Volume 10, Number 12—December 2004
Dispatch
Isolation and Molecular Identification of Nipah Virus from Pigs
Figure
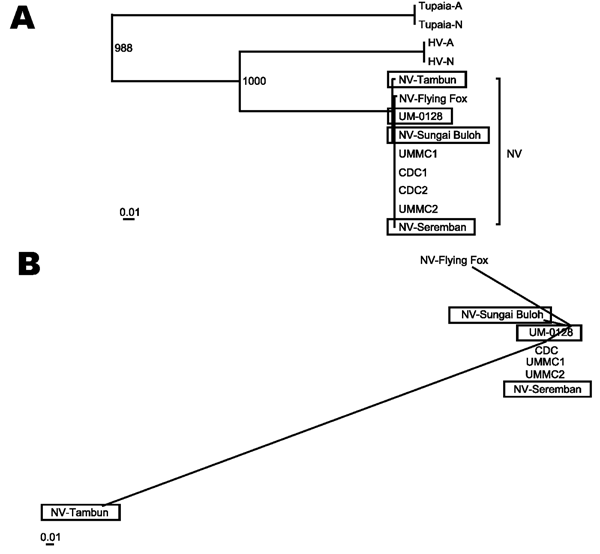
Figure. Phylogenetic trees illustrating the relationships of the pig Nipah virus isolates to all other known Nipah viruses and the related members of subfamily Paramyxovirinae. A) The maximum likelihood tree was drawn by using alignments of the full genome sequences. All the new isolates described in the study are shown in boxes. Abbreviations used and accession numbers not described elsewhere in the text are in parenthesis: Tupaia paramyxovirus (Tupaia-A) (AF079780); (Tupaia-N) (NC_002199), and Hendra virus (HV-A) (AF017149); (HV-N) (NC_001906). B) Unrooted maximum likelihood plot was constructed by using alignments of all the nucleotide differences in the Nipah virus gene coding regions (N, P, M, F, and G) shown in [[ANCHOR###TA1###Table A1###Anchor]], [[ANCHOR###TA2###Table A2###Anchor]], and [[ANCHOR###TA3###Table A3###Anchor]] by artificially treating all the differences as a single stretch of nucleotide sequence.