Volume 10, Number 2—February 2004
THEME ISSUE
2004 SARS Edition
Laboratory Study
Interferon-β 1a and SARS Coronavirus Replication
Figure 2
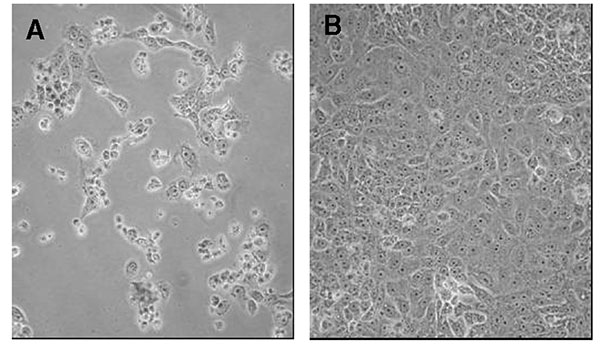
Figure 2. Interferon (IFN)-β 1a inhibition of SARS-CoV cytopathicity in Vero E-6 cells. Vero E-6 cells were infected with the Tor2 isolate of SARS-CoV and incubated for 72 h in the absence (left panel) or presence (right panel) of 500,000 IU of recombinant human IFN-β 1a. Cell rounding and detachment were prominent in the absence of IFN-β 1a. Minimal cell rounding or death was noted in the intact monolayer at 72 h postinoculation in the presence of IFN-β 1a (note: IFN-β 1a administered 1 h postinfection).
Page created: January 25, 2011
Page updated: January 25, 2011
Page reviewed: January 25, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.