Volume 10, Number 4—April 2004
Dispatch
Phocine Distemper in German Seals, 2002
Figure 1
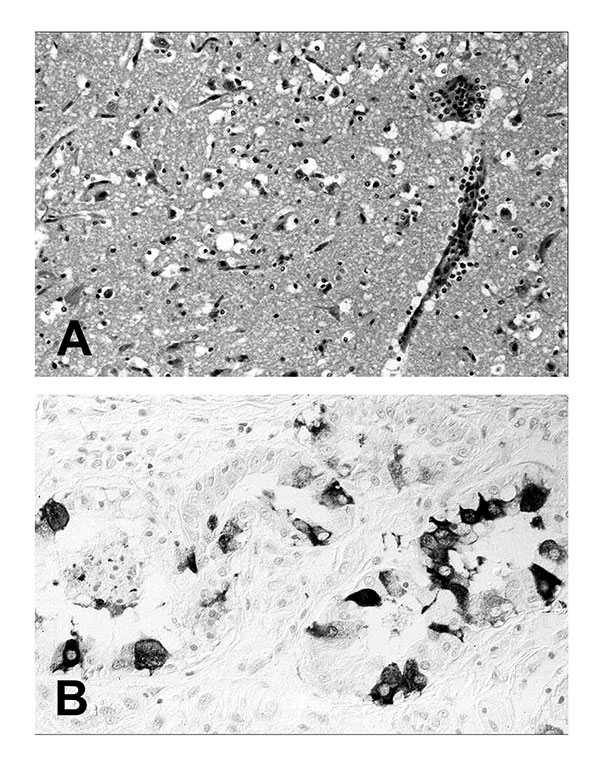
Figure 1. Tissue lesions from a harbor seal (Phoca vitulina) with phocine distemper virus infection. (A) Cerebral cortex with nonsuppurative encephalitis. Hematoxylin and eosin staining. (B) Immunohistochemical labeling of morbilliviral antigen in glandular epithelial cells of the lung. Avidin-biotin-peroxidase technique with Papanicolaou’s hematoxylin counterstain.
Page created: February 09, 2011
Page updated: February 09, 2011
Page reviewed: February 09, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.