Volume 10, Number 7—July 2004
Research
Molecular Analysis of Plasmodium ovale Variants
Figure 1
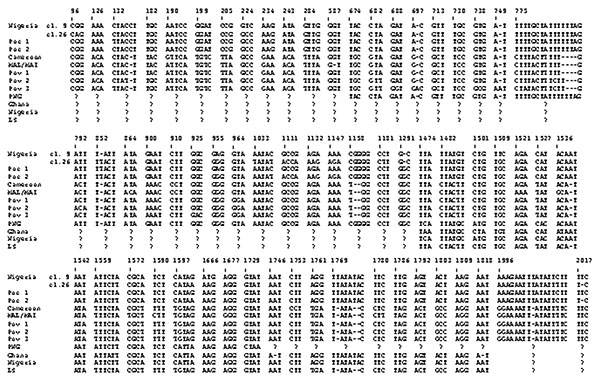
Figure 1. Different nucleotide sequences of the SSUrRNA genes among various Plasmodium ovale isolates. Numbers of nucleotides are based on the P. ovale clone 9 sequence. Boldface letters show different nucleotides in each isolate. Poc 1–2 and Pov 1–3 indicate two and three different sequences obtained from the classic and variant P. ovale isolates, respectively. Nigeria, Nigerian I/CDC strain; PNG, Papua New Guinean isolate; LS, a strain from the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine. Please see www.cdc.gov/ncidod/eid/03-0411-G1.htm for a larger reproduction of this figure.
Page created: January 27, 2011
Page updated: January 27, 2011
Page reviewed: January 27, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.