Volume 11, Number 6—June 2005
Research
Community-associated Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Canada
Figure 2
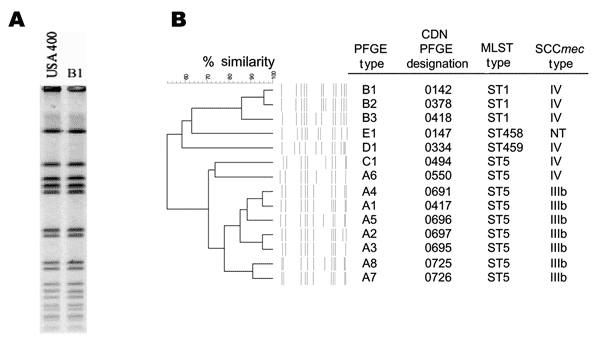
Figure 2. . A) Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE) fingerprint of USA400 and PFGE pattern B1. B) Dendrogram showing relationship of the unique fingerprints, along with the PFGE type designation (11) and other molecular characteristics of each subtype. CDN, Canadian Diseases Network; MLST, multilocus sequence typing; SCC, staphylococcal chromosome cassette.
References
- Udo EE, Pearman JW, Grubb WB. Genetic analysis of community isolates of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Western Australia. J Hosp Infect. 1993;25:97–108. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Baggett HC, Hennessy TW, Leman R, Hamlin C, Bruden D, Reasonover A, An outbreak of community-onset methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus skin infections in southwestern Alaska. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2003;24:397–402. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Fergie JE, Purcell K. Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in south Texas children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2001;20:860–3. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hussain FM, Boyle-Vavra S, Daum RS. Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus colonization in healthy children attending an outpatient pediatric clinic. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2001;20:763–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Four pediatric deaths from community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus—Minnesota and North Dakota, 1997–1999. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1999;48:707–10.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gwynne-Jones DP, Stott NS. Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: a cause of musculoskeletal sepsis in children. J Pediatr Orthop. 1999;19:413–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Naimi TS, LeDell KH, Boxrud DJ, Groom AV, Steward CD, Johnson SK, Epidemiology and clonality of community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Minnesota, 1996–1998. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;33:990–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Dufour P, Gillet Y, Bes M, Lina G, Vandenesch F, Floret D, Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in France: emergence of a single clone that produces Panton-Valentine leukocidin. Clin Infect Dis. 2002;35:819–24. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Livermore DM. Antibiotic resistance in staphylococci. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2000;16:S3–10. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Embil J, Ramotar K, Romance L, Alfa M, Conly J, Cronk S, Methicillin-resistant S. aureus intertertiary care institutions on the Canadian prairies 1990–1992. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 1994;15:646–51. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Shahin R, Johnson IL, Jamieson F, McGeer A, Tolkin J, Ford-Jones EL. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus carriage in a child care center following a case of disease. Toronto Child Care Center Study Group. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1999;153:864–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Cooper CL, Dyck B, Ormiston D, Olekson K, McLeod J, Nicolle LE, Bed utilization of patients with methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) in a Canadian tertiary care centre. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2002;23:483–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bacteria that grow aerobically [approved standard M7-A5]. 5th ed. Wayne (PA): The Committee; 2000.
- Walker ES, Levy F, Shorman M, David G, Abdalla J, Sarubbi FA. A decline in mupirocin resistance in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus accompanied administrative control of prescriptions. J Clin Microbiol. 2004;42:2792–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Lina G, Piemont Y, Godail-Gamont F, Bes M, Peter M-O, Gauduchon V, Involvement of Panton-Valentine leukocidin-producing Staphylococcus aureus in primary skin infections and pneumonia. Clin Infect Dis. 1999;29:1128–32. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Becker K, Roth R, Peters G. Rapid and specific detection of toxigenic Staphylococcus aureus: use of two multiplex PCR enzyme immunoassays for amplification and hybridization of staphylococcal enterotoxin genes, exfoliative toxin genes, and toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 gene. J Clin Microbiol. 1998;36:2548–53.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mulvey MR, Chui L, Ismail J, Louie L, Murphy C, Chang N, Development of a Canadian standardized protocol for subtyping methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus using pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. J Clin Microbiol. 2001;39:3481–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Tenover FC, Arbeit RD, Goering RV, Mickelson PA, Murray BE, Persing DH, Interpreting chromosomal DNA restriction patterns produced by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis: criteria for bacterial strain typing. J Clin Microbiol. 1995;33:2233–9.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Simor AE, Ofner-Agostini M, Bryce E, McGeer A, Paton S, Mulvey MR, Laboratory characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Canadian hospitals: results of 5 years of national surveillance, 1995–1999. J Infect Dis. 2002;186:652–60. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Simor AE, Boyd D, Louie L, McGeer A, Mulvey M, Willey BM. Characterization and proposed nomenclature of epidemic strains of MRSA in Canada. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 1999;10:333–6.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Enright MC, Day NP, Davies CE, Peacock SJ, Spratt BG. Multilocus sequence typing for characterization of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible clones of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 2002;38:1008–15.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Oliveira DC, de Lencastre H. Multiplex PCR strategy for rapid identification of structural types and variants of the mec element in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002;46:2155–61. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Christianson S, Mulvey MR. A comparative genomic hybridization study of epidemic strains of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Canada. 14th European Congress of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, Prague, Czech Republic, May 1–4, 2004. Poster no. P1012.
- Baba T, Takeuchi F, Kuroda M, Yuzawa H, Aoki K, Oguchi A, Genome and virulence determinants of high virulence community-acquired MRSA. Lancet. 2002;25:1819–27. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- McDougal LK, Steward CD, Killgore GE, Chaitram JM, McAllister SK, Tenover FC. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis typing of oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from the United States: establishing a national database. J Clin Microbiol. 2003;41:5113–20. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Kurbis CA, Wylie JL. Community-based cluster of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Manitoba. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2001;12:149–52.
- Ma XX, Ito T, Tiensasitorn C, Jamklang M, Chongtrakool P, Boyle-Vavra S, Novel type of staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec identified in community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002;46:1147–52. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Deplano A, Tassios PT, Glupczynski Y, Godfroid E, Struelens MJ. In vivo deletion of the methicillin resistance mec region from the chromosome of Staphylococcus aureus strains. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2000;46:617–20. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Inglis B, el-Adhami W, Stewart PR. Methicillin-sensitive and -resistant homologues of Staphylococcus aureus occur together among clinical isolates. J Infect Dis. 1993;67:323–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Udo EE, Al-Sweih N, Noronha BC. 1999. A chromosomal location of the mupA gene in Staphylococcus aureus expressing high-level mupirocin resistance. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2003;51:1283–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gilbart J, Perry CR, Slocombe B. High-level mupirocin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus: evidence for two distinct isoleucyl-tRNA synthetases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993;37:32–8.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Udo EE, Farook VS, Mokadas EM, Jacob LE, Sanyal SC. Molecular fingerprinting of mupirocin-resistant methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from a burn unit. Int J Infect Dis. 1998–1999;3:82–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Mulvey MR, Bryce E, Boyd D, Ofner-Agostini M, Christianson S, Simor AE, Ambler class A extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella spp. in Canadian hospitals. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004;48:1204–14. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
1Members of the Saskatchewan CA-MRSA Study Group: N. Antonishyn, Provincial Laboratory Saskatchewan Health, Regina, SK; T. Du, National Microbiology Laboratory, Winnipeg, MB; J. Embil, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, MB; A. Graessli, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, MB; J. Irvine, Keewatin Yatthe & Mamaweetan Churchill Regional Health Authority, La Ronge, SK; M. Khan, Kelsey Trail Health Region, Melfort, SK; S. Martin, Kelsey Trail Health Region, Nipawin, SK; R. McDonald, Provincial Laboratory Saskatchewan Health, Regina, SK; M. Nsungu, Northern Intertribal Health Authority, Prince Albert, SK; S. Paton, Public Health Agency of Canada, Ottawa, ON; C. Celin, National Microbiology Laboratory, Winnipeg, MB; D. Spreitzer, National Microbiology Laboratory, Winnipeg, MB; D. Stockdale, Keewatin Yatthe & Mamaweetan Churchill Regional Health Authority, La Ronge, SK.