Volume 10, Number 6—June 2004
Research
Antimicrobial Resistance among Campylobacter Strains, United States, 1997–2001
Figure 2
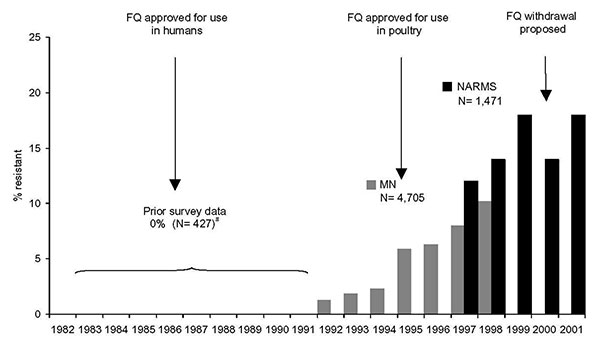
Figure 2. Quinolone- and fluoroquinolone-resistant Campylobacter jejuni in the United States, 1982–2001. FQ, fluoroquinolone; MN, Minnesota quinolone resistance among C. jejuni strains data (adapted from 18) NARMS, National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System. Prior survey data adapted from reference 19 and 30.
References
- Mead PS, Slutsker L, Dietz V, McCaig LF, Bresee JS, Shapiro C, Food-related illness and death in the United States. Emerg Infect Dis. 1999;5:607–25. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Preliminary FoodNet data on the incidence of foodborne illnesses—selected sites, United States, 2002. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2003;52:340–3.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Altekruse SF, Stern NJ, Fields PI, Swerdlow DL. Campylobacter jejuni—an emerging foodborne pathogen. Emerg Infect Dis. 1999;5:28–35. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Allos BM. Campylobacter jejuni infections: update on emerging issues and trends. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;32:1201–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Salazar-Lindo E, Sack RB, Chea-Woo E, Kay BA, Piscoya ZA, Leon-Barua R, Early treatment with erythromycin of Campylobacter jejuni–associated dysentery in children. J Pediatr. 1986;109:355–60. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Goodman LJ, Trenholme GM, Kaplan RL, Segreti J, Hines D, Petrak R, Empiric antimicrobial therapy of domestically acquired acute diarrhea in urban adults. Arch Intern Med. 1990;150:541–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mattila L, Peltola H, Siitonen A, Kyronseppa H, Simula I, Kataja M. Short-term treatment of traveler’s diarrhea with norfloxacin: a double- blind, placebo-controlled study during two seasons. Clin Infect Dis. 1993;17:779–82.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dryden MS, Gabb RJ, Wright SK. Empirical treatment of severe acute community-acquired gastroenteritis with ciprofloxacin. Clin Infect Dis. 1996;22:1019–25.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Endtz HP, Mouton RP, van der Reyden T, Ruijs GJ, Biever M, van Klingeren B. Fluoroquinolone resistance in Campylobacter spp isolated from human stools and poultry products. [see comments]. Lancet. 1990;335:787. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gaunt PN, Piddock LJ. Ciprofloxacin resistant Campylobacter spp. in humans: an epidemiological and laboratory study. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1996;37:747–57. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Prats G, Mirelis B, Llovet T, Munoz C, Miro E, Navarro F. Antibiotic resistance trends in enteropathogenic bacteria isolated in 1985–1987 and 1995–1998 in Barcelona. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2000;44:1140–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Engberg J, Aarestrup FM, Taylor DE, Gerner-Smidt P, Nachamkin I. Quinolone and macrolide resistance in Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli: resistance mechanisms and trends in human isolates. Emerg Infect Dis. 2001;7:24–34. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Harris NV, Thompson D, Martin DC, Nolan CM. A survey of Campylobacter and other bacterial contaminants of pre-market chicken and retail poultry and meats, King County, Washington. Am J Public Health. 1986;76:401–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Adak GK, Cowden JM, Nicholas S, Evans HS. The Public Health Laboratory Service national case-control study of primary indigenous sporadic cases of Campylobacter infection. Epidemiol Infect. 1995;115:15–22. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Eberhart-Phillips J, Walker N, Garrett N, Bell D, Sinclair D, Rainger W, Campylobacteriosis in New Zealand: results of a case-control study. J Epidemiol Community Health. 1997;51:686–91. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Enrofloxacin for poultry; opportunity for Hearing. [cited 2002 Nov 18]. Available from: http://www.fda.gov/OHRMS/DOCKETS/98fr/103100a.htm. DHHS; 2000
- Smith KE, Besser JM, Hedberg CW, Leano FT, Bender JB, Wicklund JH, Quinolone-resistant Campylobacter jejuni infections in Minnesota, 1992–1998. N Engl J Med. 1999;340:1525–32. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tenover FC, Baker CN, Fennell CL, Ryan CA. Antimicrobial resistance in Campylobacter species. In: Nachamkin I, Blaser MJ, Tompkins LS, editors. Campylobacter jejuni current status and future trends. Washington: American Society of Microbiology; 1992. p. 66–73.
- Patton CM, Nicholson MA, Ostroff SM, Ries AA, Wachsmuth IK, Tauxe RV. Common somatic O and heat-labile serotypes among Campylobacter strains from sporadic infections in the United States. J Clin Microbiol. 1993;31:1525–30.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Barrett TJ, Patton CM, Morris GK. Differentiation of Campylobacter species using phenotypic characterization. Lab Med. 1988;19:96–102.
- Murray PR. Manual of clinical microbiology. In: Microbiology. 7th ed. Washington: ASM Press; 1999. p. 1773.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System Annual Report 2001. Atlanta: Department of Health and Human Services. [cited 2003 Nov]. Available from: http://www.cdc.gov/narms/annual/2001/annual_01.htm
- Linton D, Lawson AJ, Owen RJ, Stanley J. PCR detection, identification to species level, and fingerprinting of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli direct from diarrheic samples. J Clin Microbiol. 1997;35:2568–72.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gonzalez I, Grant KA, Richardson PT, Park SF, Collins MD. Specific identification of the enteropathogens Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli by using a PCR test based on the ceuE gene encoding a putative virulence determinant. J Clin Microbiol. 1997;35:759–63.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing: eighth informational supplement. Wayne (PA): The Committee; 1998.
- Hunt JM. Campylobacter. In: Food and Drug Administration bacteriological analytical manual. 7th ed. Arlington (VA): AOAC International; 1992. p. 77–91.
- Lastovica A, Skirrow M. Clinical significance of Campylobacter and related species other than Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli. In: Blaser M, editor. Campylobacter. Washington: American Society for Microbiology; 2000. p. 89–120.
- Nachamkin I, Ung H, Li M. Increasing fluoroquinolone resistance in Campylobacter jejuni, Pennsylvania, USA, 1982–2001. Emerg Infect Dis. 2002;8:1501–3. Nachamkin I. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli to ciprofloxacin, erythromycin and tetracycline from 1982 to 1992. Med Microbiol Lett. 1994;3:300–5.
- Kiehlbauch J, Simon M, Makowski J. Use of filtration to isolate Campylobacter and related organisms from stools. In: Newell DG, editor. Campylobacters, Helicobacters, and related organisms. New York: Plenum Press; 1996. p. 47–9.
- McCaig LF, Besser RE, Hughes JM. Antimicrobial drug prescription in ambulatory care settings, United States, 1992–2000. Emerg Infect Dis. 2003;9:432–7.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Marano NVD, Fiorentino T, Segler S, Carter M, Kassenborg H, Smith K, Fluoroquinolone-resistant Campylobacter causes longer duration of diarrhea than fluoroquinolone-susceptible Campylobacter strains in FoodNet sites. 2nd International Conference on Emerging Infectious Diseases. Atlanta, GA, 2000.
- Kuschner RA, Trofa AF, Thomas RJ, Hoge CW, Pitarangsi C, Amato S, Use of azithromycin for the treatment of Campylobacter enteritis in travelers to Thailand, an area where ciprofloxacin resistance is prevalent. Clin Infect Dis. 1995;21:536–41.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kassenbourg H, Smith K, Vugia D, Rabatsky-Ehr T, Bates M, Dumas N, Fluoroquinolone-resistant infections: eating poultry outside the home and foreign travel are risk factors. Clin Infect Dis. 2004. In press. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Zhao C, Ge B, De Villena J, Sudler R, Yeh E, Zhao S, Prevalence of Campylobacter spp., Escherichia coli, and Salmonella serovars in retail chicken, turkey, pork, and beef from the greater Washington, D.C. area. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2001;67:5431–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ge B, White DG, McDermott PF, Girard W, Zhao S, Hubert S, Antimicrobial-resistant Campylobacter species from retail raw meats. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2003;69:3005–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Animal Health Institute. Antimicrobial volume survey. [cited 2002 Dec 12]. Available from: www.ahi.org
- McDermott PF, Bodeis SM, English LL, White DG, Walker RD, Zhao S, Ciprofloxacin resistance in Campylobacter jejuni evolves rapidly in chickens treated with fluoroquinolones. J Infect Dis. 2002;185:837–40. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Endtz HP, Ruijs GJ, van Klingeren B, Jansen WH, van der Reyden T, Mouton RP. Quinolone resistance in Campylobacter isolated from man and poultry following the introduction of fluoroquinolones in veterinary medicine. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991;27:199–208. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bager F, Emborg H, Heuer O. DANMAP 2001—Use of antimicrobial agents and occurrence of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria from food animals, foods and humans in Denmark. Vol. 2002. Copenhagen: Statens Serum Institut; 2001.
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. The human health impact of fluoroquinolone-resistant Campylobacter attributed to the consumption of chicken. [cited 2002 15 Jun]. Available from: http://www.fda.gov/cvm/antimicrobial/revisedRA.pdf
- Baker CN. The E-test and Campylobacter jejuni. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1992;15:469–72. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
Page created: February 22, 2011
Page updated: February 22, 2011
Page reviewed: February 22, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.