Volume 10, Number 9—September 2004
Research
Silent Nucleotide Polymorphisms and a Phylogeny for Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Figure 3
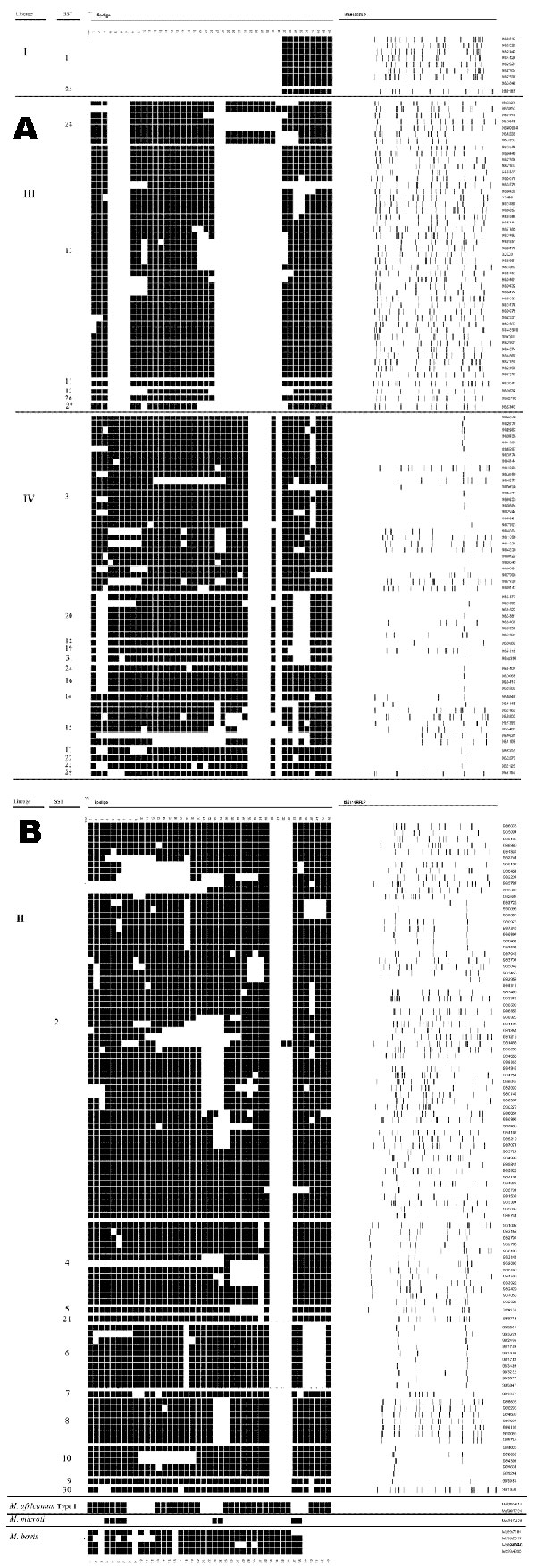
Figure 3. Relationship between Mycobacterium tuberculosis synonymous sequence type (SST), and lineage (left hand column), spoligotype pattern (middle column), and IS6110 restriction fragment length polymorphism.
Page created: March 30, 2011
Page updated: March 30, 2011
Page reviewed: March 30, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.