.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kaper JB. Defining EPEC. In: Proceedings of the International Symposium on Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC). Rev Microbiol. 1996;27:130–3.
- Campos LC, Whittam TS, Gomes TAT, Andrade JRC, Trabulsi LR. Escherichia coli serogroup O111 includes several clones of diarrheogenic strains with diferrent virulence properties. Infect Immun. 1994;62:3282–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rodrigues J, Scaletsky ICA, Campos LC, Gomes TAT, Whittan ST, Trabulsi LR. Clonal structure and virulence factors in strains of Escherichia coli of the classic serogroup O55. Infect Immun. 1996;64:2680–6.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- do Valle GR, Gomes TA, Irino K, Trabulsi LR. The traditional enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) serogroup O125 comprises serotypes which are mainly associated with the category of enteroaggregative E. coli. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1997;152:95–100. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Scotland SM, Smith HR, Cheasty T, Said B, Willshaw GA, Stokes N, Use of gene probes and adhesion tests to characterize Escherichia coli belonging to enteropathogenic serogroups isolated in the United Kingdom. J Med Microbiol. 1996;44:438–43.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gonçalves AG, Campos LC, Gomes TA, Rodrigues J, Sperandio V, Whittam TS, Virulence properties and clonal structures of strains of Escherichia coli O119 serotypes. Infect Immun. 1997;65:2034–40.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Rosa AC, Mariano AT, Pereira AM, Tibana A, Gomes TAT, Andrade JR. Enteropathogenicity markers in Escherichia coli isolated from infants with acute diarrhoea and healthy controls in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. J Med Microbiol. 1998;47:781–90.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Giammanco A, Maggio M, Giammanco G, Morelli R, Minelli F, Scheutz F, Characteristics of Escherichia coli strains belonging to enteropathogenic E. coli serogroups isolated in Italy from children with diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol. 1996;34:689–94.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Peixoto J, Bando S, Ordoñez J, Botelho B, Trabulsi L, Moreira-Filho C. Genetic differences between Escherichia coli O26 strains isolated in Brazil and in other countries. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2001;196:239–44. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bortolini M, Trabulsi LR, Keller R, Frankel G, Sperandio V. Lack of expression of bundle-forming pili in some clinical isolates of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) is due to a conserved large deletion in the bfp operon. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1999;179:169–74. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Pelayo JS, Scaletsky IC, Pedroso MZ, Sperandio V, Giron JA, Frankel G, Virulence properties of atypical EPEC strains. J Med Microbiol. 1999;48:41–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Whittam TS, McGraw EA. Clonal analysis of EPEC serogroups. Rev Microbiol. 1996;27:7–16.
- Fernandes RM, Ramos SR, Rassi V, Blake PA, Gomes TAT. Use of plasmid profiles to differentiate strains within specific serotypes of classical enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Braz J Med Biol Res. 1992;25:667–72.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Levine MM, Bergquist EJ, Nalin DR, Waterman DH, Hornick RB, Young CR, Escherichia coli strains that cause diarrhoea but do not produce heat-labile or heat-stable enterotoxins and are non-invasive. Lancet. 1978;1:1119–22. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Smith H, Scotland S, Cheasty T, Willshaw G, Rowe B. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli infections in the United Kingdom. Rev Microbiol, São Paulo. 1996;27:45–9.
- Levine MM, Nataro JP, Karch H, Baldini MM, Kaper JB, Black RE, The diarrheal response of humans to some classic serotypes of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli is dependent on a plasmid encoding an enteroadhesiveness factor. J Infect Dis. 1985;152:550–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Toledo MRF, Alvariza MCB, Murahovschi J, Ramos SRTS, Trabulsi LR. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli serotypes and endemic diarrhea in infants. Infect Immun. 1983;39:586–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gomes TAT, Rassi V, MacDonald KL, Ramos SR, Trabulsi LR, Vieira MA, Enteropathogens associated with acute diarrheal disease in urban infants in Sao Paulo, Brazil. J Infect Dis. 1991;164:331–7.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Martinez MB, Taddei CR, Ruiz-Tagle A, Trabulsi LR, Giron JA. Antibody response of children with enteropathogenic Escherichia coli infection to the bundle-forming pilus and locus of enterocyte effacement-encoded virulence determinants. J Infect Dis. 1999;179:269–74. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Parissi-Crivelli A, Parissi-Crivelli J, Girón J. Recognition of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli virulence determinants by human colostrum and serum antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 2000;38:2696–700.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Loureiro I, Frankel G, Adu-Bobie J, Dougan G, Trabulsi LR, Carneiro-Sampaio MM. Human colostrum contains IgA antibodies reactive to enteropathogenic Escherichia coli virulence-associated proteins:intimin, BfpA, EspA, and EspB. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1998;27:166–71. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Viljanen M, Peltola T, Junnila S, Olkkonen L, Järvinen H, Kuistila M, Outbreak of diarrhoea due Escherichia coli O111:B4 in schoolchildren and adults: association of Vi antigen-like reactivity. Lancet. 1990;336:831–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kauffmann F, Orskov F. Die Bakteriologie der Escherichia coli-Enteritis. In: Adam A, editor. Säuglings-Enteritis. Stuttgart: Georg Thieme Verlag; 1956. p.1-41.
- Bokete TN, Whittam TS, Wilson RA, Clausen CR, O'Callahan CM, Mosely SL, Genetic and phenotypic analysis of Escherichia coli with enteropathogenic characteristics isolated from Seattle children. J Infect Dis. 1997;175:1382–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gomes TAT, Vieira MA, Wachsmuth IK, Blake PA, Trabulsi LR. Serotype-specific prevalence of Escherichia coli strains with EPEC adherence factor genes in infants with and without diarrhea in São Paulo, Brazil. J Infect Dis. 1989;160:131–5.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Griffin P. Epidemiology of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli infections in humans in the United States. In: Kaper JB, editor. Escherichia coli O157:H7 and other Shiga toxin-producing E. coli strains. Washington: American Society of Microbiology; 1998. p. 15-22.
- Gyles C. Escherichia coli in domestic animals. Wallinggford, UK: CAB International; 1994.
- Saridakis H. Non production of Shiga-like toxins by Escherichia coli serogroup O26. Rev Microbiol, São Paulo. 1994;25:154–5.
- Ewing W, Davis D, Montague T. Studies on the occurrence of Escherichia coli serotypes associated with diarrheal disease. Atlanta: US Department of Health, Education and Welfare, Public Health Service, Communicable Disease Center; 1963.
- Trabulsi L, Campos L, Whittam T, Gomes T, Rodrigues J, Gonçalves A. Traditional and non-traditional enteropathogenic Escherichia coli serogroups. Rev Microbiol, São Paulo. 1996;27:1–6.
- Vieira M, Andrade J, Trabulsi L, Rosa A, Dias A, Ramos S, Phenotypic and genotypic characteristics of Escherichia coli strains of non-enteropathogenic E. coli (EPEC) serogroups that carry eae and lack the EPEC adherence factor and Shiga toxin DNA probe sequences. J Infect Dis. 2001;183:762–72. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hedberg C, Savarino S, Besser J, Paulus C, Thelen V, Myers L, An outbreak of foodborne illness caused by Escherichia coli O39:NM, an agent not fitting into the existing scheme for classifying diarrheogenic E. coli. J Infect Dis. 1997;176:1625–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: July 15, 2010
Page updated: July 15, 2010
Page reviewed: July 15, 2010
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.