Volume 10, Number 2—February 2004
THEME ISSUE
2004 SARS Edition
Laboratory Study
Ultrastructural Characterization of SARS Coronavirus
Figure 2
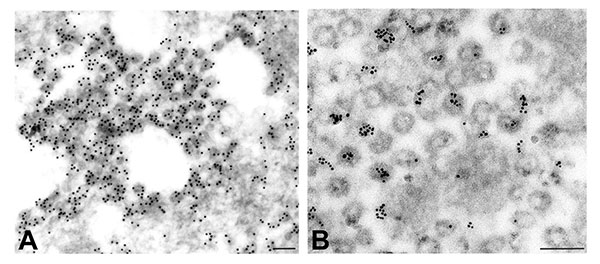
Figure 2. Detection of viral proteins and viral RNA associated with intracytoplasmic virions. A) Immunogold labeling of viral proteins by using hyperimmune mouse ascitic fluid directed against severe acute respiratory syndrome–associated coronavirus (12 nm gold). B) Ultrastructural in situ hybridization detection of viral RNA by using a pool of polymerase and nucleocapsid riboprobes (6 nm gold). Bars, 100 nm.
Page created: January 31, 2011
Page updated: January 31, 2011
Page reviewed: January 31, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.