Volume 12, Number 10—October 2006
Research
Human Prion Disease and Relative Risk Associated with Chronic Wasting Disease
Figure 1
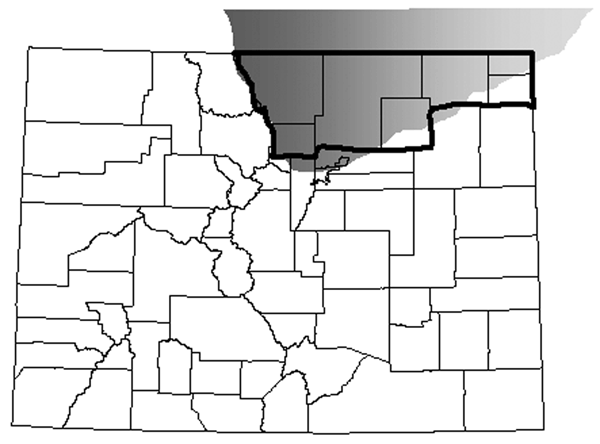
Figure 1. Location of chronic wasting disease (CWD)–endemic area in northeastern Colorado, USA (7) (gray shading) in relationship to Colorado counties regarded as CWD counties (bold outline) for purposes of comparing Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease rates and relative risk among resident human populations.
References
- Williams ES, Young S. Chronic wasting disease of captive mule deer: A spongiform encephalopathy. J Wildl Dis. 1980;16:89–98.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Williams ES, Miller MW. Chronic wasting disease in North American deer and elk. Rev Sci Tech. 2002;21:305–16.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Williams ES, Miller MW. Transmissible spongiform encephalopathies in non-domestic animals: origin, transmission, and risk factors. Rev Sci Tech. 2003;22:145–56.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Williams ES, Miller MW, Kreeger TJ, Kahn RH, Thorne ET. Chronic wasting disease of deer and elk: a review with recommendations for management. J Wildl Manage. 2002;66:551–63. DOIGoogle Scholar
- Belay ED, Maddox RA, Williams ES, Miller MW, Gambetti P, Schonberger LB. Chronic wasting disease and potential transmission to humans. Emerg Infect Dis. 2004;10:977–84.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Prusiner SB. Shattuck lecture–neurodegenerative diseases and prions. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:1516–26. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Miller MW, Williams ES, McCarty CW, Spraker TR, Kreeger TJ, Larsen CT, Epizootiology of chronic wasting disease in free-ranging cervids in Colorado and Wyoming. J Wildl Dis. 2000;36:676–90.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Spraker TR, Miller MW, Williams ES, Getzy DM, Adrian WJ, Schoonveld GG, Spongiform encephalopathy in free-ranging mule deer (Odocoileus hemionus), white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus), and Rocky Mountain elk (Cervus elaphus nelsoni) in northcentral Colorado. J Wildl Dis. 1997;33:1–6.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Alpers MP. Epidemiology and clinical aspects of kuru. In: Prusiner SB, McKinley MP, editors. Prions: novel infectious pathogens causing scrapie and Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. San Diego: Academic Press; 1987. p. 451−65.
- Anderson RM, Donnelly CA, Ferguson NM, Woolhouse ME, Watt CJ, Udy HJ, Transmission dynamics and epidemiology of BSE in British cattle. [Erratum, Nature 1997;386:302]. Nature. 1996;382:779–88. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Raymond GJ, Hope J, Kocisko DA, Priola SA, Raymond LD, Bossers A, Molecular assessment of the potential transmissibilities of BSE and scrapie to humans. Nature. 1997;388:285–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Raymond GJ, Bossers A, Raymond LD, O'Rourke KI, McHolland LE, Bryant PK III, Evidence of a molecular barrier limiting susceptibility of humans, cattle and sheep to chronic wasting disease. EMBO J. 2000;19:4425–30. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- World Health Organization. WHO consultation on public health and animal transmissible spongiform encephalopathies: epidemiology, risk and research requirements. Geneva. Organization. 2000;:52.
- Belay ED, Gambetti P, Schonberger LB, Parchi P, Lyon DR, Capellari S, Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in unusually young patients who consumed venison. Arch Neurol. 2001;58:1673–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Food and Drug Administration Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy Advisory Committee. Transcripts of open meeting, January 18, 2001, Bethesda, Maryland, USA [cited 20006 Aug 8]. Available from http://www.fda.gov/ohrms/dockets/ac/01/transcripts/3681t2_02.pdf
- Hamir AN, Cutlip RC, Miller JM, Williams ES, Stack MJ, Miller MW, Preliminary findings on the experimental transmission of chronic wasting disease agent of mule deer to cattle. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2001;13:91–6. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Gould DH, Voss JL, Miller MW, Bachand AM, Cummings BA, Frank AA. Survey of cattle in northeast Colorado for evidence of chronic wasting disease: geographical and high-risk targeted sample. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2003;15:274–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Will RG. Epidemiology of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Br Med Bull. 1993;49:960–70.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Will RG, Ironside JW, Zeidler M, Cousens SN, Estibeiro K, Alperovitch A, A new variant of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in the UK. Lancet. 1996;347:921–5. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ghani AC, Ferguson NM, Donnelly CA, Hagenaars TJ, Anderson RM. Epidemiological determinants of the pattern and magnitude of the vCJD epidemic in Great Britain. Proc Biol Sci. 1998;265:2443–52. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ghani AC, Ferguson NM, Donnelly CA, Anderson RM. Predicted vCJD mortality in Great Britain. Nature. 2000;406:583–4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ghani AC, Ferguson NM, Donnelly CA, Anderson RM. Updated projections of future vCJD deaths in the UK. BMC Infect Dis. 2003;3:4. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ghani AC, Ferguson NM, Donnelly CA, Anderson RM. Factors determining the pattern of the variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD) epidemic in Great Britain. Proc Biol Sci. 2003;270:689–98. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- National Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease Surveillance Unit. CJD statistics (June 2, 2006) [cited 2006 Aug 8]. Available from http://www.cjd.ed.ac.uk/figures.htm
- Clarke P, Ghani AC. Projections of the future course of the primary vCJD epidemic in the UK: inclusion of subclinical infection and the possibility of wider genetic susceptibility. J R Soc Interface. 2005;2:19–31. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bruce ME, Will RG, Ironside JW, McConnell I, Drummond D, Suttie A, Transmission to mice indicate that 'new variant' CJD is caused by the BSE agent. Nature. 1997;389:498–501. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bruce M, Chree A, Williams ES, Fraser H. Perivascular PrP amyloid in the brains of mice infected with chronic wasting disease. Brain Pathol. 2000;10:662–3.
- Race RE, Raines A, Baron TGM, Miller MW, Jenny A, Williams ES. Comparison of abnormal prion protein glycoform patterns from transmissible spongiform encephalopathy agent-infected deer, elk, sheep, and cattle. J Virol. 2002;76:12365–8. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Hamir AN, Kunkle RA, Cutlip RC, Miller JM, O'Rourke KI, Williams ES, Experimental transmission of chronic wasting disease agent to cattle by the intracerebral route. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2005;17:276–81. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Bosque PJ. Bovine spongiform encephalopathy, chronic wasting disease, scrapie, and the threat to humans from prion disease epizootics. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2002;2:488–95. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Majeed A, Lehmann P, Kirby L, Coleman MP. Mortality from dementias and neurodegenerative disorders in people aged 15–64 in England and Wales in 1979–96. BMJ. 1998;317:320–1. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Collinge J, Rossor M. A new variant of prion disease. Lancet. 1996;347:916–7. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- National Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease Surveillance Unit. Incidence of variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease onsets and deaths in the UK, January 1994–December 2004 [cited 2006 Aug 8]. Available from http://www.cjd.ed.ac.uk/vcjdq.htm
- Colorado Demography Office. Population totals [cited 2006 Aug 8]. Available from http://dola.colorado.gov/demog
- National Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease Surveillance Unit. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease surveillance in the UK, twelfth annual report, 2003 [cited 2006 Aug 8]. Available from http://www.cjd.ed.ac.uk/twelfth/rep2003.htm
- Belay ED, Maddox RA, Gambetti P, Schonberger LB. Monitoring the occurrence of emerging forms of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in the United States. Neurology. 2003;60:176–81.PubMedGoogle Scholar
- Ladogana A, Puopolo M, Croes EA, Budka H, Jarius C, Collins S, Mortality from Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and related disorders in Europe, Australia, and Canada. Neurology. 2005;64:1586–91. DOIPubMedGoogle Scholar
- Colorado Demography Office. Population by age and gender [cited 2006 Aug 8]. Available from http://dola.colorado.gov/demog/CreateTable1.cfm
Page created: December 05, 2011
Page updated: December 05, 2011
Page reviewed: December 05, 2011
The conclusions, findings, and opinions expressed by authors contributing to this journal do not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the Public Health Service, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, or the authors' affiliated institutions. Use of trade names is for identification only and does not imply endorsement by any of the groups named above.